This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.

In human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as 1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand; (2) the wrist joint or radiocarpal joint, the joint between the radius and the carpus and
(3) the anatomical region surrounding the carpus including the distal parts of the bones of the forearm and the proximal parts of the metacarpus or five metacarpal bones and the series of joints between these bones, thus referred to as wrist joints. This region also includes the carpal tunnel, the anatomical snuff box, bracelet lines, the flexor retinaculum, and the extensor retinaculum.

The trapezoid bone is a carpal bone in tetrapods, including humans. It is the smallest bone in the distal row of carpal bones that give structure to the palm of the hand. It may be known by its wedge-shaped form, the broad end of the wedge constituting the dorsal, the narrow end the palmar surface; and by its having four articular facets touching each other, and separated by sharp edges. It is homologous with the "second distal carpal" of reptiles and amphibians.
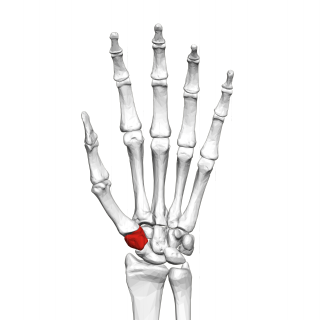
The trapezium bone is a carpal bone in the hand. It forms the radial border of the carpal tunnel.

The scaphoid bone is one of the carpal bones of the wrist. It is situated between the hand and forearm on the thumb side of the wrist. It forms the radial border of the carpal tunnel. The scaphoid bone is the largest bone of the proximal row of wrist bones, its long axis being from above downward, lateralward, and forward. It is approximately the size and shape of a medium cashew.

The hamate bone or unciform bone is a bone in the human wrist readily distinguishable by its wedge shape and a hook-like process ("hamulus") projecting from its palmar surface.

The lunate bone is a carpal bone in the human hand. It is distinguished by its deep concavity and crescentic outline. It is situated in the center of the proximal row carpal bones, which lie between the ulna and radius and the hand. The lunate carpal bone is situated between the lateral scaphoid bone and medial triquetral bone.

The ulnar artery is the main blood vessel, with oxygenated blood, of the medial aspect of the forearm. It arises from the brachial artery and terminates in the superficial palmar arch, which joins with the superficial branch of the radial artery. It is palpable on the anterior and medial aspect of the wrist.

The flexor pollicis brevis is a muscle in the hand that flexes the thumb. It is one of three thenar muscles. It has both a superficial part and a deep part.

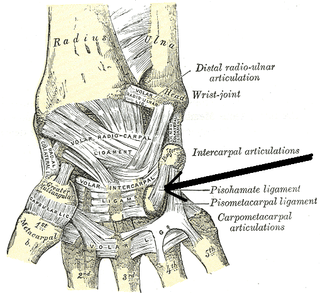
The carpometacarpal (CMC) joints are five joints in the wrist that articulate the distal row of carpal bones and the proximal bases of the five metacarpal bones.
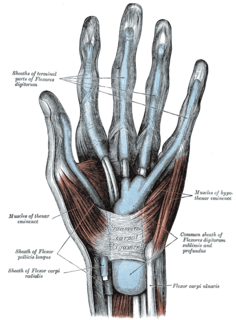
The flexor retinaculum is a fibrous band on the palmar side of the hand near the wrist. It arches over the carpal bones of the hands, covering them and forming the carpal tunnel.
The intermetacarpal joints are in the hand formed between the metacarpal bones. The bases of the second, third, fourth and fifth metacarpal bones articulate with one another by small surfaces covered with cartilage. The metacarpal bones are connected together by dorsal, palmar, and interosseous ligaments.

The palmar branch of the median nerve is a branch of the median nerve which arises at the lower part of the forearm.

The Palmar carpometacarpal ligaments are a series of bands on the palmar surface of the carpometacarpal joints that connect the carpal bones to the second through fifth metacarpal bones. The second metacarpal is connected to the trapezium. The third metacarpal is connected to the trapezium, to the capitate, and to the hamate. The fourth and fifth metacarpals are connected to the hamate.
The radiate carpal ligament is a group of about seven fibrous bands which diverge in all directions on the palmar surface of the carpal bones. The majority of the bands radiate from the capitate to the scaphoid, lunate, and triquetral bones.
A palmar ligament is one of several ligaments in or near the palm of the hand:
Carpometacarpal ligaments may refer to:
Carpal ligament may refer to: