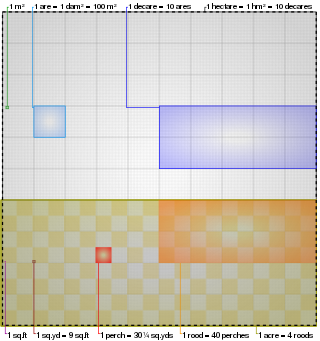
The acre is a unit of land area used in the British imperial and the United States customary systems. It is traditionally defined as the area of one chain by one furlong, which is exactly equal to 10 square chains, 1⁄640 of a square mile, 4,840 square yards, or 43,560 square feet, and approximately 4,047 m2, or about 40% of a hectare. Based upon the international yard and pound agreement of 1959, an acre may be declared as exactly 4,046.8564224 square metres. The acre is sometimes abbreviated ac but is usually spelled out as the word "acre".

The imperial system of units, imperial system or imperial units is the system of units first defined in the British Weights and Measures Act 1824 and continued to be developed through a series of Weights and Measures Acts and amendments.
The rod, perch, or pole is a surveyor's tool and unit of length of various historical definitions. In British imperial and US customary units it is defined as 16+1⁄2 feet, equal to exactly 1⁄320 of a mile, or 5+1⁄2 yards, and is exactly 5.0292 meters. The rod is useful as a unit of length because integer multiples of it can form one acre of square measure (area). The 'perfect acre' is a rectangular area of 43,560 square feet, bounded by sides 660 feet long and 66 feet wide or, equivalently, 40 rods by 4 rods. An acre is therefore 160 square rods or 10 square chains.
A system of units of measurement, also known as a system of units or system of measurement, is a collection of units of measurement and rules relating them to each other. Systems of measurement have historically been important, regulated and defined for the purposes of science and commerce. Instances in use include the International System of Units or SI, the British imperial system, and the United States customary system.
The following systems arose from earlier systems, and in many cases utilise parts of much older systems. For the most part they were used to varying degrees in the Middle Ages and surrounding time periods. Some of these systems found their way into later systems, such as the Imperial system and even SI.
A league is a unit of length. It was common in Europe and Latin America, but is no longer an official unit in any nation. Derived from an ancient Celtic unit and adopted by the Romans as the leuga, the league became a common unit of measurement throughout western Europe. Since the Middle Ages, many values have been specified in several countries.

A span is the distance measured by a human hand, from the tip of the thumb to the tip of the little finger. In ancient times, a span was considered to be half a cubit. Sometimes the distinction is made between the great span or full span and little span or short span.

Metrication in Canada began in 1970 and ceased in 1985. While Canada has converted to the metric system for many purposes, there is still significant use of non-metric units and standards in many sectors of the Canadian economy and everyday life today. This is mainly due to historical ties with the United Kingdom, the traditional use of the imperial system of measurement in Canada, proximity to the United States, and strong public opposition to metrication during the transition period.
The Weights and Measures Act is a Canadian law governing the units of measurements used in Canada.
In Guatemala the metric system is official but it uses a mixture of U.S., metric and Spanish customary units.
The term "cuerda" refers to a unit of measurement in some Spanish-speaking regions, including Puerto Rico, Guatemala, Cuba, Spain, and Paraguay. In Puerto Rico, the term cuerda refers to the unit of area measurement. In Guatemala, cuerda is both a unit of length measurement as well as of area measurement. As a unit of area measurement, the Guatemalan cuerda can have various meanings. In Cuba, cuerda refers to a unit of volume measurement; in Spain and Paraguay, it refers to a unit of distance (length).
The History of measurement systems in Pakistan begins in early Indus Valley civilization when pastoral societies used barter to exchange goods or services and needed units of measurement.
A number of different units of measurement were used in Argentina as its national system was derived from Spanish Castillian. The metric system was legally optional since 1863 and has been compulsory since 1887.
A number of different units of measurement were used in Brazil to measure quantities including length, area, volume, and mass as those units were derived from Portugal and had significant local variances.
A number of different units of measurement were used in Chile to measure quantities like length, mass, area, capacity, etc. From 1848, the metric system has been compulsory in Chile.
A number of units of measurement were used in Honduras for length, mass, volume etc. In Honduras, the metric system was adopted in 1910, and has been compulsory since 1912, under a joint convention between Costa Rica, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua and El Salvador.
A number of units of measurement were used in Nicaragua to measure measurements in mass, area, volume, etc. In Nicaragua, the metric system was adopted in 1910, and has been compulsory since 1912, by a joint convention between Costa Rica, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua and El Salvador.
A number of units of measurement were used in Mexico to measure length, mass, area, capacity, etc. The Metric system was optional from 1857, and has been compulsory since 1896.
A number of units of measurement were used in Paraguay to measure quantities including length, mass, area, capacity, etc. Metric system had been optional since 1890, and adopted since 1899 in Paraguay.
A number of units of measurement were used in Peru to measure length, mass, area, etc. The Metric system adopted in 1862 and has been compulsory since 1869 in Peru.




