
Aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to reduce pain, fever, and/or inflammation, and as an antithrombotic. Specific inflammatory conditions which aspirin is used to treat include Kawasaki disease, pericarditis, and rheumatic fever.

Salicylic acid is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H4COOH. A colorless (or, white), bitter-tasting solid, it is a precursor to and a metabolite of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid). It is a plant hormone, and has been listed by the EPA Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) Chemical Substance Inventory as an experimental teratogen. The name is from Latin salix for willow tree, from which it was initially identified and derived. It is an ingredient in some anti-acne products. Salts and esters of salicylic acid are known as salicylates.

Reye syndrome is a rapidly worsening brain disease. Symptoms of Reye syndrome may include vomiting, personality changes, confusion, seizures, and loss of consciousness. While liver toxicity typically occurs in the syndrome, jaundice usually does not. Death occurs in 20–40% of those affected with Reye syndrome, and about a third of those who survive are left with a significant degree of brain damage.

Methyl salicylate (oil of wintergreen or wintergreen oil) is an organic compound with the formula C8H8O3. It is the methyl ester of salicylic acid. It is a colorless, viscous liquid with a sweet, fruity odor reminiscent of root beer (in which it is used as a flavoring), but often associatively called "minty", as it is an ingredient in mint candies. It is produced by many species of plants, particularly wintergreens. It is also produced synthetically, used as a fragrance and as a flavoring agent.
ATC code N02Analgesics is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup N02 is part of the anatomical group N Nervous system.
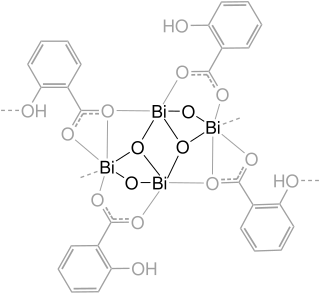
Bismuth subsalicylate, sold generically as pink bismuth and under brand names including Pepto-Bismol, Pepti-Calm and BisBacter, is a medication used to treat temporary discomfort of the stomach and gastrointestinal tract, such as nausea, heartburn, indigestion, upset stomach, and diarrhea.
Kaopectate is an orally taken medication from Arcadia Consumer Healthcare for the treatment of mild diarrhea. It is also sometimes used to treat indigestion, nausea, and stomach ulcers. The active ingredients have varied over time, and are different between the United States and Canada. The original active ingredients were kaolinite and pectin. In the US, the active ingredient is now bismuth subsalicylate. In Switzerland, attapulgite is used.

Dextromoramide is a powerful opioid analgesic approximately three times more potent than morphine but shorter acting. It is subject to drug prohibition regimes, both internationally through UN treaties and by the criminal law of individual nations, and is usually prescribed only in the Netherlands.
Salicylate testing is a category of drug testing that is focused on detecting salicylates such as acetysalicylic acid for either biochemical or medical purposes.
Bengay, spelled Ben-Gay before 1995, is a topical analgesic heat rub for temporary relief from muscle and joint pain associated with arthritis, bruises, simple backaches, overuse, sprains and strains.

Magnesium salicylate is a common analgesic and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat mild to moderate musculoskeletal pain such as in tendons and muscles. It is also used to treat joint pain like arthritis, general back pain, and headaches.
Sodium salicylate is a sodium salt of salicylic acid. It can be prepared from sodium phenolate and carbon dioxide under higher temperature and pressure. Historically, it has been synthesized by refluxing methyl salicylate with an excess of sodium hydroxide.

Aloxiprin is a medical drug used for the treatment of pain and inflammation associated with muscular skeletal and joint disorders. It is used for its properties as an anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and analgesic drug. It is a chemical compound of aluminium hydroxide and aspirin.

Femoxetine is a drug related to paroxetine that was being developed as an antidepressant by Danish pharmaceutical company Ferrosan in 1975 before acquisition of the company by Novo Nordisk. It acts as a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI). Development was halted to focus attention on paroxetine instead, as femoxetine could not be administered as a daily pill.

Salicylate poisoning, also known as aspirin poisoning, is the acute or chronic poisoning with a salicylate such as aspirin. The classic symptoms are ringing in the ears, nausea, abdominal pain, and a fast breathing rate. Early on, these may be subtle, while larger doses may result in fever. Complications can include swelling of the brain or lungs, seizures, low blood sugar, or cardiac arrest.
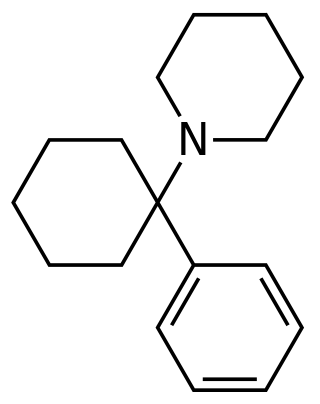
Arylcyclohexylamines, also known as arylcyclohexamines or arylcyclohexanamines, are a chemical class of pharmaceutical, designer, and experimental drugs.
The molecular formula C11H15NO4 (molar mass: 225.24 g/mol) may refer to:

Sutezolid is an oxazolidinone antibiotic currently in development as a treatment for extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis. It differs from linezolid by replacement of the morpholine oxygen with a sulfur atom.

Eprobemide (INN) is a pharmaceutical drug that was used as an antidepressant in Russia. It is a non-competitive reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A that exhibits selective action on serotonin deamination. Eprobemide differs from moclobemide only in the linker that connects the morpholine fragment with the chlorobenzamide — moclobemide has two carbon atoms while eprobemide has three. Its registration was cancelled on December 30, 2003.

3-MeO-PCMo is a dissociative anesthetic drug which is similar in structure to phencyclidine and been sold online as a designer drug. The inhibitory effect of 3-MeO-PCMo on the reduction in the density of the drebrin clusters by NMDAR stimulation with glutamic acid is lower than that of PCP or 3-MeO-PCP, with half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values of 26.67 μM (3-MeO-PCMo), 2.02 μM (PCP) and 1.51 μM (3-MeO-PCP).














