
Ectopic pregnancy is a complication of pregnancy in which the embryo attaches outside the uterus. Signs and symptoms classically include abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding, but fewer than 50 percent of affected women have both of these symptoms. The pain may be described as sharp, dull, or crampy. Pain may also spread to the shoulder if bleeding into the abdomen has occurred. Severe bleeding may result in a fast heart rate, fainting, or shock. With very rare exceptions, the fetus is unable to survive.

Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone for the maternal recognition of pregnancy produced by trophoblast cells that are surrounding a growing embryo, which eventually forms the placenta after implantation. The presence of hCG is detected in some pregnancy tests. Some cancerous tumors produce this hormone; therefore, elevated levels measured when the patient is not pregnant may lead to a cancer diagnosis and, if high enough, paraneoplastic syndromes, however, it is not known whether this production is a contributing cause, or an effect of carcinogenesis. The pituitary analog of hCG, known as luteinizing hormone (LH), is produced in the pituitary gland of males and females of all ages.

An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac within the ovary. Often they cause no symptoms. Occasionally they may produce bloating, lower abdominal pain, or lower back pain. The majority of cysts are harmless. If the cyst either breaks open or causes twisting of the ovary, it may cause severe pain. This may result in vomiting or feeling faint, and even cause head aches.

The trophoblast is the outer layer of cells of the blastocyst. Trophoblasts are present four days after fertilization in humans. They provide nutrients to the embryo and develop into a large part of the placenta. They form during the first stage of pregnancy and are the first cells to differentiate from the fertilized egg to become extraembryonic structures that do not directly contribute to the embryo. After blastulation, the trophoblast is contiguous with the ectoderm of the embryo and is referred to as the trophectoderm. After the first differentiation, the cells in the human embryo lose their totipotency because they can no longer form a trophoblast. They become pluripotent stem cells.

A molar pregnancy, also known as a hydatidiform mole, is an abnormal form of pregnancy in which a non-viable fertilized egg implants in the uterus. It falls under the category of gestational trophoblastic diseases and was previously known as a hydatidiform mole. During a molar pregnancy, the uterus contains a growing mass characterized by swollen chorionic villi, resembling clusters of grapes. The occurrence of a molar pregnancy can be attributed to the fertilized egg lacking an original maternal nucleus. As a result, the products of conception may or may not contain fetal tissue. These molar pregnancies are categorized into two types: partial moles and complete moles, where the term 'mole' simply denotes a clump of growing tissue or a ‘growth'.

Choriocarcinoma is a malignant, trophoblastic cancer, usually of the placenta. It is characterized by early hematogenous spread to the lungs. It belongs to the malignant end of the spectrum in gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD). It is also classified as a germ cell tumor and may arise in the testis or ovary.
Gestational choriocarcinoma is a form of gestational trophoblastic neoplasia, which is a type of gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD), that can occur during pregnancy. It is a rare disease where the trophoblast, a layer of cells surrounding the blastocyst, undergoes abnormal developments, leading to trophoblastic tumors. The choriocarcinoma can metastasize to other organs, including the lungs, kidney, and liver. The amount and degree of choriocarcinoma spread to other parts of the body can vary greatly from person to person.
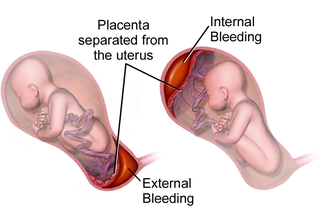
Placental abruption is when the placenta separates early from the uterus, in other words separates before childbirth. It occurs most commonly around 25 weeks of pregnancy. Symptoms may include vaginal bleeding, lower abdominal pain, and dangerously low blood pressure. Complications for the mother can include disseminated intravascular coagulopathy and kidney failure. Complications for the baby can include fetal distress, low birthweight, preterm delivery, and stillbirth.
Dilation and evacuation (D&E) is the dilation of the cervix and surgical evacuation of the uterus after the first trimester of pregnancy. It is a method of abortion as well as a common procedure used after miscarriage to remove all pregnancy tissue.

Complications of pregnancy are health problems that are related to, or arise during pregnancy. Complications that occur primarily during childbirth are termed obstetric labor complications, and problems that occur primarily after childbirth are termed puerperal disorders. While some complications improve or are fully resolved after pregnancy, some may lead to lasting effects, morbidity, or in the most severe cases, maternal or fetal mortality.

Dactinomycin, also known as actinomycin D, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes Wilms tumor, rhabdomyosarcoma, Ewing's sarcoma, trophoblastic neoplasm, testicular cancer, and certain types of ovarian cancer. It is given by injection into a vein.
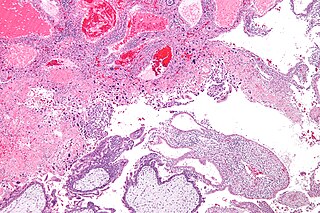
Gestational trophoblastic neoplasia (GTN) is group of rare diseases related to pregnancy and included in gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) in which abnormal trophoblast cells grow in the uterus. GTN can be classified into benign and malignant lesions. Benign lesions include placental site nodule and hydatidiform moles while malignant lesions have four subtypes including invasive mole, gestational choriocarcinoma, placental site trophoblastic tumor (PSTT) and epithelioid trophoblastic tumor (ETT). The choriocarcinoma has 2 significant subtypes including gestational and non-gestational and they are differentiated by their different biological feature and prognosis. Signs and symptoms of GTN will appear vary from person to person and depending upon the type of the disease. They may include uterine bleeding not related to menstruation, pain or pressure in pelvis, large uterus and high blood pressure during pregnancy. The cause of this disease is unknown but the identification of the tumor based on total beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (β-hCG) in the serum.
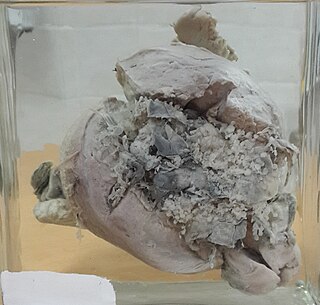
Invasive hydatidiform mole is a type of neoplasia that grows into the muscular wall of the uterus. It is formed after conception. It may spread to other parts of the body, such as the vagina, vulva, and lung.

A placental disease is any disease, disorder, or pathology of the placenta.

Placental site trophoblastic tumor is a form of gestational trophoblastic disease, which is thought to arise from intermediate trophoblast.
Theca lutein cyst is a type of bilateral functional ovarian cyst filled with clear, straw-colored fluid. These cysts result from exaggerated physiological stimulation due to elevated levels of beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (beta-hCG) or hypersensitivity to beta-hCG. On ultrasound and MRI, theca lutein cysts appear in multiples on ovaries that are enlarged.
Sylvia Dorothy Lawler was an English geneticist who worked in the field of human genetics.

Min Chiu Li was a Chinese-American oncologist and cancer researcher. Li was the first scientist to use chemotherapy to cure widely metastatic, malignant cancer.
Early pregnancy bleeding refers to vaginal bleeding before 14 weeks of gestational age. If the bleeding is significant, hemorrhagic shock may occur. Concern for shock is increased in those who have loss of consciousness, chest pain, shortness of breath, or shoulder pain.
Hypertensive disease of pregnancy, also known as maternal hypertensive disorder, is a group of high blood pressure disorders that include preeclampsia, preeclampsia superimposed on chronic hypertension, gestational hypertension, and chronic hypertension.














