
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi was an Indian lawyer, anti-colonial nationalist and political ethicist who employed nonviolent resistance to lead the successful campaign for India's independence from British rule. He inspired movements for civil rights and freedom across the world. The honorific Mahātmā, first applied to him in South Africa in 1914, is now used throughout the world.
Wardha is a city and a municipal council in Wardha district in the Indian state of Maharashtra. The administrative headquarter of Wardha district is situated here. Wardha gets its name from Wardha River which flows on the northern, western and southern boundaries of the district. Founded in 1866, the town is now an important centre for cotton trade. Wardha was an important part of the Gandhian era.

Devdas Mohandas Gandhi was the fourth and youngest son of Mahatma Gandhi. He was born in the Colony of Natal and came to India with his parents as a grown man. He became active in his father's movement, spending many terms in jail. He also became a prominent journalist, serving as editor of Hindustan Times. He was also the first pracharak of the Dakshina Bharat Hindi Prachar Sabha (DBHPS), established by Mohandas Gandhi in Tamil Nadu in 1918. The purpose of the Sabha was to propagate Hindi in southern India.

Varanasi district is a district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, with the holy city of Varanasi as the district headquarters. It is also the headquarters of the Varanasi division which contains 4 districts.

Mahatma Gandhi Kashi Vidyapith is a public university located in Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh, India. Established in 10 February 1921 as Kashi Vidyapith and later renamed, it is administered under the state legislature of the government of Uttar Pradesh. It got University status in 1974 as Deemed to be University and State University status in 2009 by The Uttar Pradesh State Universities (Amendment) Act, 2008. The university has more than 400+ affiliated colleges spread over six districts. It is one of the largest state universities in Uttar Pradesh, with hundreds of thousands of students, both rural and urban. It offers a range of professional and academic courses in arts, science, commerce, agriculture science, law, computing and management.
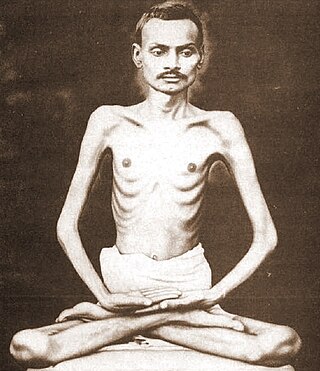
Shrimad Rajchandra was a Jain poet, mystic, philosopher, scholar, and reformer. Born in Vavaniya, a village near Morbi, he claimed to have recollection of his past lives at the age of seven. He performed Avadhāna, a memory retention and recollection test that gained him popularity, but he later discouraged it in favour of his spiritual pursuits. He wrote much philosophical poetry including Atma Siddhi. He also wrote many letters and commentaries and translated some religious texts. He is known for his teachings on Jainism and his spiritual guidance to Mahatma Gandhi.
Gandhigiri is a neologism in India which is used to express the tenets of Gandhism in contemporary terms. The term became popular due to its usage in the 2006 Hindi film, Lage Raho Munna Bhai.

Central universities in India are public universities established by an Act of Parliament and are under the purview of the Department of Higher Education in the Ministry of Education, except for nine universities which are under the purview of other ministries. In general, universities in India are recognised by the University Grants Commission (UGC), which draws its power from the University Grants Commission Act, 1956. In addition, 15 Professional Councils are established, controlling different aspects of accreditation and coordination. Central universities, in addition, are covered by the Central Universities Act, 2009, which regulates their purpose, powers, governance etc., and established 12 new universities.

Dattatreya Balkrishna Kalelkar, popularly known as Kaka Kalelkar, was an Indian independence activist, social reformer, journalist and an eminent follower of the philosophy and methods of Mahatma Gandhi.

Ramjee Singh is a former Member of Parliament and vice-chancellor of Jain Vishva Bharati University. He is an eminent Gandhian and is the author of a number of books on him. He was also the director of Gandhian Institute of Studies, Varanasi, India. In January 2020 he was awarded the fourth highest civilian award in the country: The Padma Shri for Social Work. His life has been a blend of being a Gandhian academician as well as an activist. Singh has declared Mahatma Gandhi as the Bodhisattva of the 20th century.

Jagdish Chandra Jain was a scholar, indologist, educationist, writer, and freedom fighter during the freedom struggle of India. He authored over 80 books on a variety of subjects, including Jain philosophy, Prakrit literature, and Hindi textbooks for children. Jain was the chief prosecution witness in Gandhi's murder trial. He repeatedly tried to warn the government of the conspiracy to assassinate Mahatma Gandhi, which became to known to him after Madan Lal Pahwa, a Punjabi refugee and one of the conspirators of the murder of Mahatma Gandhi, confided to him of their plan. Jain's attempts to warn the government met deaf ears. He recounted his personal experiences in two books: I Could Not Save Bapu and The Forgotten Mahatma. He died from cardiac arrest in July 1993 in Bombay at the age of 84.
Girishwar Misra is a social scientist, psychologist and author from India.

Apoorvanand is professor at the Hindi Department, Faculty of Arts, University of Delhi. He is also a regular columnist and political commentator. He is known for his frequent interventions in day-to-day politics. He claimed in his video that Delhi riots should be seen by lens of communal with all responsibility on Hindus criticizing Delhi CM over calling names of Hindu victims.

Mahatma Gandhi Central University (MGCU), is a central university located in Motihari, Bihar, India. MGCU has 7 schools and 20 academic departments.
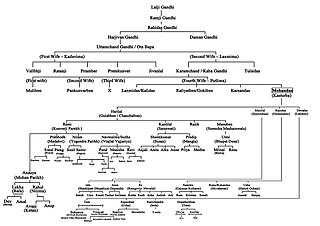
The Gandhi family is the family of Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, commonly known as Mahatma Gandhi; Mahatma meaning "high souled" or "venerable" in Sanskrit; the particular term 'Mahatma' was accorded Mohandas Gandhi for the first time while he was still in South Africa, and not commonly heard as titular for any other civil figure even of similarly rarefied stature or living or posthumous presence.

Namvar Singh was an Indian literary critic, linguist, academician and theoretician. He received his doctorate degree from Banaras Hindu University where he also taught for some time. He served as a professor of Hindi literature in several other universities. He was the founder and first chairman of Jawaharlal Nehru University's Centre of Indian Languages and continued to remain as a professor emeritus after his retirement in 1992.

Prabhat Ranjan is a Hindi novelist, fiction writer, and translator. He is currently professor of Hindi at Zakir Husain Delhi College(Evening) in the University of Delhi, Delhi. He runs an online literary website Jankipul.com since 10 years.
Beharia is a village in Suri II Block of the Birbhum district in West Bengal. It is administered by Purandarpur gram panchayat. The total area of the village is 221.2 hectares.

Mahatma Gandhi University, West Bengal is a university in Mahishadal, Purba Medinipur district, West Bengal. The university was established in 2018 as Purba Medinipur University under The Purba Medinipur University Act, 2017. In 2018 it was renamed through The Purba Medinipur University (Amendment) Act, 2018. It became active with the appointment of the first vice-chancellor, Subrata Kumar De, in November 2020. It offers education in Bengali, English, History and Mathematics.















