
Epoxide hydrolases (EHs), also known as epoxide hydratases, are enzymes that metabolize compounds that contain an epoxide residue; they convert this residue to two hydroxyl residues through an epoxide hydrolysis reaction to form diol products. Several enzymes possess EH activity. Microsomal epoxide hydrolase, soluble epoxide hydrolase, and the more recently discovered but not as yet well defined functionally, epoxide hydrolase 3 (EH3) and epoxide hydrolase 4 (EH4) are structurally closely related isozymes. Other enzymes with epoxide hydrolase activity include leukotriene A4 hydrolase, Cholesterol-5,6-oxide hydrolase, MEST (gene) (Peg1/MEST), and Hepoxilin-epoxide hydrolase. The hydrolases are distinguished from each other by their substrate preferences and, directly related to this, their functions.
An angiogenesis inhibitor is a substance that inhibits the growth of new blood vessels (angiogenesis). Some angiogenesis inhibitors are endogenous and a normal part of the body's control and others are obtained exogenously through pharmaceutical drugs or diet.

Tolfenamic acid is a member of the anthranilic acid derivatives class of NSAID drugs. Like other members of the class, it is a COX inhibitor and prevents formation of prostaglandins.

Ursolic acid, is a pentacyclic triterpenoid identified in the epicuticular waxes of apples as early as 1920 and widely found in the peels of fruits, as well as in herbs and spices like rosemary and thyme.
Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase, also known as ALOX5, 5-lipoxygenase, 5-LOX, or 5-LO, is a non-heme iron-containing enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ALOX5 gene. Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase is a member of the lipoxygenase family of enzymes. It transforms essential fatty acids (EFA) substrates into leukotrienes as well as a wide range of other biologically active products. ALOX5 is a current target for pharmaceutical intervention in a number of diseases.
Histone deacetylase inhibitors are chemical compounds that inhibit histone deacetylases. Since deacetylation of histones produces transcriptionally silenced heterochromatin, HDIs can render chromatin more transcriptionally active and induce epigenomic changes.

Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), also known as prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (HUGO PTGS2), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTGS2 gene. In humans it is one of three cyclooxygenases. It is involved in the conversion of arachidonic acid to prostaglandin H2, an important precursor of prostacyclin, which is expressed in inflammation.

Oxicam is a class of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), meaning that they have anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic therapeutic effects. Oxicams bind closely to plasma proteins. Most oxicams are unselective inhibitors of the cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes. The exception is meloxicam with a slight (10:1) preference for COX-2, which, however, is only clinically relevant at low doses.
In biochemistry, docosanoids are signaling molecules made by the metabolism of twenty-two-carbon fatty acids (EFAs), especially the omega-3 fatty acid, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) by lipoxygenase, cyclooxygenase, and cytochrome P450 enzymes. Other docosanoids are metabolites of n-3 docosapentaenoic acid (DPA), n-6 DPA, and docosatetraenoic acid. Prominent docosanoid metabolites of DPA and n-3 DHA are members of the specialized pro-resolving mediators class of polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolites that possess potent anti-inflammation, tissue healing, and other activities.

Krüppel-like factor 4 is a member of the KLF family of zinc finger transcription factors, which belongs to the relatively large family of SP1-like transcription factors. KLF4 is involved in the regulation of proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis and somatic cell reprogramming. Evidence also suggests that KLF4 is a tumor suppressor in certain cancers, including colorectal cancer. It has three C2H2-zinc fingers at its carboxyl terminus that are closely related to another KLF, KLF2. It has two nuclear localization sequences that signals it to localize to the nucleus. In embryonic stem cells (ESCs), KLF4 has been demonstrated to be a good indicator of stem-like capacity. It is suggested that the same is true in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs).

Leukotriene B4 receptor 2, also known as BLT2, BLT2 receptor, and BLTR2, is an Integral membrane protein that is encoded by the LTB4R2 gene in humans and the Ltbr2 gene in mice.

Carmofur (INN) or HCFU (1-hexylcarbamoyl-5-fluorouracil) is a pyrimidine analogue used as an antineoplastic agent. It is a derivative of fluorouracil, being a lipophilic-masked analog of 5-FU that can be administered orally.

Anoctamin-1 (ANO1), also known as Transmembrane member 16A (TMEM16A), is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ANO1 gene. Anoctamin-1 is a voltage-gated calcium-activated anion channel, which acts as a chloride channel and a bicarbonate channel. additionally Anoctamin-1 is apical iodide channel. It is expressed in smooth muscle, epithelial cells, vomeronasal neurons, olfactory sustentacular cells, and is highly expressed in interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC) throughout the gastrointestinal tract.

Wogonin is an O-methylated flavone, a flavonoid-like chemical compound which is found in Scutellaria baicalensis.

Spiruchostatins are a group of chemical compounds isolated from Pseudomonas sp. as gene expression-enhancing substances. They possess novel bicyclic depsipeptides involving 4-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylhexanoic acid and 4-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylheptanoic acid residues. The two main forms are spiruchostatin A and spiruchostatin B.
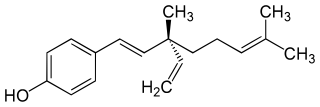
Bakuchiol is a meroterpenoid in the class terpenophenol.

Gintonin is a glycolipoprotein fraction isolated from Panax ginseng. The non-saponin ingredient was designated as gintonin, where gin was derived from ginseng, ton from the tonic effects of ginseng, and in from protein. The main component of gintonin is a complex of lysophosphatidic acids (LPA) and ginseng proteins such as ginseng major latex-like protein151 (GLP151) and ginseng ribonuclease-like storage protein.

Celastrol (tripterine) is a chemical compound isolated from the root extracts of Tripterygium wilfordii and Tripterygium regelii. Celastrol is a pentacyclic nortriterpen quinone and belongs to the family of quinone methides. In mice, celastrol is an NR4A1 agonist that alleviates inflammation and induces autophagy. Also in mice, celastrol increase expression of IL1R1, which is the receptor for the cytokine interleukin-1 (IL-1). IL1R1 knock-out mice exposed to celastrol exhibit no leptin-sensitizing or anti-obesity effect.
Directed enzyme prodrug therapy (DEPT) uses enzymes artificially introduced into the body to convert prodrugs, which have no or poor biologically activity, to the active form in the desired location within the body. Many chemotherapy drugs for cancer lack tumour specificity and the doses required to reach therapeutic levels in the tumour are often toxic to other tissues. DEPT strategies are an experimental method of reducing the systemic toxicity of a drug, by achieving high levels of the active drug only at the desired site. This article describes the variations of DEPT technology.

Doxifluridine (5'-deoxy-5-fluorouridine) is a second generation nucleoside analog prodrug developed by Roche and used as a cytostatic agent in chemotherapy in several Asian countries including China and South Korea. Doxifluridine is not FDA-approved for use in the USA. It is currently being evaluated in several clinical trials as a stand-alone or combination therapy treatment.















