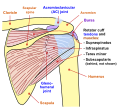
Ligaments
The joint is stabilized by three ligaments:
Superior acromioclavicular ligament
This ligament is a quadrilateral band, covering the superior part of the articulation, and extending between the upper part of the lateral end of the clavicle and the adjoining part of the upper surface of the acromion.
It is composed of parallel fibers, which interlace with the aponeuroses of the trapezius and deltoideus; below, it is in contact with the articular disk when this is present.
Inferior acromioclavicular ligament
This ligament is somewhat thinner than the preceding; it covers the under part of the articulation, and is attached to the adjoining surfaces of the two bones.
It is in relation, above, in rare cases with the articular disk; below, with the tendon of the supraspinatus
The coracoacromial ligament is a strong triangular band, extending between the coracoid process and the acromion.
It is attached, by its apex, to the summit of the acromion just in front of the articular surface for the clavicle; and by its broad base to the whole length of the lateral border of the coracoid process. [2]
This ligament, together with the coracoid process and the acromion, forms a vault for the protection of the head of the humerus.
It is in relation, above, with the clavicle and under surface of the deltoid; below, with the tendon of the supraspinatus, a bursa being interposed. [3]
Its lateral border is continuous with a dense lamina that passes beneath the deltoid upon the tendons of the supraspinatus and infraspinatus.
The ligament is sometimes described as consisting of two marginal bands and a thinner intervening portion, the two bands being attached respectively to the apex and the base of the coracoid process, and joining at the acromion.
When the pectoralis minor is inserted, as occasionally is the case, into the capsule of the shoulder-joint instead of into the coracoid process, it passes between these two bands, and the intervening portion of the ligament is then deficient.
The coracoclavicular ligament serves to connect the clavicle with the coracoid process of the scapula. [4]
It does not properly belong to the acromioclavicular joint articulation, but is usually described with it, since it forms a most efficient means of retaining the clavicle in contact with the acromion. It consists of two fasciculi, called the trapezoid ligament and conoid ligament.
These ligaments are in relation, in front, with the subclavius and deltoid; behind, with the trapezius.