Related Research Articles
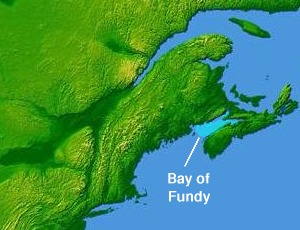
The Bay of Fundy is a bay between the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Nova Scotia, with a small portion touching the U.S. state of Maine. It is an arm of the Gulf of Maine. Its tidal range is the highest in the world. The name is probably a corruption of the French word fendu, meaning 'split'.

Eastport is a city and archipelago in Washington County, Maine, United States. The population was 1,288 at the 2020 census, making Eastport the least-populous city in Maine. The principal island is Moose Island, which is connected to the mainland by a causeway. Eastport is the easternmost city in the continental United States.

Lubec is a town in Washington County, Maine, United States. It is the easternmost municipality in the contiguous U.S. and is the country's closest continental location to Africa.

Passamaquoddy Pleasant Point Reservation is one of two reservations of the federally recognized Passamaquoddy tribe in Washington County, Maine, United States. The population was 692 as of the 2020 census.

Grand Manan is a Canadian island in the Bay of Fundy, part of the province of New Brunswick. Grand Manan is also the name of an incorporated village, which includes the main island and numerous nearby islands; White Head Island, small islands near it, and Machias Seal Island are not part of the village.

Campobello Island is the largest and only inhabited island in Campobello, a civil parish in southwestern New Brunswick, Canada, near the border with Maine, United States. The island's permanent population in 2021 was 949. It is the site of the Roosevelt Campobello International Park and of Herring Cove Provincial Park.

The Passamaquoddy are a Native American/First Nations people who live in northeastern North America. Their traditional homeland, Peskotomuhkatikuk, straddles the Canadian province of New Brunswick and the U.S. state of Maine in a region called Dawnland. They are one of the constituent nations of the Wabanaki Confederacy.

Machias Seal Island is an island in disputed water between the Gulf of Maine and the Bay of Fundy, about 16 km (10 mi) southeast from Cutler, Maine, and 19 km (12 mi) southwest of Grand Manan Island, New Brunswick. Sovereignty of the island is disputed by the United States and Canada. The Canadian Coast Guard continues to staff a lighthouse on the island; the first lighthouse was constructed there in 1832.
Deer Island is one of the Fundy Islands in the Bay of Fundy, Canada. It is at the entrance to Passamaquoddy Bay. The island was first settled by colonists around 1770.


Cobscook Bay is located in Washington County in the state of Maine. It opens into Passamaquoddy Bay, within the Bay of Fundy. Cobscook Bay is immediately south of the island city of Eastport, the main island of which straddles the two bays. In the 1930s, Cobscook Bay was part of the aborted Passamaquoddy Bay Tidal Power Project to generate electricity from its large tidal range.
Old Sow is the largest tidal whirlpool in the Western Hemisphere, located off the southwestern shore of Deer Island, New Brunswick, Canada, and off the northeast shore of Moose Island, the principal island of Eastport, Maine.
Johnson Bay is a bay in Lubec, Maine, United States.

West Isles is a civil parish in Charlotte County, New Brunswick, Canada.
The Quoddy Tides is a community newspaper published in Eastport, Maine covering several communities in Washington County, Maine and Charlotte County, New Brunswick. It styles itself the "most easterly published newspaper in the United States". It is published on the second and fourth Friday of each month. The first issue was published on November 29, 1968.

State Route 190 (SR 190) is a 7.1-mile (11.4 km) state highway that travels from Water Street in Eastport to U.S. Route 1 (US 1) in Perry. It serves as the connector route to Eastport from the mainland. Though the road travels in a southeast–northwesterly direction, the road is signed as north–south.
Concouguash, christian name Francis Joseph Neptune, (1735–1834) was chief of the Passamaquoddy tribe during the American Revolutionary War. He succeeded his father, Bahgulwet, who died in 1778, and was succeeded by his own son, John Francis Neptune, in 1824. The term "chief" later became the word for governor. Becoming chief is passed along through family lineage and requires acceptance from the Passamaquoddies, Penobscots and Maliseet tribes. These three tribes share similar chief induction ceremonies, conducted simultaneously with eyewitnesses from each tribe present.
Oak Bay is the northernmost section of Passamaquoddy Bay, into which the St. Croix River empties. Its extent fluctuates with the Bay of Fundy tidal changes, so that its northern section changes from approximately 30 feet (9.1 m) in depth at high tide to exposed ocean floor at low tide. The rural community of Oak Bay lies on the shores of this embayment.

The Grand Harbour Lighthouse was a Canadian lighthouse marking the entrance to Grand Harbour, Grand Manan, New Brunswick. It was built and first lit in 1879 and was decommissioned in 1963. It was severely damaged in the Groundhog Day gale of 1976 and destroyed by a gale in November 2013.
References
- ↑ Lindsell, Robert. The Rail Lines of Northern New England. Pepperell, Massachusetts USA: Branch Line Press, 2000: 314-315.
- ↑ Sides, Hampton. Blood and Thunder: The Epic Story of Kit Carson and the Conquest of the American West. New York: Anchor Books, 2006: 286-7.
- ↑ 'The Haunted Lighthouse', S1 E2, "The Adventures of Superman", 1952.