
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of use, but largely include an increased risk of gastrointestinal ulcers and bleeds, heart attack, and kidney disease.
An antipyretic is a substance that reduces fever. Antipyretics cause the hypothalamus to override a prostaglandin-induced increase in temperature. The body then works to lower the temperature, which results in a reduction in fever.
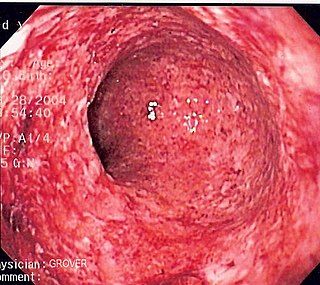
Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease characterized by recurrent episodes of intestinal inflammation, primarily manifesting as diarrhea and abdominal pain. Unlike ulcerative colitis, inflammation can occur anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract, though it most frequently affects the ileum and colon, involving all layers of the intestinal wall. Symptoms may be non-specific and progress gradually, often delaying diagnosis. About one-third of patients have colonic disease, another third have ileocolic disease, and the remaining third have isolated ileal disease. Systemic symptoms such as chronic fatigue, weight loss, and low-grade fevers are common. Organs such as the skin and joints can also be affected. Complications can include bowel obstructions, fistulas, nutrition problems, and an increased risk of intestinal cancers.

Inflammation is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function.

Diclofenac, sold under the brand name Voltaren among others, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat pain and inflammatory diseases such as gout. It can be taken orally, inserted rectally as a suppository, injected intramuscularly, injected intravenously, applied to the skin topically, or through eye drops. Improvements in pain last up to eight hours. It is also available as the fixed-dose combination diclofenac/misoprostol (Arthrotec) to help protect the stomach.

Naproxen, sold under the brand name Aleve among others, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat pain, menstrual cramps, and inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout and fever. It is taken orally. It is available in immediate and delayed release formulations. Onset of effects is within an hour and lasts for up to twelve hours. Naproxen is also available in salt form, naproxen sodium, which has better solubility when taken orally.
Anti-inflammatory or antiphlogistic is the property of a substance or treatment that reduces inflammation or swelling. Anti-inflammatory drugs, also called anti-inflammatories, make up about half of analgesics. These drugs remedy pain by reducing inflammation as opposed to opioids, which affect the central nervous system to block pain signaling to the brain.

Oxaprozin, also known as oxaprozinum, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), used to relieve the inflammation, swelling, stiffness, and joint pain associated with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Chemically, it is a propionic acid derivative. Safety and efficacy has been established in children over 6 years with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis only, and there is an increased risk of adverse reactions in the elderly population.

Magnesium salicylate is a common analgesic and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to treat mild to moderate musculoskeletal pain such as in tendons and muscles. It is also used to treat joint pain like arthritis, general back pain, and headaches.
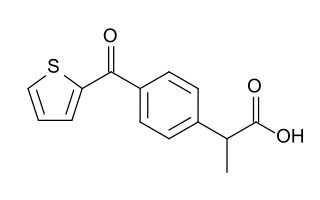
Suprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) developed by Janssen Pharmaceutica that was marketed as 1% eye drops under the trade name Profenal.

Lenabasum (also known as ajulemic acid, 1',1'-dimethylheptyl-delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol-11-oic acid, DMH-D8-THC-11-OIC, AB-III-56, HU-239, IP-751, CPL 7075, CT-3, JBT-101, Anabasum, and Resunab) is a synthetic cannabinoid that shows anti-fibrotic and anti-inflammatory effects in pre-clinical studies without causing a subjective "high". Although its design was inspired by a metabolite of delta-9-THC known as delta-9-THC-11-oic acid, lenabasum is an analog of the delta-8-THC metabolite delta-8-THC-11-oic acid. It is being developed for the treatment of inflammatory and fibrotic conditions such as systemic sclerosis, dermatomyositis and cystic fibrosis. It does not share the anti-emetic effects of some other cannabinoids, but may be useful for treating chronic inflammatory conditions where inflammation fails to resolve. Side effects include dry mouth, tiredness, and dizziness. The mechanism of action is through activation of the CB2 receptor leading to production of specialized proresolving eicosanoids such as lipoxin A4 and prostaglandin J2. Studies in animals at doses up to 40 mg/kg show minimal psychoactivity of lenabasum, compared to that produced by tetrahydrocannabinol. Lenabasum is being developed by Corbus Pharmaceuticals (formerly JB Therapeutics) for the treatment of orphan chronic life-threatening inflammatory diseases. Development since been discontinued.
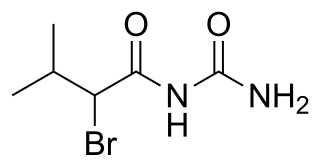
Bromisoval (INN), commonly known as bromovalerylurea, is a hypnotic and sedative of the bromoureide group discovered by Knoll in 1907 and patented in 1909. It is marketed over the counter in Asia under various trade names, usually in combination with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.

Meclofenamic acid is a drug used for joint, muscular pain, arthritis and dysmenorrhea. It is a member of the anthranilic acid derivatives class of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and was approved by the US FDA in 1980. Like other members of the class, it is a cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitor, preventing the formation of prostaglandins.

Etofenamate is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used for the treatment of joint and muscular pain. It is available for topical application as a cream, a gel or as a spray.
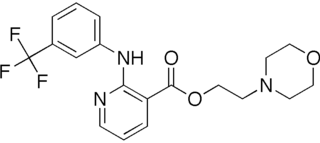
Morniflumate is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID).
Glafenine is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). Use of glafenine is limited due to the risk of anaphylaxis and acute kidney failure.
A drug class is a group of medications and other compounds that share similar chemical structures, act through the same mechanism of action, have similar modes of action, and/or are used to treat similar diseases. The FDA has long worked to classify and license new medications. Its Drug Evaluation and Research Center categorizes these medications based on both their chemical and therapeutic classes.

Epiestriol, or epioestriol, also known as 16β-epiestriol or simply 16-epiestriol, as well as 16β-hydroxy-17β-estradiol, is a minor and weak endogenous estrogen, and the 16β-epimer of estriol. Epiestriol is used clinically in the treatment of acne. In addition to its estrogenic actions, epiestriol has been found to possess significant anti-inflammatory properties without glycogenic activity or immunosuppressive effects, an interesting finding that is in contrast to conventional anti-inflammatory steroids such as hydrocortisone.

Zaltoprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used as an analgesic, antipyretic, and anti-inflammatory agent. It is a selective COX-2 inhibitor and also inhibits bradykinin-induced pain responses without blocking bradykinin receptors.

Glucametacin is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug used for the treatment of mild or moderate pain associated with rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and other rheumatological disorders. It has analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects.

















