
Peterborough is a cathedral city in the City of Peterborough district of Cambridgeshire, England. The city and its surroundings, the Soke of Peterborough, had an independent county council between 1889 and 1965. It formed part of the short-lived Huntingdon and Peterborough between 1965 and 1974. Before 1889, it was a liberty of Northamptonshire.

The Greater London Authority (GLA), colloquially known by the metonym City Hall, is the devolved regional governance body of Greater London, England. It consists of two political branches: the executive Mayoralty and the 25-member London Assembly, which serves as a means of checks and balances on the former. Since May 2016, both branches have been under the control of the London Labour Party. The authority was established in 2000, following a local referendum, and derives most of its powers from the Greater London Authority Act 1999 and the Greater London Authority Act 2007.
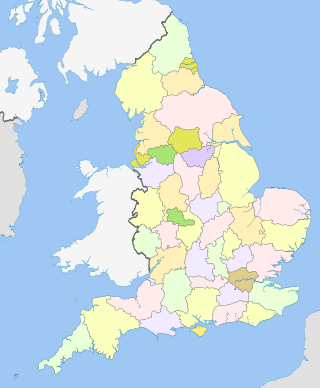
The counties of England are divisions of England. There are currently 48 ceremonial counties, which have their origin in the historic counties of England established in the Middle Ages. The current ceremonial counties are the result of the Lieutenancies Act 1997 and are based on the Local Government Act 1972 administrative counties which included a number of new counties such as Greater Manchester and Tyne and Wear. However, some counties introduced by the Local Government Act 1972, including Avon, Cleveland and Humberside no longer exist. The term "county", relating to any of its meanings, is used as the geographical basis for a number of institutions such as police and fire services, sports clubs and other non-government organisations.

The City of Peterborough, commonly known as Peterborough, is a unitary authority district with city status in the ceremonial county of Cambridgeshire, England. The area is named after its largest settlement, Peterborough but also covers a wider area of outlying villages and hamlets.
The new towns in the United Kingdom were planned under the powers of the New Towns Act 1946 and later acts to relocate populations in poor or bombed-out housing following the Second World War. They were developed in three waves. Later developments included the expanded towns: existing towns which were substantially expanded to accommodate what was called the "overspill" population from densely populated areas of deprivation.

The Local Government Act 1972 is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales on 1 April 1974. It was one of the most significant Acts of Parliament to be passed by the Heath Government of 1970–74.
Development corporations or development firms are organizations established by governments in several countries for the purpose of urban development. They often are responsible for the development of new suburban areas or the redevelopment of existing ones.

The London Government Act 1963 is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, which created Greater London and a new local government structure within it. The Act significantly reduced the number of local government districts in the area, resulting in local authorities responsible for larger areas and populations. The upper tier of local government was reformed to cover the whole of the Greater London area and with a more strategic role; and the split of functions between upper and lower tiers was recast. The Act classified the boroughs into inner and outer London groups. The City of London and its corporation were essentially unreformed by the legislation. Subsequent amendments to the Act have significantly amended the upper tier arrangements, with the Greater London Council abolished in 1986, and the Greater London Authority introduced in 2000. As of 2016, the London boroughs are more or less identical to those created in 1965, although with some enhanced powers over services such as waste management and education.
The New South Wales Department of Planning and Environment (DPE) is a department of the New South Wales Government, responsible for effective and sustainable planning to support the growth in the state of New South Wales, Australia. It makes plans based on evidence for the state's cities and regions, working with the community, business and local government to create places for people in NSW to live, work and spend their leisure time, while ensuring good access to transport and other services like shops and restaurants. The department is also responsible for the evidence-based assessment of state significant development applications.

The Local Government Act 1958 was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom affecting local government in England and Wales outside London. Among its provisions it included the establishment of Local Government Commissions to review the areas and functions of local authorities, and introduced new procedures for carrying these into action.

Peterborough City Council is the local authority for Peterborough in the East of England. It is a unitary authority, having the powers of a non-metropolitan county and district council combined. The City was incorporated as a municipal borough in 1874; from 1888, it fell within the jurisdiction of the Soke of Peterborough county council and from 1965, Huntingdon and Peterborough county council. In 1974, it was replaced by a wholly new non-metropolitan district, broadly corresponding to the Soke, in the new enlarged Cambridgeshire. In 1998, Peterborough became independent of Cambridgeshire as a unitary authority, but the city continues to form part of that county for ceremonial purposes as defined by the Lieutenancies Act 1997.
The New Towns Acts were a series of Acts of the Parliament of the United Kingdom to found new settlements or to expand substantially existing ones, to establish Development Corporations to deliver them, and to create a Commission to wind up the Corporations and take over their assets and liabilities. Of these, the more substantive acts were the New Towns Act 1946 and the Town Development Act 1952. "The New Towns Act [1946] was intended to pre-emptively direct urban growth and infrastructural development into new towns, thereby decentralising population and economic opportunity while inhibiting urban sprawl."
The history of local government in England is one of gradual change and evolution since the Middle Ages. England has never possessed a formal written constitution, with the result that modern administration is based on precedent, and is derived from administrative powers granted to older systems, such as that of the shires.

The Queensgate shopping centre is located in the centre of the UK city of Peterborough, in Cambridgeshire. It contains over 100 stores and parking for 2,300 cars in four onsite multi-storey car parks. Queensgate bus station is located within the shopping centre and only a short walk from Peterborough railway station. Peterborough Shop Mobility provide wheelchairs and electric scooters to help those with limited mobility. The centre was opened by Queen Beatrix of the Netherlands on 9 March 1982.
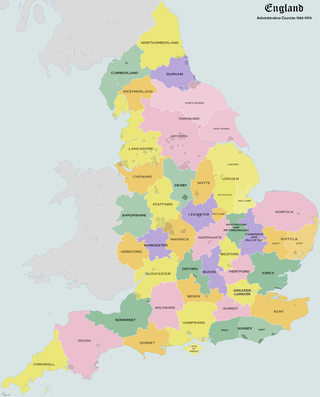
Administrative counties were subnational divisions of England used for local government from 1889 to 1974. They were created by the Local Government Act 1888, which established an elected county council for each area. Some geographically large historic counties were divided into several administrative counties, each with its own county council. The administrative counties operated until 1974, when they were replaced by a system of metropolitan and non-metropolitan counties under the Local Government Act 1972.
While purpose-built towns and cities have many precedents in antiquity - the 195 BC iteration of Chang'an providing a case in point - the New Towns movement refers to an ideologically-driven social campaign. An associated government-driven building and development program to realise the creation of new towns took place in two tranches in the United Kingdom after World War II. Towns were planned and built with two main intentions: to remedy overcrowding and congestion, and to organize scattered ad hoc settlements. An additional purpose was to rehouse people in freshly built, fully planned towns that were completely self-sufficient for the community. Ideological aspects of environmental determinism predominated in this last purpose.

The regions of England, formerly known as the government office regions, are the highest tier of sub-national division in England. They were established in 1994 and follow the 1974–96 county borders. They are a continuation of the former 1940s standard regions which followed the 1889–1974 administrative county borders. Between 1994 and 2011, all nine regions had partly devolved functions; they no longer fulfil this role, continuing to be used for limited statistical purposes.
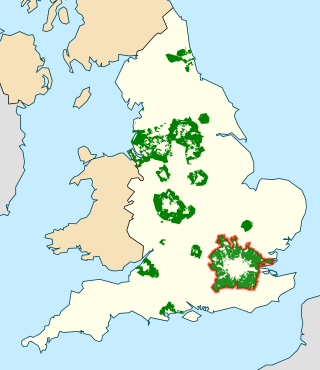
The Metropolitan Green Belt is a statutory green belt around London, England. It comprises parts of Greater London, Berkshire, Buckinghamshire, Essex, Hertfordshire, Kent and Surrey, parts of two of the three districts of Bedfordshire and a small area in Copthorne, Sussex. As of 2017/18, Government statistics show the planning designation covered 513,860 hectares of land.

Crawley Development Corporation was set up in February 1947 by the Government of the United Kingdom to establish, administer and control the development of the New Town of Crawley in accordance with the New Towns Act 1946. The Corporation had the task of growing the ancient Sussex market town of Crawley from a population of 9,000 to 40,000 by the early 1960s, expanding its commercial and industrial base and developing a balanced, socially cohesive community. A master plan supplied by planning consultant Anthony Minoprio would guide the Corporation's work. The "energy and enthusiasm" of its chairman Thomas Bennett helped it meet many of its targets early, and it was formally dissolved in 1962. Its assets passed to the Commission for New Towns in that year; they are now owned privately or by the local authority, Crawley Borough Council.

The Mayor of Greater Manchester is the directly elected metro mayor of Greater Manchester, responsible for strategic governance in the region that includes health, transport, housing, strategic planning, waste management, policing, the Greater Manchester Fire and Rescue Service and skills. The creation of the Mayor of Greater Manchester was agreed between the then Chancellor of the Exchequer, George Osborne, and Greater Manchester's 10 district council leaders. As well as having specific powers, the mayor chairs the Greater Manchester Combined Authority, also assuming the powers of the Greater Manchester Police and Crime Commissioner.












