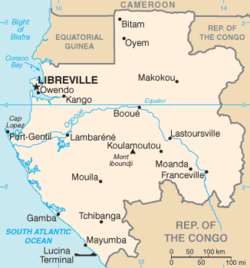



This article shows a list of cities and towns in Gabon : [1]




This article shows a list of cities and towns in Gabon : [1]
| Order | City | Population | Province | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Census 2003 | census 2013 | |||
| 1. | Libreville | 538,195 | 703,940 | Estuaire |
| 2. | Mandji (Port-Gentil) | 105,712 | 136,462 | Ogooué-Maritime |
| 3. | Masuku (Franceville) | 103,840 | 110,568 | Haut-Ogooué |
| 4. | Owendo | 51,661 | 79,300 | Estuaire |
| 5. | Oyem | 35,241 | 60,685 | Woleu-Ntem |
| 6. | Moanda | 42,703 | 59,154 | Haut-Ogooué |
| 7. | Ntoum | 12,711 | 51,954 | Estuaire |
| 8. | Lambaréné | 24,883 | 38,775 | Moyen-Ogooué |
| 9. | Mouila | 21,074 | 36,061 | Ngounié |
| 10. | Akanda | - | 34,548 | Estuaire |

Gabon, officially the Gabonese Republic, is a country on the Atlantic coast of Central Africa, on the equator, bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the north, the Republic of the Congo on the east and south, and the Gulf of Guinea to the west. It has an area of 270,000 square kilometres (100,000 sq mi) and a population of 2.3 million people. There are coastal plains, mountains, and a savanna in the east. Libreville is the country's capital and largest city.
Little is known of the history of Gabon before European contact. Bantu migrants settled the area beginning in the 14th century. Portuguese explorers and traders arrived in the area in the late 15th century. The coast subsequently became a centre of the transatlantic slave trade with European slave traders arriving to the region in the 16th century. In 1839 and 1841, France established a protectorate over the coast. In 1849, captives released from a captured slave ship founded Libreville. In 1862–1887, France expanded its control including the interior of the state, and took full sovereignty. In 1910 Gabon became part of French Equatorial Africa and in 1960, Gabon became independent.

Libreville is the capital and largest city of Gabon, located on the Gabon Estuary. Libreville occupies 65 square kilometres (25 sq mi) of the northwestern province of Estuaire. Libreville is also a port on the Gabon Estuary, near the Gulf of Guinea. As of the 2013 census, its population was 703,904.

The president of Gabon is the head of state of Gabon. A total of three people have served as president since the post was formed in 1960.

The Teke people or Bateke, also known as the Tyo or Tio, are a Bantu Central African ethnic group that speak the Teke languages and that mainly inhabit the south, north, and center of the Republic of the Congo, the west of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, with a minority in the south-east of Gabon. Omar Bongo, who was President of Gabon in the late 20th century, was a Teke.

The Gabon national football team represents Gabon in men's international football. The team's nickname is The Panthers and it is governed by the Gabonese Football Federation. They have never qualified for the FIFA World Cup, but have qualified eight times for the Africa Cup of Nations. Gabon is a member of both FIFA and Confederation of African Football (CAF).

Port-Gentil or Mandji is the second-largest city of Gabon, and it is a leading seaport. It is the center of Gabon's petroleum and timber industries. The city is located on a delta island in the Ogooue delta. Nearby Cape Lopez is Gabon's westernmost point. As of 2013 census, it had a population of 136,462.

In World War II, French West Africa was not a major scene of major fighting. Only one large-scale action took place there: the Battle of Dakar. The region remained under the control of Vichy France after the fall of France and until the Allied invasion of North Africa. French Gabon, the only colony of French Equatorial Africa not to join Free France after the armistice, fell to invading Free French Forces from the neighbouring colonies after the Battle of Gabon, further isolating West Africa.
Tchibanga is a city in the Nyanga Province of southern Gabon, situated on the Nyanga River. It has an estimated population of 24,000 (2008). The town lies on the N6 road and is home to Tchibanga Airport and a market. It lies near the Ivela Falls.

Franceville is one of the four largest cities in Gabon, with a population of 110,568 at the 2013 census. It lies on the Mpassa River and at the end of the Trans-Gabon Railway and the N3 road. It grew from a village named Masuku.

Ali Bongo Ondimba, also known as Ali Bongo and Ali Ben Bongo, is a Gabonese former politician who was the third president of Gabon from 2009 to 2023. He is a member of the Gabonese Democratic Party. He is the son of Omar Bongo, who was president of Gabon from 1967 until his death in 2009. During his father's presidency, he was Minister of Foreign Affairs from 1989 to 1991, represented Bongoville as a deputy in the National Assembly from 1991 to 1999, and was the Minister of Defense from 1999 to 2009. After his father's death, he won the 2009 Gabonese presidential election. He was reelected in 2016, in elections marred by numerous irregularities, arrests, human rights violations, and post-election protests and violence.

Gabon is a Christian majority nation, with around ten percent of the population being Muslim according to 2020 figures. Almost all of them follow Sunni Islam. Due to the secular nature of the country's constitution, Muslims are free to proselytize and build places of worship in the country.

The 2012 Africa Cup of Nations, also known as the Orange Africa Cup of Nations for sponsorship reasons, was the 28th edition of the Africa Cup of Nations, the football championship of Africa organized by the Confederation of African Football (CAF).

The Gabon talapoin, also known as the northern talapoin, is a small species of African monkey native to riparian habitats in Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, the western Republic of the Congo and the far western Democratic Republic of Congo. It may have been introduced to Bioko and the Canary Islands. Classified in the genus Miopithecus, it was given the name Miopithecus ogouensis, based on the River Ogooué, distinguishing it from the other species, the Angolan talapoin, also known as Miopithecus talapoin.

Bruno Ecuele Manga is a Gabonese professional footballer who plays as a centre-back for the Gabon national team. He is known for being a tough tackler.

Jessica Michele Kiper is an American actress, best known as a contestant from Survivor: Gabon where she placed third. She was more commonly known to the viewing audience during her run on Survivor by the nickname "Sugar". She returned to Survivor to compete on the show's 20th season, Survivor: Heroes vs. Villains, as part of the Heroes tribe, and was the first to be eliminated.

The 2009 Gabonese helicopter crash occurred in the Atlantic Ocean off Gabon at 8:08 p.m. on January 17, 2009. Ten soldiers were in the Eurocopter AS 532 when it crashed, leaving eight military personnel dead. Three soldiers initially survived the French military helicopter crash which occurred shortly after take-off from the amphibious assault ship FS Foudre. One of the rescued soldiers died from injuries at Libreville Hospital. The helicopter came down off the coastal city of Nyonie between Port-Gentil and Libreville during a joint exercise with Gabonese troops. The cause of the crash is not known.

The National Gendarmerie of Gabon is the national police force of Gabon responsible for law enforcement in Gabon. It is under the direct command of the President of Gabon. The Gendarmerie is also in charge of the Gabonese Republican Guard.

On 7 January 2019, members of the Armed Forces of Gabon announced a coup d'état in Gabon. Military officers claimed that they had ousted President Ali Bongo, who was re-elected in 2016 after a controversial election and protests. During the absence of Ali Bongo, who was receiving medical treatment in Morocco, armed rebels in the capital city Libreville took hostages and declared that they had established a "National Restoration Council" to "restore democracy in Gabon". Widespread internet outages occurred throughout the country, though it is unknown whether the Internet was shut down by the rebels themselves or by civilians. Gabon's government later declared that it had reasserted control.
The 2018–19 Gabon Championnat National D1 will be the 51st season in top-flight football in Gabon.
![]() Media related to Cities in Gabon at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Cities in Gabon at Wikimedia Commons