
Asia is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometers, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilizations. Its 4.7 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population.

A developed country, or high-income country, is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy, and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations. Most commonly, the criteria for evaluating the degree of economic development are the gross domestic product (GDP), gross national product (GNP), the per capita income, level of industrialization, amount of widespread infrastructure and general standard of living. Which criteria are to be used and which countries can be classified as being developed are subjects of debate. Different definitions of developed countries are provided by the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank; moreover, HDI ranking is used to reflect the composite index of life expectancy, education, and income per capita. Another commonly used measure of a developed country is the threshold of GDP (PPP) per capita of at least US$22,000. In 2023, 40 countries fit all four criteria, while an additional 15 countries fit three out of four.

The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistical composite index of life expectancy, education, and per capita income indicators, which is used to rank countries into four tiers of human development. A country scores a higher level of HDI when the lifespan is higher, the education level is higher, and the gross national income GNI (PPP) per capita is higher. It was developed by Pakistani economist Mahbub ul-Haq and was further used to measure a country's development by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)'s Human Development Report Office.
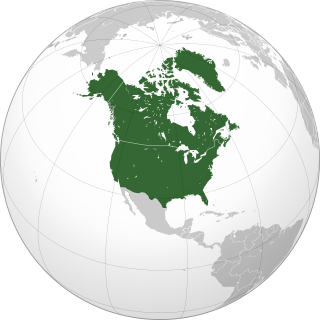
Northern America is the northernmost subregion of North America. The boundaries may be drawn slightly differently. In one definition, it lies directly north of Middle America. Northern America's land frontier with the rest of North America then coincides with the Mexico–United States border. Geopolitically, according to the United Nations' scheme of geographical regions and subregions, Northern America consists of Bermuda, Canada, Greenland, Saint Pierre and Miquelon and the United States.
The Human Poverty Index (HPI) was an indication of the poverty of community in a country, developed by the United Nations to complement the Human Development Index (HDI) and was first reported as part of the Human Development Report in 1997. It is developed by United Nations Development Program which also publishes indexes like HDI It was considered to better reflect the extent of deprivation in deprived countries compared to the HDI. In 2010, it was supplanted by the UN's Multidimensional Poverty Index.

The Human Development Report (HDR) is an annual Human Development Index report published by the Human Development Report Office of the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP).
The Gender Development Index (GDI) is an index designed to measure gender equality.

Determining the boundaries between the continents is generally a matter of geographical convention. Several slightly different conventions are in use. The number of continents is most commonly considered seven but may range as low as four when Afro-Eurasia and the Americas are both considered as single continents. An island can be considered to be associated with a given continent by either lying on the continent's adjacent continental shelf or being a part of a microcontinent on the same principal tectonic plate. An island can also be entirely oceanic while still being associated with a continent by geology or by common geopolitical convention. Another example is the grouping into Oceania of the Pacific Islands with Australia and Zealandia.

The continent of Australia, sometimes known in technical contexts by the names Sahul, Australia-New Guinea, Australinea, or Meganesia to distinguish it from the country of Australia, is located within the Southern and Eastern hemispheres. The continent includes mainland Australia, Tasmania, the island of New Guinea, the Aru Islands, the Ashmore and Cartier Islands, most of the Coral Sea Islands, and some other nearby islands. Situated in the geographical region of Oceania, Australia is the smallest of the seven traditional continents.

Multidimensional Poverty Indices use a range of indicators to calculate a summary poverty figure for a given population, in which a larger figure indicates a higher level of poverty. This figure considers both the proportion of the population that is deemed poor, and the 'breadth' of poverty experienced by these 'poor' households, following the Alkire & Foster 'counting method'. The method was developed following increased criticism of monetary and consumption based poverty measures, seeking to capture the deprivations in non-monetary factors that contribute towards well-being. While there is a standard set of indicators, dimensions, cutoffs and thresholds used for a 'Global MPI', the method is flexible and there are many examples of poverty studies that modify it to best suit their environment. The methodology has been mainly, but not exclusively, applied to developing countries.
Although for many decades, it was customary to focus on GDP and other measures of national income, there has been growing interest in developing broad measures of economic well-being. National and international approaches include the Beyond GDP programme developed by the European Union, the Better Lives Compendium of Indicators developed by the OECD, as well as many alternative metrics of wellbeing or happiness. One of the earliest attempts to develop such an index at national level was Bhutan's Gross National Happiness Index and there are a now a number of similar projects ongoing around the world, including a project to develop for the UK an assessment of national well-being, commissioned by the Prime Minister David Cameron and led by the Office for National Statistics.








