
The Northumberland Strait is a strait in the southern part of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence in eastern Canada. The strait is formed by Prince Edward Island and the gulf's eastern, southern, and western shores.
British Columbia Ferry Services Inc., operating as BC Ferries (BCF), is a former provincial Crown corporation, now operating as an independently managed, publicly owned Canadian company. BC Ferries provides all major passenger and vehicle ferry services for coastal and island communities in the Canadian province of British Columbia. Set up in 1960 to provide a similar service to that provided by the Black Ball Line and the Canadian Pacific Railway, which were affected by job action at the time, BC Ferries has become the largest passenger ferry line in North America, operating a fleet of 41 vessels with a total passenger and crew capacity of over 27,000, serving 47 locations on the B.C. coast.

Campobello Island is the largest and only inhabited island in Campobello, a civil parish in southwestern New Brunswick, Canada, near the border with Maine, United States. The island's permanent population in 2021 was 949. It is the site of the Roosevelt Campobello International Park and of Herring Cove Provincial Park.

Okanagan Lake is a lake in the Okanagan Valley of British Columbia, Canada. The lake is 135 km (84 mi) long, between 4 and 5 km wide, and has a surface area of 348 km2.
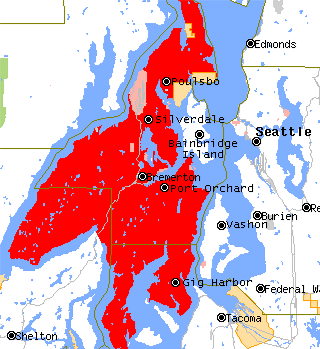
The Kitsap Peninsula lies west of Seattle across Puget Sound, in Washington state in the Pacific Northwest. Hood Canal separates the peninsula from the Olympic Peninsula on its west side. The peninsula, a.k.a. "Kitsap", encompasses all of Kitsap County except Bainbridge and Blake Islands, as well as the northeastern part of Mason County and the northwestern part of Pierce County. The highest point on the Kitsap Peninsula is Gold Mountain. The U.S. Navy's Puget Sound Naval Shipyard, and Naval Base Kitsap are on the peninsula. Its main city is Bremerton.

McNeil Island is an island in the northwest United States in south Puget Sound, located southwest of Tacoma, Washington. With a land area of 6.63 square miles (17.2 km2), it lies just north of Anderson Island; Fox Island is to the north, across Carr Inlet, and to the west, separated from Key Peninsula by Pitt Passage. The Washington mainland lies to the east, across the south basin of Puget Sound.
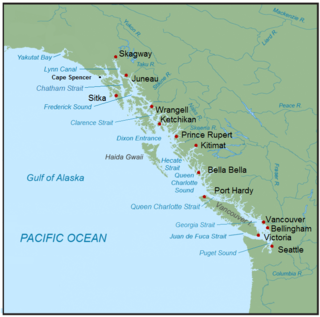
The Inside Passage is a coastal route for ships and boats along a network of passages which weave through the islands on the Pacific Northwest coast of the North American Fjordland. The route extends from southeastern Alaska in the United States, through western British Columbia in Canada, to northwestern Washington state in the United States. Ships using the route can avoid some of the bad weather in the open ocean and may visit some of the many isolated communities along the route. The Inside Passage is heavily travelled by cruise ships, freighters, tugs with tows, fishing craft, pleasure craft, and ships of the Alaska Marine Highway, BC Ferries, and Washington State Ferries systems. Coast Guard vessels of both Canada and the United States patrol and transit in the Passage.

Raymond Island is a small island in the Gippsland Lakes in eastern Victoria, Australia, about 300 km (190 mi) from Melbourne. The island is approximately 6 km (3.7 mi) long by 2 km (1.2 mi) wide, and is just 200 m (660 ft) off the coast, across from the town of Paynesville. The island is named after William Odell Raymond, originally a magistrate from New South Wales, who established himself as a squatter in Gippsland in the 1840s.

Anderson Island is the southernmost island in Puget Sound and a census-designated place of Pierce County, Washington, United States. It is accessible by boat or a 20-minute ferry ride from Steilacoom. Anderson Island is just south of McNeil Island. To the northwest, Key Peninsula is across Drayton Passage. The south basin of Puget Sound separates the island from the mainland to the southeast, while to the southwest the Nisqually Reach of Puget Sound separates the island from the mainland.

Texada Island is a large island located in the Strait of Georgia of British Columbia, Canada. With an area of 300.45 km2 (116.00 sq mi), it is the largest island of the Gulf Islands and the third largest island in the Strait of Georgia after Whidbey Island in Washington and Quadra Island of the Discovery Islands. Once a major mining and logging centre home to a fairly large population, Texada's industry has largely disappeared and its population shrunk since the decline began in the 1950s. In the present, it is mostly recognized as an out-of-the-way cottage and camping destination known for its warm waters and scenic beaches.

The Key Peninsula lies along Puget Sound to the south of Kitsap Peninsula in the U.S. state of Washington. It is part of Pierce County and is bordered to the west by Case Inlet and to the east by Carr Inlet. The peninsula is approximately 16 miles (26 km) long and has two Washington State Parks.

Route 217 is a collector road in the Canadian province of Nova Scotia.

Bogø is a Danish island in the Baltic Sea, just west of Møn. The population is 1,200 with 951 living in the only town on the island, Bogø By. The island is approximately 7 km long by 3 km wide at the largest points, with a total area of 13 km2. Maximum height above sea level is 32 metres.

Long Island is a Canadian island in Digby County, Nova Scotia.
Digby Neck is a Canadian peninsula extending into the Bay of Fundy in Digby County, Nova Scotia.
Wright Sound is a waterway on the North Coast of British Columbia, Canada. Wright Sound is 135 kilometers (84 mi) south of Prince Rupert and lies at the southern opening of Grenville Channel and between Gil, Gribbell and Pitt Islands. The small town of Hartley Bay sits on its northern shore and is home to the Gitga'ata, a Tsimshian group. On the north side of Wright Sound develops the Douglas Channel.

State Route 163 (SR 163) is a 3.37-mile-long (5.42 km) state highway in the U.S. state of Washington. The highway serves the city of Tacoma and the community of Ruston in Pierce County before traveling via a ferry route to the community of Tahlequah on Vashon Island in King County. SR 163 begins at an interchange with SR 16 in Tacoma and travels north as Pearl Street through Ruston to Point Defiance, where the designation continues onto the MV Chetzemoka ferry to Tahlequah.

Lake Washington steamboats and ferries operated from about 1875 to 1951, transporting passengers, vehicles and freight across Lake Washington, a large lake to the east of Seattle, Washington. Before modern highways and bridges were built, the only means of crossing the lake, other than the traditional canoe or rowboat, was by steamboat, and, later, by ferry. While there was no easily navigable connection to Puget Sound, the Lake Washington Ship Canal now connects Lake Washington to Lake Union, and from there Puget Sound is reached by way of the Hiram M. Chittenden Locks.
Audrey was a small steam vessel that operated on Puget Sound in the early part of the 1900s. The vessel was converted to a diesel tug and operated as such for many years on Puget Sound.

The Steilacoom–Anderson Island ferry is a ferry route in southern Puget Sound which is owned and operated by Pierce County, Washington. The route also serves Ketron Island.
















