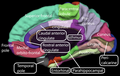
The cingulate cortex is a part of the brain situated in the medial aspect of the cerebral cortex. The cingulate cortex includes the entire cingulate gyrus, which lies immediately above the corpus callosum, and the continuation of this in the cingulate sulcus. The cingulate cortex is usually considered part of the limbic lobe.

A Brodmann area is a region of the cerebral cortex, in the human or other primate brain, defined by its cytoarchitecture, or histological structure and organization of cells.
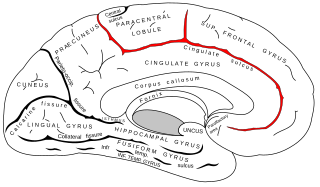
The cingulate sulcus is a sulcus on the cingulate cortex in the medial wall of the cerebral cortex. The frontal and parietal lobes are separated from the cingulate gyrus by the cingulate sulcus. It terminates as the marginal sulcus of the cingulate sulcus. It sends a ramus to separate the paracentral lobule from the frontal gyri, the paracentral sulcus.
The limbic lobe is an arc-shaped region of cortex on the medial surface of each cerebral hemisphere of the mammalian brain, consisting of parts of the frontal, parietal and temporal lobes. The term is ambiguous, with some authors including the paraterminal gyrus, the subcallosal area, the cingulate gyrus, the parahippocampal gyrus, the dentate gyrus, the hippocampus and the subiculum; while the Terminologia Anatomica includes the cingulate sulcus, the cingulate gyrus, the isthmus of cingulate gyrus, the fasciolar gyrus, the parahippocampal gyrus, the parahippocampal sulcus, the dentate gyrus, the fimbrodentate sulcus, the fimbria of hippocampus, the collateral sulcus, and the rhinal sulcus, and omits the hippocampus.

The cingulum in neuroanatomy, is a nerve tract – a collection of fibers, projecting from the cingulate gyrus to the entorhinal cortex in the brain, allowing for communication between components of the limbic system. It forms the white matter core of the cingulate gyrus, following it from the subcallosal gyrus of the frontal lobe beneath the rostrum of corpus callosum to the parahippocampal gyrus and uncus of the temporal lobe.

The parahippocampal gyrus is a grey matter cortical region of the brain that surrounds the hippocampus and is part of the limbic system. The region plays an important role in memory encoding and retrieval. It has been involved in some cases of hippocampal sclerosis. Asymmetry has been observed in schizophrenia.

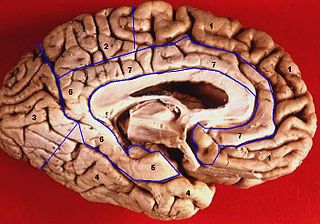
The lobes of the brain were originally a purely anatomical classification, but have been shown also to be related to different brain functions. The cerebrum, the largest portion of the human brain, is divided into lobes, but so is the cerebellum. If not specified, the expression "lobes of the brain" refers to the cerebrum.
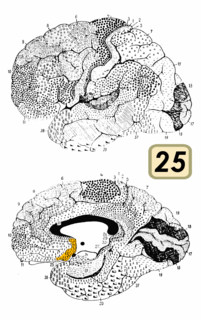
Brodmann area 25 (BA25) is the subgenual area, area subgenualis or subgenual cingulatea area in the cerebral cortex of the brain and delineated based on its cytoarchitectonic characteristics.

The posterior cerebral artery (PCA) is one of a pair of arteries that supply oxygenated blood to the occipital lobe, part of the back of the human brain. It begins near where the posterior communicating artery and the basilar artery join, and connects with the middle cerebral artery of the same side and internal carotid artery via the posterior communicating artery.

The parieto-occipital sulcus is a deep fissure in the cerebral cortex that marks the boundary between the cuneus and precuneus, and also between the parietal and occipital lobes. Only a small part can be seen on the lateral surface of the hemisphere, its chief part being on the medial surface.
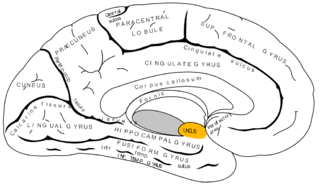
The uncus is an anterior extremity of the parahippocampal gyrus. It is separated from the apex of the temporal lobe by a slight fissure called the incisura temporalis.

The indusium griseum, consists of a thin membranous layer of grey matter in contact with the upper surface of the corpus callosum and continuous laterally with the grey matter of the cingulate cortex.

The subcallosal area is a small triangular field on the medial surface of the hemisphere in front of the subcallosal gyrus, from which it is separated by the posterior parolfactory sulcus; it is continuous below with the olfactory trigone, and above and in front with the cingulate gyrus; it is limited anteriorly by the anterior parolfactory sulcus.

The portion of the inferior frontal lobe immediately adjacent to the longitudinal fissure is named the straight gyrus,(or gyrus rectus) and is continuous with the superior frontal gyrus on the medial surface.

The lateral olfactory stria is directed across the lateral part of the anterior perforated substance and then bends abruptly medially toward the uncus of the parahippocampal gyrus.

The inferior or orbital surface of the frontal lobe is concave, and rests on the orbital plate of the frontal bone. It is divided into four orbital gyri by a well-marked H-shaped orbital sulcus. These are named, from their position, the medial, anterior, lateral, and posterior, orbital gyri. The medial orbital gyrus presents a well-marked antero-posterior sulcus, the olfactory sulcus, for the olfactory tract; the portion medial to this is named the straight gyrus, and is continuous with the superior frontal gyrus on the medial surface.

The superior frontal gyrus is situated above the superior frontal sulcus and is continued on to the medial surface of the hemisphere, the medial frontal gyrus. The medial and superior frontal gyri are two of the frontal gyri of the frontal lobe. The portion on the lateral surface of the hemisphere is usually more or less completely subdivided into an upper and a lower part by an antero-posterior sulcus, the paramedial sulcus, which, however, is frequently interrupted by bridging gyri.

The paracentral sulcus is a sulcus of the brain. It forms the paracentral lobule's anterior border. It is part of the cingulate sulcus.

The subparietal sulcus or suprasplenial sulcus is a sulcus, or crevice, on the medial surface of each cerebral hemisphere, above the splenium of the corpus callosum. It separates the precuneus from the posterior part of the cingulate gyrus. It is the posterior continuation of the cingulate sulcus. The cingulate sulcus actually "terminates" as the marginal sulcus of the cingulate sulcus. It extends posteriorly toward the calcarine sulcus.