H1 antagonists, also called H1 blockers, are a class of medications that block the action of histamine at the H1 receptor, helping to relieve allergic reactions. Agents where the main therapeutic effect is mediated by negative modulation of histamine receptors are termed antihistamines; other agents may have antihistaminergic action but are not true antihistamines.

Hives, also known as urticaria, is a kind of skin rash with red, raised, itchy bumps. Hives may burn or sting. The patches of rash may appear on different body parts, with variable duration from minutes to days, and does not leave any long-lasting skin change. Fewer than 5% of cases last for more than six weeks. The condition frequently recurs.

Angioedema is an area of swelling (edema) of the lower layer of skin and tissue just under the skin or mucous membranes. The swelling may occur in the face, tongue, larynx, abdomen, or arms and legs. Often it is associated with hives, which are swelling within the upper skin. Onset is typically over minutes to hours.

Cold urticaria is a disorder in which large red welts called hives (urticaria) form on the skin after exposure to a cold stimulus. The hives are usually itchy and often the hands, feet and other parts of the body will become itchy and swollen as well. Hives vary in size from about 7 mm in diameter to as big as about 27 mm or larger.

Dermatographic urticaria is a skin disorder and one of the most common types of urticaria, affecting 2–5% of the population.
Aquagenic pruritus is a skin condition characterized by the development of severe, intense, prickling-like epidermal itching without observable skin lesions and evoked by contact with water.

Ketotifen is an antihistamine medication and a mast cell stabilizer used to treat allergic conditions such as conjunctivitis, asthma, and urticaria (hives). Ketotifen is available in ophthalmic and oral forms: the ophthalmic form relieves eye itchiness and irritation associated with seasonal allergies, while the oral form helps prevent systemic conditions such as asthma attacks and allergic reactions. In addition to treating allergies, ketotifen has shown efficacy in managing systemic mast cell diseases such as mastocytosis and mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS), which involve abnormal accumulation or activation of mast cells throughout the body. Ketotifen is also used for other allergic-type conditions like atopic dermatitis (eczema) and food allergies.

Urticaria pigmentosa (also known as generalized eruption of cutaneous mastocytosis (childhood type) ) is the most common form of cutaneous mastocytosis. It is a rare disease caused by excessive numbers of mast cells in the skin that produce hives or lesions on the skin when irritated.
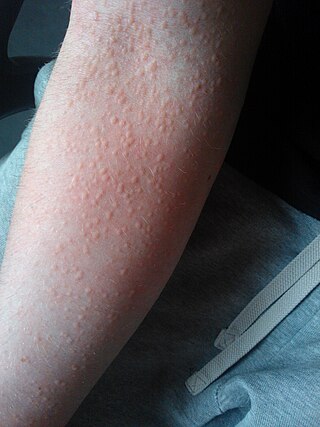
Cholinergic urticaria or also known as (CholU) and CU, is a rare form of hives (urticaria) that is triggered by an elevation in body temperature, breaking a sweat, or exposure to heat. It is also sometimes called exercise-induced urticaria or heat hives. The condition is considered to be one of the many rarest forms of allergies known to medical science.

Solar urticaria (SU) is a rare condition in which exposure to ultraviolet or UV radiation, or sometimes even visible light, induces a case of urticaria or hives that can appear in both covered and uncovered areas of the skin. It is classified as a type of physical urticaria. The classification of disease types is somewhat controversial. One classification system distinguished various types of SU based on the wavelength of the radiation that causes the breakout; another classification system is based on the type of allergen that initiates a breakout.
Aquagenic urticaria, also known as water allergy and water urticaria, is a form of physical urticaria in which hives develop on the skin after contact with water, regardless of its temperature. The condition typically results from contact with water of any type, temperature or additive.
Schnitzler syndrome or Schnitzler's syndrome is a rare disease characterised by onset around middle age of chronic hives (urticaria) and periodic fever, bone and joint pain, weight loss, malaise, fatigue, swollen lymph glands and enlarged spleen and liver.
One of the most prevalent forms of adverse drug reactions is cutaneous reactions, with drug-induced urticaria ranking as the second most common type, preceded by drug-induced exanthems. Urticaria, commonly known as hives, manifests as weals, itching, burning, redness, swelling, and angioedema—a rapid swelling of lower skin layers, often more painful than pruritic. These symptoms may occur concurrently, successively, or independently. Typically, when a drug triggers urticaria, symptoms manifest within 24 hours of ingestion, aiding in the identification of the causative agent. Urticaria symptoms usually subside within 1–24 hours, while angioedema may take up to 72 hours to resolve completely.

Acquired C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency, also referred to as acquired angioedema (AAE), is a rare medical condition that presents as body swelling that can be life-threatening and manifests due to another underlying medical condition. The acquired form of this disease can occur from a deficiency or abnormal function of the enzyme C1 esterase inhibitor (C1-INH). This disease is also abbreviated in medical literature as C1INH-AAE. This form of angioedema is considered acquired due to its association with lymphatic malignancies, immune system disorders, or infections. Typically, acquired angioedema presents later in adulthood, in contrast to hereditary angioedema which usually presents from early childhood and with similar symptoms.
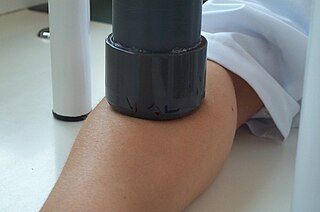
Pressure urticaria or delayed pressure urticaria is a physical urticaria caused by pressure applied to the skin, and is characterized by the development of swelling and pain that usually occurs 3 to 12 hours after local pressure has been applied.
Senile pruritus is one of the most common conditions in the elderly or people over 65 years of age with an emerging itch that may be accompanied with changes in temperature and textural characteristics. In the elderly, xerosis, is the most common cause for an itch due to the degradation of the skin barrier over time. However, the cause of senile pruritus is not clearly known. Diagnosis is based on an elimination criteria during a full body examination that can be done by either a dermatologist or non-dermatologist physician.
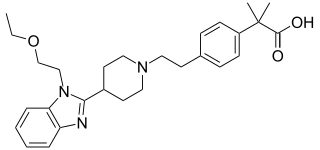
Bilastine is an antihistamine medication used to treat hives (urticaria), allergic rhinitis and itchy inflamed eyes (allergic conjunctivitis) caused by an allergy. It is a second-generation antihistamine and takes effect by selectively inhibiting the histamine H1 receptor, preventing these allergic reactions. Bilastine has an effectiveness similar to cetirizine, fexofenadine, and desloratadine.

Chronic spontaneous urticaria(CSU) also known as Chronic idiopathic urticaria(CIU) is defined by the presence of wheals, angioedema, or both for more than six weeks. The most common symptoms of chronic spontaneous urticaria are angioedema and hives that are accompanied by itchiness.

Mosquito bite allergies, also termed hypersensitivity to mosquito bites, are excessive reactions of varying severity to mosquito bites. They are allergic hypersensitivity reactions caused by the non-toxic allergenic proteins contained in the saliva injected by a female mosquito at the time it takes its blood meal, and are not caused by any toxin or pathogen. By general agreement, mosquito bite allergies do not include the ordinary wheal and flare responses to these bites although these reactions are also allergic in nature. Ordinary mosquito bite allergies are nonetheless detailed here because they are the best understood reactions to mosquito bites and provide a basis for describing what is understood about them.
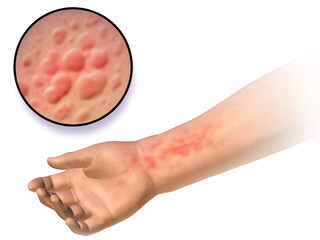
Autoimmune urticaria, also known as chronic autoimmune urticaria, is a type of chronic urticaria characterized by the presence of autoantibodies in the patient's immune system that target the body's own mast cells, leading to episodes of hives (urticaria). This immunologically distinct type of urticaria is considered autoimmune because the immune system, which normally protects the body from foreign organisms, mistakenly attacks the body's own cells, causing inflammation and other symptoms.













