
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths in a particular population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically expressed in units of deaths per 1,000 individuals per year; thus, a mortality rate of 9.5 in a population of 1,000 would mean 9.5 deaths per year in that entire population, or 0.95% out of the total. It is distinct from "morbidity", which is either the prevalence or incidence of a disease, and also from the incidence rate.
Crime has been recorded in the United States since its founding and has fluctuated significantly over time, with a sharp rise after 1900 and reaching a broad bulging peak between the 1970s and early 1990s. After 1992, crime rates have generally trended downwards each year, with the exceptions of a slight increase in property crimes in 2001 and increases in violent crimes in 2005-2006, 2014-2016 and 2020-2021. While official federal crime data beginning in 2021 has a wide margin of error due to the incomplete adoption of the National Incident-Based Reporting System by government agencies, federal data for 2020-2021 and limited data from select U.S. cities collected by the nonpartisan Council on Criminal Justice showed significantly elevated rates of homicide and motor vehicle theft in 2020-2022. Although overall crime rates have fallen far below the peak of crime seen in the United States during the late 1980s and early 1990s, the homicide rate in the U.S. has remained high, relative to other "high income"/developed nations, with eight major U.S. cities ranked among the 50 cities with the highest homicide rate in the world in 2022. The aggregate cost of crime in the United States is significant, with an estimated value of $4.9 trillion reported in 2021. Data from the first half of 2023, from government and private sector sources show that the murder rate has dropped, as much as 12% in as many as 90 cities across the United States. The drop in homicide rates is not uniform across the country however, with some cities such as Memphis, TN, showing an uptick in murder rates.
The fundaments of the Brazilian Unified Health System (SUS) were established in the Brazilian Constitution of 1988, under the principles of universality, integrality and equity. It has a decentralized operational and management system, and social participation is present in all administrative levels. The Brazilian health system is a complex composition of public sector (SUS), private health institutions and private insurances. Since the creation of SUS, Brazil has significantly improved in many health indicators, but a lot needs to be done in order to achieve Universal Health Coverage (UHC).

Health in Switzerland relates to a variety of issues. Namely, water and sanitation, diet and fitness, various addictions, mental fitness, communicable diseases, hygiene and the environment.
Australia is a high income country, and this is reflected in the good status of health of the population overall. In 2011, Australia ranked 2nd on the United Nations Development Programme's Human Development Index, indicating the level of development of a country. Despite the overall good status of health, the disparities occurring in the Australian healthcare system are a problem. The poor and those living in remote areas as well as indigenous people are, in general, less healthy than others in the population, and programs have been implemented to decrease this gap. These include increased outreach to the indigenous communities and government subsidies to provide services for people in remote or rural areas.

The Tajikistan health system is influenced by the former Soviet legacy. It is ranked as the poorest country within the WHO European region, including the lowest total health expenditure per capita. Tajikistan is ranked 129th as Human Development Index of 188 countries, with an Index of 0.627 in 2016. In 2016, the SDG Index value was 56. In Tajikistan health indicators such as infant and maternal mortality rates are among the highest of the former Soviet republics. In the post-Soviet era, life expectancy has decreased because of poor nutrition, polluted water supplies, and increased incidence of cholera, malaria, tuberculosis, and typhoid. Because the health care system has deteriorated badly and receives insufficient funding and because sanitation and water supply systems are in declining condition, Tajikistan has a high risk of epidemic disease.

In the post-Soviet era, the quality of Uzbekistan’s health care has declined. Between 1992 and 2003, spending on health care and the ratio of hospital beds to population both decreased by nearly 50 percent, and Russian emigration in that decade deprived the health system of many practitioners. In 2004 Uzbekistan had 53 hospital beds per 10,000 population. Basic medical supplies such as disposable needles, anesthetics, and antibiotics are in very short supply. Although all citizens nominally are entitled to free health care, in the post-Soviet era bribery has become a common way to bypass the slow and limited service of the state system. In the early 2000s, policy has focused on improving primary health care facilities and cutting the cost of inpatient facilities. The state budget for 2006 allotted 11.1 percent to health expenditures, compared with 10.9 percent in 2005.

The major causes of deaths in Finland are cardiovascular diseases, malignant tumors, dementia and Alzheimer's disease, respiratory diseases, alcohol related diseases and accidental poisoning by alcohol. In 2010 the leading causes of death among men aged 15 to 64 were alcohol related deaths, ischaemic heart disease, accident, suicides, lung cancer and cerbrovascular diseases. Among women the leading causes were breast cancer, alcohol related deaths, accidents, suicides, ischaemic heart disease and lung cancer.
The current population of Myanmar is 54.05 million. It was 27.27 million in 1970. The general state of healthcare in Myanmar is poor. The military government of 1962-2011 spent anywhere from 0.5% to 3% of the country's GDP on healthcare. Healthcare in Myanmar is consistently ranked among the lowest in the world. In 2015, in congruence with a new democratic government, a series of healthcare reforms were enacted. In 2017, the reformed government spent 5.2% of GDP on healthcare expenditures. Health indicators have begun to improve as spending continues to increase. Patients continue to pay the majority of healthcare costs out of pocket. Although, out of pocket costs were reduced from 85% to 62% from 2014 to 2015. They continue to drop annually. The global average of healthcare costs paid out of pocket is 32%. Both public and private hospitals are understaffed due to a national shortage of doctors and nurses. Public hospitals lack many of the basic facilities and equipment. WHO consistently ranks Myanmar among the worst nations in healthcare.

The epidemiology of cancer is the study of the factors affecting cancer, as a way to infer possible trends and causes. The study of cancer epidemiology uses epidemiological methods to find the cause of cancer and to identify and develop improved treatments.
Cancer survival rates vary by the type of cancer, stage at diagnosis, treatment given and many other factors, including country. In general survival rates are improving, although more so for some cancers than others. Survival rate can be measured in several ways, median life expectancy having advantages over others in terms of meaning for people involved, rather than as an epidemiological measure.

Worldwide, breast cancer is the most common invasive cancer in women. Breast cancer comprises 22.9% of invasive cancers in women and 16% of all female cancers.

Lesotho's Human development index value for 2018 was 0.518—which put the country in the low human development category—positioning it at 164 out of 189 countries and territories. Health care services in Lesotho are delivered primarily by the government and the Christian Health Association of Lesotho. Access to health services is difficult for many people, especially in rural areas. The country's health system is challenged by the relentless increase of the burden of disease brought about by AIDS, and a lack of expertise and human resources. Serious emergencies are often referred to neighbouring South Africa. The largest contribution to mortality in Lesotho are communicable diseases, maternal, perinatal and nutritional conditions.
Zambia is a landlocked country in Sub Saharan Africa which experiences a burden of both communicable and non-communicable diseases. In line with WHO agenda for equity in health, it has adopted the Universal Health Coverage agenda to mitigate the challenges faced within the health sector. The Ministry of Health (MOH) provides information pertaining to Zambian health. The main focus of the Ministry of Health has been provision of uninterrupted care with emphasis on health systems strengthening and services via the primary health care approach.
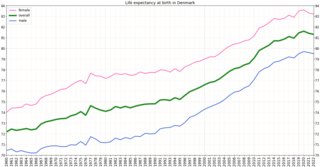
As of 2012, Denmark had a life expectancy of 79.5 years at birth, up from 75 years in 1990. This ranks it 37th among 193 nations, behind the other Nordic countries. The National Institute of Public Health of the University of Southern Denmark has calculated 19 major risk factors among Danes that contribute to a lowering of the life expectancy; this includes smoking, alcohol, drug abuse and physical inactivity. The large number of Danes becoming overweight is an increasing problem and results in an annual additional consumption in the health care system of DKK 1,625 million. In a 2012 study, Denmark had the highest cancer rate of all countries listed by the World Cancer Research Fund International; researchers suggest the reasons are better reporting, but also lifestyle factors like heavy alcohol consumption, smoking and physical inactivity. Denmark had the second highest death rate from alcohol of any region in Europe in 2015 at 6.9 per 100,000 population.

Brunei's healthcare system is managed by the Brunei Ministry of Health and funded by the General Treasury. It consists of around 15 health centers, ten clinics and 22 maternal facilities, considered to be of reasonable standard. There are also two private hospitals. Cardiovascular disease, cancer, and diabetes are the leading cause of death in the country, with life expectancy around 75 years, a vast improvement from 1961. Brunei's human development index (HCI) improved from 0.81 in 2002 to 0.83 in 2021, expanding at an average annual rate of 0.14%. According to the UN's Human Development Report 2020, the HCI for girls in the country is greater than for boys, though aren't enough statistics in Brunei to break down HCI by socioeconomic classes. Brunei is the second country in Southeast Asia after Singapore to be rated 47th out of 189 nations on the UN HDI 2019 and has maintained its position in the Very High Human Development category. Being a culturally taboo subject, the rate of suicide has not been investigated.
Health indicators are quantifiable characteristics of a population which researchers use as supporting evidence for describing the health of a population. Typically, researchers will use a survey methodology to gather information about a population sample, use statistics in an attempt to generalize the information collected to the entire population, and then use the statistical analysis to make a statement about the health of the population. Health indicators are often used by governments to guide health care policy or to make goals for improving population health.









