
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressants, especially for treatment-resistant depression and atypical depression. They are also used to treat panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, Parkinson's disease, and several other disorders.

Monoamine oxidases (MAO) are a family of enzymes that catalyze the oxidation of monoamines, employing oxygen to clip off their amine group. They are found bound to the outer membrane of mitochondria in most cell types of the body. The first such enzyme was discovered in 1928 by Mary Bernheim in the liver and was named tyramine oxidase. The MAOs belong to the protein family of flavin-containing amine oxidoreductases.

Phenelzine, sold under the brand name Nardil among others, is a non-selective and irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine family which is primarily used as an antidepressant and anxiolytic to treat depression and anxiety. Along with tranylcypromine and isocarboxazid, phenelzine is one of the few non-selective and irreversible MAOIs still in widespread clinical use.

Tryptamine is an indolamine metabolite of the essential amino acid tryptophan. The chemical structure is defined by an indole—a fused benzene and pyrrole ring, and a 2-aminoethyl group at the second carbon. The structure of tryptamine is a shared feature of certain aminergic neuromodulators including melatonin, serotonin, bufotenin and psychedelic derivatives such as dimethyltryptamine (DMT), psilocybin, psilocin and others.
A dopamine reuptake inhibitor (DRI) is a class of drug which acts as a reuptake inhibitor of the monoamine neurotransmitter dopamine by blocking the action of the dopamine transporter (DAT). Reuptake inhibition is achieved when extracellular dopamine not absorbed by the postsynaptic neuron is blocked from re-entering the presynaptic neuron. This results in increased extracellular concentrations of dopamine and increase in dopaminergic neurotransmission.
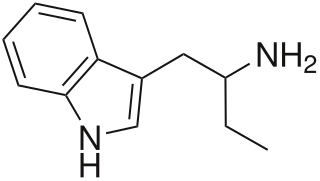
α-Ethyltryptamine, also known as etryptamine, is an entactogen and stimulant drug of the tryptamine family. It was originally developed and marketed as an antidepressant under the brand name Monase by Upjohn in the 1960s before being withdrawn due to toxicity.

Selegiline, also known as L-deprenyl and sold under the brand names Eldepryl, Zelapar, and Emsam among others, is a medication which is used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease and major depressive disorder. It has also been studied and used off-label for a variety of other indications, but has not been formally approved for any other use. The medication, in the form licensed for depression, has modest effectiveness for this condition that is similar to that of other antidepressants. Selegiline is provided as a swallowed tablet or capsule or an orally disintegrating tablet (ODT) for Parkinson's disease and as a patch applied to skin for depression.

Rasagiline, sold under the brand name Azilect among others, is a medication which is used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. It is used as a monotherapy to treat symptoms in early Parkinson's disease or as an adjunct therapy in more advanced cases. The drug is taken by mouth.

Pargyline, sold under the brand name Eutonyl among others, is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) medication which has been used to treat hypertension but is no longer marketed. It has also been studied as an antidepressant, but was never licensed for use in the treatment of depression. The drug is taken by mouth.

Molindone, sold under the brand name Moban, is an antipsychotic medication which is used in the United States in the treatment of schizophrenia. It is taken by mouth.

Naphthylaminopropane, also known as naphthylisopropylamine (NIPA), is an experimental drug that was under investigation for the treatment of alcohol and stimulant addiction.

(–)-Benzofuranylpropylaminopentane is an experimental drug related to selegiline which acts as a monoaminergic activity enhancer (MAE). It is orally active in animals.

5-Fluoro-α-methyltryptamine, also known as PAL-212 or PAL-544, is a putative stimulant, entactogen, and psychedelic tryptamine derivative related to α-methyltryptamine (αMT).

Monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAOB gene.
Reuptake inhibitors (RIs) are a type of reuptake modulators. It is a drug that inhibits the plasmalemmal transporter-mediated reuptake of a neurotransmitter from the synapse into the pre-synaptic neuron. This leads to an increase in extracellular concentrations of the neurotransmitter and an increase in neurotransmission. Various drugs exert their psychological and physiological effects through reuptake inhibition, including many antidepressants and psychostimulants.

Levoamphetamine is a stimulant medication which is used in the treatment of certain medical conditions. It was previously marketed by itself under the brand name Cydril, but is now available only in combination with dextroamphetamine in varying ratios under brand names like Adderall and Evekeo. The drug is known to increase wakefulness and concentration in association with decreased appetite and fatigue. Pharmaceuticals that contain levoamphetamine are currently indicated and prescribed for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), obesity, and narcolepsy in some countries. Levoamphetamine is taken by mouth.
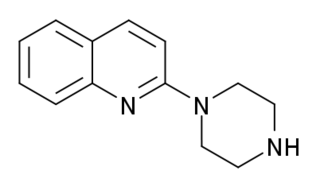
Quipazine, also known as 1-(2-quinolinyl)piperazine, is a serotonergic drug of the arylpiperazine family and an analogue of 1-(2-pyridinyl)piperazine which is used in scientific research. It was first described in the 1960s and was originally intended as an antidepressant but was never developed or marketed for medical use.

Kavain is the main kavalactone found mostly in the roots of the kava plant.

A monoamine releasing agent (MRA), or simply monoamine releaser, is a drug that induces the release of one or more monoamine neurotransmitters from the presynaptic neuron into the synapse, leading to an increase in the extracellular concentrations of the neurotransmitters and hence enhanced signaling by those neurotransmitters. The monoamine neurotransmitters include serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine; MRAs can induce the release of one or more of these neurotransmitters.

3-Chlorostyrylcaffeine (CSC), or 8-(3-chlorostyryl)caffeine (8-CSC), is a potent and selective adenosine A2A receptor antagonist which is used in scientific research.



















