
Parvoviruses are a family of animal viruses that constitute the family Parvoviridae. They have linear, single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) genomes that typically contain two genes encoding for a replication initiator protein, called NS1, and the protein the viral capsid is made of. The coding portion of the genome is flanked by telomeres at each end that form into hairpin loops that are important during replication. Parvovirus virions are small compared to most viruses, at 23–28 nanometers in diameter, and contain the genome enclosed in an icosahedral capsid that has a rugged surface.

Podoviridae was a family of bacteriophage in the order Caudovirales often associated with T-7 like phages. The family and order Caudovirales have now been abolished, with the term podovirus now used to refer to the morphology of viruses in this former family. There were 130 species in this family, assigned to 3 subfamilies and 52 genera. This family was characterized by having very short, noncontractile tails. Many former phages in the former family Podoviriade are now classified in the Autographiviridae

Comovirinae is a subfamily of viruses in the order Picornavirales, in the family Secoviridae; its genera were formerly classified in the family Comoviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 62 species in this subfamily, assigned to 3 genera.

Alphaherpesvirinae is a subfamily of viruses in the family Herpesviridae, primarily distinguished by reproducing more quickly than other subfamilies in the Herpesviridae. In animal virology the most important herpesviruses belong to the Alphaherpesvirinae. Pseudorabies virus is the causative agent of Aujeszky's disease in pigs and Bovine herpesvirus 1 is the causative agent of bovine infectious rhinotracheitis and pustular vulvovaginitis. Mammals serve as natural hosts. There are currently 45 species in this subfamily, divided among 5 genera with one species unassigned to a genus. Diseases associated with this subfamily include: HHV-1 and HHV-2: skin vesicles or mucosal ulcers, rarely encephalitis and meningitis, HHV-3: chickenpox (varicella) and shingles, GaHV-2: Marek's disease.

The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) authorizes and organizes the taxonomic classification of and the nomenclature for viruses. The ICTV develops a universal taxonomic scheme for viruses, and thus has the means to appropriately describe, name, and classify every virus taxon. The members of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses are considered expert virologists. The ICTV was formed from and is governed by the Virology Division of the International Union of Microbiological Societies. Detailed work, such as identifying new taxa and delimiting the boundaries of species, genera, families, etc. typically is performed by study groups of experts in the families.
Amdoparvovirus is a genus of viruses in the family Parvoviridae in the subfamily Parvovirinae. Mustelids, skunk, and raccoons serve as natural hosts. There are five species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include progressive disorder of immune system.

Avulavirinae is a subfamily of viruses in the family Paramyxoviridae. Members of the subfamily are collectively known as avulaviruses. All members of the subfamily primarily infect birds. Avulavirinae was previously recognized as the genus Avulavirus before being elevated to a subfamily. The term avula comes from "avian rubula", distinguishing it from rubulaviruses of the subfamily Rubulavirinae due to avulaviruses only infecting birds and translating protein V from an edited RNA transcript. The most notable avulavirus is the Newcastle disease virus, a strain of Avian orthoavulavirus 1.

Dependoparvovirus is a genus in the subfamily Parvovirinae of the virus family Parvoviridae; they are Group II viruses according to the Baltimore classification.

Erythroparvovirus is a genus of viruses in subfamily Parvovirinae of the virus family Parvoviridae. Primates serve as natural hosts. There are seven species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include fifth disease and skin lesions.

The Herpesvirales is an order of dsDNA viruses with animal hosts, characterised by a common morphology consisting of an icosahedral capsid enclosed in a glycoprotein-containing lipid envelope. Common infections in humans caused by members of this order include cold sores, genital herpes, chickenpox, shingles, and glandular fever. Herpesvirales is the sole order in the class Herviviricetes, which is the sole class in the phylum Peploviricota.

Betaflexiviridae is a family of viruses in the order Tymovirales. Plants and fungi serve as natural hosts. There are 108 species in this family, assigned to 13 genera in two subfamilies. Diseases associated with this family include mosaic and ringspot symptoms.

Secoviridae is a family of viruses in the order Picornavirales. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 8 genera and 86 species in this family, one of which is unassigned to a genus. The family was created in 2009 with the grouping of families Sequiviridae, now dissolved, and Comoviridae, now subfamily Comovirinae, along with the then unassigned genera Cheravirus, Sadwavirus, and Torradovirus.
Proboscivirus is a genus of viruses in the order Herpesvirales, in the family Herpesviridae, in the subfamily Betaherpesvirinae. Elephants serve as natural hosts. EEHV1 causes asymptomatic infection in African elephants but causes fatal haemorrhagic disease in Asian elephants. The name "Proboscivirus" comes from the Greek word προβοσκίς or "proboscis" meaning "the elephant trunk," for which the virus accordingly uses as a means of contraction and transmission to enter the elephant's body.
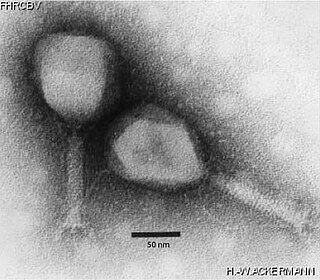
Tevenvirinae is a subfamily of viruses in the family Straboviridae of class Caudoviricetes. The subfamily was previously placed in the morphology-based family Myoviridae, which was found to be paraphyletic in genome studies and abolished in the 2021 International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) classification. Bacteria and archaea serve as natural hosts. There are 148 species in this subfamily, included in 14 genera.
Eucampyvirinae is a subfamily of viruses in the class Caudoviricetes. Bacteria of the genus Campylobacter serve as natural hosts. There are 9 species in this subfamily, assigned to 2 genera. Prior to 2022, eucampyvirinae was in the class Caudovirales, in the family Myoviridae.
Gokushovirinae is a subfamily of viruses in the family Microviridae. There are 8 species in this subfamily, divided among 4 genera.
Ackermannviridae is a family of viruses in the class Caudoviricetes. Gammaproteobacteria in the phylum Pseudomonadota serve as natural hosts. There are two subfamilies, ten genera, and 63 species in the family.
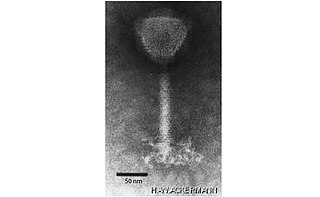
Herelleviridae is a family of bacterial viruses of the order Caudovirales infecting members of the phylum Firmicutes. The family has five subfamilies, 33 genera and 92 species. In average, replication of family members is supported by 70% isolates of primary host species.
Straboviridae is a family of bacteriophages in the class Caudoviricetes. The viruses in this family were formerly place in the morphology-based family Myoviridae, which was found to be paraphyletic in genome studies and abolished in the 2021 International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) classification, although the term myovirus is still used to refer to the morphology of viruses in this new family. Bacteria and archaea serve as natural hosts. In average, replication of family members is supported by 34% isolates of primary host species. There were 209 species in this family, assigned to 36 genera and three subfamilies.












