
Epilepsy is a group of non-communicable neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures. An epileptic seizure is the clinical manifestation of an abnormal, excessive, and synchronized electrical discharge in the brain cells called neurons. The occurrence of two or more unprovoked seizures defines epilepsy. The occurrence of just one seizure may warrant the definition in a more clinical usage where recurrence may be able to be prejudged. Epileptic seizures can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking due to abnormal electrical activity in the brain. These episodes can result in physical injuries, either directly such as broken bones or through causing accidents. In epilepsy, seizures tend to recur and may have no immediate underlying cause. Isolated seizures that are provoked by a specific cause such as poisoning are not deemed to represent epilepsy. People with epilepsy may be treated differently in various areas of the world and experience varying degrees of social stigma due to the alarming nature of their symptoms.

An epileptic seizure, informally known as a seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much of the body with loss of consciousness, to shaking movements involving only part of the body with variable levels of consciousness, to a subtle momentary loss of awareness. These episodes usually last less than two minutes and it takes some time to return to normal. Loss of bladder control may occur.
Absence seizures are one of several kinds of generalized seizures. In the past, absence epilepsy was referred to as "pyknolepsy," a term derived from the Greek word "pyknos," signifying "extremely frequent" or "grouped". These seizures are sometimes referred to as petit mal seizures ; however, usage of this terminology is no longer recommended. Absence seizures are characterized by a brief loss and return of consciousness, generally not followed by a period of lethargy. Absence seizures are most common in children. They affect both sides of the brain.

Myoclonus is a brief, involuntary, irregular twitching of a muscle, a joint, or a group of muscles, different from clonus, which is rhythmic or regular. Myoclonus describes a medical sign and, generally, is not a diagnosis of a disease. It belongs to the hyperkinetic movement disorders, among tremor and chorea for example.
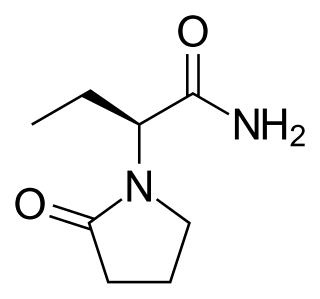
Levetiracetam, sold under the brand name Keppra among others, is a medication used to treat epilepsy. It is used for partial-onset, myoclonic, or tonic–clonic seizures and is taken either by mouth as an immediate or extended release formulation or by injection into a vein.

The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, adequate-protein, low-carbohydrate dietary therapy that in conventional medicine is used mainly to treat hard-to-control (refractory) epilepsy in children. The diet forces the body to burn fats rather than carbohydrates.

Lennox–Gastaut syndrome (LGS) is a complex, rare, and severe childhood-onset epilepsy syndrome. It is characterized by multiple and concurrent seizure types including tonic seizure, cognitive dysfunction, and slow spike waves on electroencephalogram (EEG), which are very abnormal. Typically, it presents in children aged 3–5 years and most of the time persists into adulthood with slight changes in the electroclinical phenotype. It has been associated with perinatal injuries, congenital infections, brain malformations, brain tumors, genetic disorders such as tuberous sclerosis and numerous gene mutations. Sometimes LGS is observed after infantile epileptic spasm syndrome. The prognosis for LGS is marked by a 5% mortality in childhood and persistent seizures into adulthood.
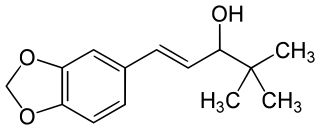
Stiripentol, sold under the brand name Diacomit, is an anticonvulsant medication used for the treatment of Dravet syndrome - a serious genetic brain disorder.
Reflex seizures are epileptic seizures that are consistently induced by a specific stimulus or trigger, making them distinct from other epileptic seizures, which are usually unprovoked. Reflex seizures are otherwise similar to unprovoked seizures and may be focal, generalized, myoclonic, or absence seizures. Epilepsy syndromes characterized by repeated reflex seizures are known as reflex epilepsies. Photosensitive seizures are often myoclonic, absence, or focal seizures in the occipital lobe, while musicogenic seizures are associated with focal seizures in the temporal lobe.
In the field of neurology, seizure types are categories of seizures defined by seizure behavior, symptoms, and diagnostic tests. The International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) 2017 classification of seizures is the internationally recognized standard for identifying seizure types. The ILAE 2017 classification of seizures is a revision of the prior ILAE 1981 classification of seizures. Distinguishing between seizure types is important since different types of seizures may have different causes, outcomes, and treatments.
Idiopathic generalized epilepsy (IGE) is a group of epileptic disorders that are believed to have a strong underlying genetic basis. IGE is considered a subgroup of Genetic Generalized Epilepsy (GGE). Patients with an IGE subtype are typically otherwise normal and have no structural brain abnormalities. People also often have a family history of epilepsy and seem to have a genetically predisposed risk of seizures. IGE tends to manifest itself between early childhood and adolescence although it can be eventually diagnosed later. The genetic cause of some IGE types is known, though inheritance does not always follow a simple monogenic mechanism.
Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy (JME), also known as Janz syndrome or impulsive petit mal, is a form of hereditary, idiopathic generalized epilepsy, representing 5–10% of all epilepsy cases. Typically it first presents between the ages of 12 and 18 with myoclonic seizures. These events typically occur after awakening from sleep, during the evening or when sleep-deprived. JME is also characterized by generalized tonic–clonic seizures, and a minority of patients have absence seizures. It was first described by Théodore Herpin in 1857. Understanding of the genetics of JME has been rapidly evolving since the 1990s, and over 20 chromosomal loci and multiple genes have been identified. Given the genetic and clinical heterogeneity of JME some authors have suggested that it should be thought of as a spectrum disorder.
Ring chromosome 20, ring-shaped chromosome 20 or r(20) syndrome is a rare human chromosome abnormality where the two arms of chromosome 20 fuse to form a ring chromosome. The syndrome is associated with epileptic seizures, behaviour disorders and intellectual disability.

Generalized epilepsy is a form of epilepsy characterised by generalised seizures with no apparent cause. Generalized seizures, as opposed to focal seizures, are a type of seizure that impairs consciousness and distorts the electrical activity of the whole or a larger portion of the brain.

A generalized tonic–clonic seizure, commonly known as a grand mal seizure or GTCS, is a type of generalized seizure that produces bilateral, convulsive tonic and clonic muscle contractions. Tonic–clonic seizures are the seizure type most commonly associated with epilepsy and seizures in general and the most common seizure associated with metabolic imbalances. It is a misconception that they are the sole type of seizure, as they are the main seizure type in approximately 10% of those with epilepsy.

GLUT1 deficiency syndrome, also known as GLUT1-DS, De Vivo disease or Glucose transporter type 1 deficiency syndrome, is an autosomal dominant genetic metabolic disorder associated with a deficiency of GLUT1, the protein that transports glucose across the blood brain barrier. Glucose Transporter Type 1 Deficiency Syndrome has an estimated birth incidence of 1 in 90,000 to 1 in 24,300. This birth incidence translates to an estimated prevalence of 3,000 to 7,000 in the U.S.
Progressive Myoclonic Epilepsies (PME) are a rare group of inherited neurodegenerative diseases characterized by myoclonus, resistance to treatment, and neurological deterioration. The cause of PME depends largely on the type of PME. Most PMEs are caused by autosomal dominant or recessive and mitochondrial mutations. The location of the mutation also affects the inheritance and treatment of PME. Diagnosing PME is difficult due to their genetic heterogeneity and the lack of a genetic mutation identified in some patients. The prognosis depends largely on the worsening symptoms and failure to respond to treatment. There is no current cure for PME and treatment focuses on managing myoclonus and seizures through antiepileptic medication (AED).

Epilepsy is a neurological condition of recurrent episodes of unprovoked epileptic seizures. A seizure is an abnormal neuronal brain activity that can cause intellectual, emotional, and social consequences. Epilepsy affects children and adults of all ages and races, it is one of the most common neurological disorders of the nervous system. As well as, this condition is more common among children than adults affecting about 6 out of 1000 US children that are between the age of 0 to 5 years old. The epileptic seizures can be of different types depending on the part of the brain that was affected, seizures are classified in 2 main types partial seizure or genralized seizure.
Jeavons syndrome is a type of epilepsy. It is one of the most distinctive reflex syndromes of idiopathic generalized epilepsy characterized by the triad of eyelid myoclonia with and without absences, eye-closure-induced seizures, EEG paroxysms, or both, and photosensitivity. Eyelid myoclonia with or without absences is a form of epileptic seizure manifesting with myoclonic jerks of the eyelids with or without a brief absence. These are mainly precipitated by closing of the eyes and lights. Eyelid myoclonia is the defining seizure type of Jeavons syndrome.
People with epilepsy may be classified into different syndromes based on specific clinical features. These features include the age at which seizures begin, the seizure types, and EEG findings, among others. Identifying an epilepsy syndrome is useful as it helps determine the underlying causes as well as deciding what anti-seizure medication should be tried. Epilepsy syndromes are more commonly diagnosed in infants and children. Some examples of epilepsy syndromes include benign rolandic epilepsy, childhood absence epilepsy and juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Severe syndromes with diffuse brain dysfunction caused, at least partly, by some aspect of epilepsy, are also referred to as epileptic encephalopathies. These are associated with frequent seizures that are resistant to treatment and severe cognitive dysfunction, for instance Lennox-Gastaut syndrome and West syndrome.





