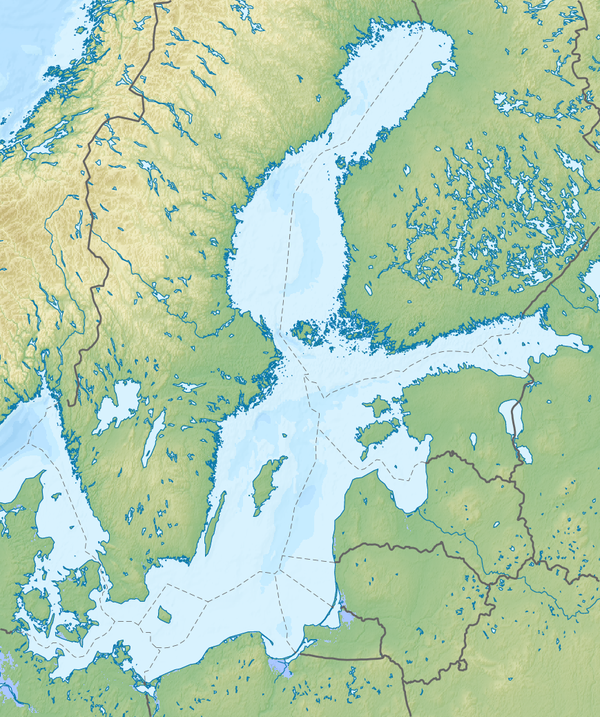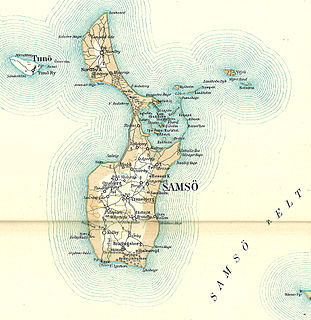
Samsø is a Danish island in the Kattegat 15 kilometers (9.3 mi) off the Jutland Peninsula. Samsø is located in Samsø municipality. The community has 3,724 inhabitants (2017) called Samsings and is 114 km² in area. Due to its central location, the island was used during the Viking Age as a meeting place. The etymology of the island's name is unknown.

Horns Rev is a shallow sandy reef of glacial deposits in the eastern North Sea, about 15 km (9.3 mi) off the westernmost point of Denmark, Blåvands Huk. The reef contains the Horns Rev Offshore Wind Farm.
Ørsted A/S is a Danish multinational power company based in Fredericia, Denmark. It is the largest energy company in Denmark. The company adopted its current name on 6 November 2017.

Tunø is a Danish island in the Kattegat, approximately 4 km west of the neighbouring island of Samsø. The island covers an area of 3.52 square kilometres, has a circumference of 9.5 km (5.9 mi) and has total of 66 inhabitants as of November 2022. It comes under the administration of Odder municipality. Tunø By is the only village on the island, with the hamlet of Løkkegårde as the second most populated area.
EnBW Energie Baden-Württemberg AG, or simply EnBW, is a publicly-traded energy company headquartered in Karlsruhe, Germany. As its name indicates, EnBW is based in the German state of Baden-Württemberg.

Denmark was a pioneer in developing commercial wind power during the 1970s, and today a substantial share of the wind turbines around the world are produced by Danish manufacturers such as Vestas—the world's largest wind-turbine manufacturer—along with many component suppliers. In Denmark's electricity sector wind power produced the equivalent of 47% of Denmark's total electricity consumption in 2019, an increase from 43.4% in 2017, 39% in 2014, and 33% in 2013. In 2012, the Danish government adopted a plan to increase the share of electricity production from wind to 50% by 2020, and to 84% by 2035. Denmark had the 4th best energy architecture performance in the world in 2017 according to the World Economic Forum, and the second best energy security in the world in 2019 according to the World Energy Council.

The Nysted Wind Farm is a Danish offshore wind farm close to the Rødsand sand bank near Lolland. Gravity base foundations are used rather than piles due to ice conditions.

The Middelgrunden wind farm stands on the shoal Middelgrunden, between shipping lanes in the Øresund, 3.5 km outside Copenhagen, Denmark. When it was built in 2000, it was the world's largest offshore farm, with 20 turbines and a capacity of 40 MW. The farm delivers about 4% of the power for Copenhagen.

EnBW Baltic 1 is the first commercial offshore wind farm of Germany in the Baltic Sea. Siemens supplied 21 SWT 2.3-93 wind turbines for the 48.3 megawatt wind farm. EnBW Baltic 1 is located about 16 kilometres (9.9 mi) north of the Darss-Zingst Peninsula and covers about seven square kilometers. Work started in July 2010; the wind farm was officially commissioned on 2 May 2011.

Blyth Offshore Wind Farm was a small coastal wind farm located 0.5 miles (0.80 km) off the coast of Blyth, Northumberland, England.

Anholt Offshore Wind Farm is a Danish offshore wind power wind farm in the Kattegat, between Djursland and Anholt island. With a nameplate capacity of 400 megawatts (MW), it is one of the largest offshore wind farm in the world and was the largest in Denmark from 2013 to 2019. A cable from the wind farm to Anholt replaces most of the diesel-powered electricity on the island.
Bladt Industries A/S is an international steel contractor specialising in large-scale and highly complex steel structures. Bladt Industries operate within three key areas of business providing steel solutions for the wind and renewable energy sector, for the oil and gas industry and for infrastructure. Bladt Industries was established in 1965 as the company Jørgen Bladt A/S.
Vindeby Offshore Wind Farm was the first offshore wind farm in the world, erected in 1991 off the coast of the town of Vindeby on the Danish island of Lolland. It was decommissioned for cost reasons in 2017 after 25 years of useful life.

Tunø Knob Offshore Wind Farm is an offshore wind farm in the Bay of Aarhus, Denmark. It is located on the sandbar Tunø Knob, west of the Tunø island.

Avedøre Holme Offshore Wind Farm is a nearshore wind farm right off the coast of Avedøre, Copenhagen. It was commissioned in 2009 with three 3.6 MW Siemens turbines as a demonstrator project for future offshore wind turbines. Ørsted owns two turbines, and a private collective owns the third. Ørsted and partners build a 2MW hydrogen electrolysis station at Avedøre Power Station supplied by Ørsted's two turbines.

EnBW Baltic 2 is an offshore wind farm in the German section of the Kriegers Flak reef in the Baltic Sea. The wind farm uses 80 Siemens SWT 3.6-120 wind turbines for a total capacity of 288 megawatt. Baltic 2 is connected to Germany via Baltic 1, but is also connected to Denmark via the adjacent offshore wind farm ″Kriegers Flak″ in 2020, creating a 400 MW AC offshore grid synchronized to the east Denmark network. The cable to Denmark costs €350m, of which €150m comes from the EU.

Horns Rev is an offshore wind farm in Danish waters in the North Sea.