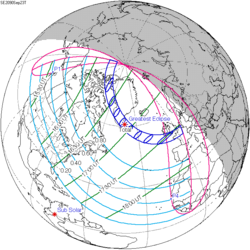
| Partial eclipse | |
| Gamma | 1.045 |
|---|---|
| Magnitude | 0.8907 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Coordinates | 62°54′N111°42′E / 62.9°N 111.7°E |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 1:33:18 |
| References | |
| Saros | 151 (16 of 72) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9611 |
A partial solar eclipse will occur at the Moon's ascending node of orbit between Friday, January 25 and Saturday, January 26, 2047, [1] with a magnitude of 0.8907. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth.
Contents
- Images
- Eclipse timing
- Places experiencing partial eclipse
- Eclipse details
- Eclipse season
- Related eclipses
- Eclipses in 2047
- Metonic
- Tzolkinex
- Half-Saros
- Tritos
- Solar Saros 151
- Inex
- Triad
- Solar eclipses of 2044–2047
- Saros 151
- Metonic series
- Tritos series
- Inex series
- Notes
- References
- External links
This will be the first of four partial solar eclipses in 2047, with the others occurring on June 23, July 22, and December 16.
The partial solar eclipse will be visible for parts of East Asia, Southeast Asia, and southwestern Alaska.