
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to bone fragility, and consequent increase in fracture risk. It is the most common reason for a broken bone among the elderly. Bones that commonly break include the vertebrae in the spine, the bones of the forearm, and the hip. Until a broken bone occurs there are typically no symptoms. Bones may weaken to such a degree that a break may occur with minor stress or spontaneously. After the broken bone heals, the person may have chronic pain and a decreased ability to carry out normal activities.

Rickets is a condition that results in weak or soft bones in children, and is caused by either dietary deficiency or genetic causes. Symptoms include bowed legs, stunted growth, bone pain, large forehead, and trouble sleeping. Complications may include bone deformities, bone pseudofractures and fractures, muscle spasms, or an abnormally curved spine.

Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry is a means of measuring bone mineral density (BMD) using spectral imaging. Two X-ray beams, with different energy levels, are aimed at the patient's bones. When soft tissue absorption is subtracted out, the bone mineral density (BMD) can be determined from the absorption of each beam by bone. Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry is the most widely used and most thoroughly studied bone density measurement technology.

Prednisone is a glucocorticoid medication mostly used to suppress the immune system and decrease inflammation in conditions such as asthma, COPD, and rheumatologic diseases. It is also used to treat high blood calcium due to cancer and adrenal insufficiency along with other steroids. It is taken by mouth.
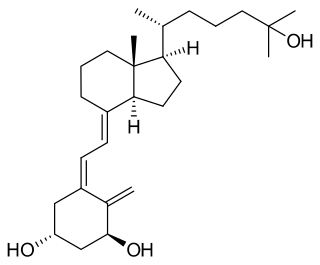
Osteomalacia is a disease characterized by the softening of the bones caused by impaired bone metabolism primarily due to inadequate levels of available phosphate, calcium, and vitamin D, or because of resorption of calcium. The impairment of bone metabolism causes inadequate bone mineralization. Osteomalacia in children is known as rickets, and because of this, use of the term "osteomalacia" is often restricted to the milder, adult form of the disease. Signs and symptoms can include diffuse body pains, muscle weakness, and fragility of the bones. In addition to low systemic levels of circulating mineral ions that result in decreased bone and tooth mineralization, accumulation of mineralization-inhibiting proteins and peptides, and small inhibitory molecules, can occur in the extracellular matrix of bones and teeth, contributing locally to cause matrix hypomineralization (osteomalacia/odontomalacia). A relationship describing local, physiologic double-negative regulation of mineralization has been termed the Stenciling Principle of mineralization, whereby enzyme-substrate pairs imprint mineralization patterns into the extracellular matrix by degrading mineralization inhibitors. The Stenciling Principle for mineralization is particularly relevant to the osteomalacia and odontomalacia observed in hypophosphatasia (HPP) and X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH).

Bisphosphonates are a class of drugs that prevent the loss of bone density, used to treat osteoporosis and similar diseases. They are the most commonly prescribed drugs used to treat osteoporosis. They are called bisphosphonates because they have two phosphonate groups. They are thus also called diphosphonates.

Paget's disease of bone is a condition involving cellular remodeling and deformity of one or more bones. The affected bones show signs of dysregulated bone remodeling at the microscopic level, specifically excessive bone breakdown and subsequent disorganized new bone formation. These structural changes cause the bone to weaken, which may result in deformity, pain, fracture or arthritis of associated joints.
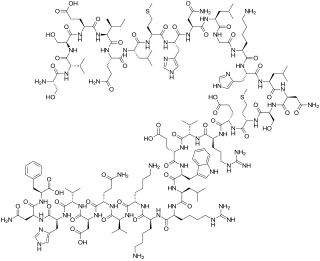
Teriparatide, sold under the brand name Forteo, is a form of parathyroid hormone (PTH) consisting of the first (N-terminus) 34 amino acids, which is the bioactive portion of the hormone. It is an effective anabolic agent used in the treatment of some forms of osteoporosis. Teriparatide is a recombinant human parathyroid hormone analog. It has an identical sequence to the 34 N-terminal amino acids of the 84-amino acid human parathyroid hormone.

Alendronic acid, sold under the brand name Fosamax among others, is a bisphosphonate medication used to treat osteoporosis and Paget's disease of bone. It is taken by mouth. Use is often recommended together with vitamin D, calcium supplementation, and lifestyle changes.
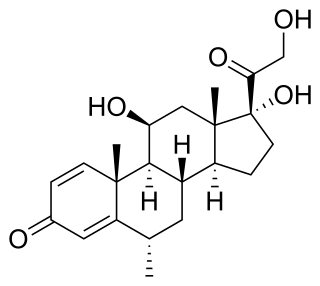
Methylprednisolone is a synthetic glucocorticoid, primarily prescribed for its anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects. It is either used at low doses for chronic illnesses or used concomitantly at high doses during acute flares. Methylprednisolone and its derivatives can be administered orally or parenterally.
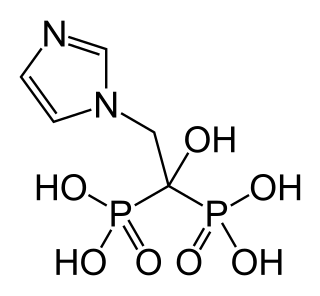
Zoledronic acid, also known as zoledronate and sold under the brand name Zometa by Novartis among others, is a medication used to treat a number of bone diseases. These include osteoporosis, high blood calcium due to cancer, bone breakdown due to cancer, Paget's disease of bone and Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). It is given by injection into a vein.

Osteopenia, known as "low bone mass" or "low bone density", is a condition in which bone mineral density is low. Because their bones are weaker, people with osteopenia may have a higher risk of fractures, and some people may go on to develop osteoporosis. In 2010, 43 million older adults in the US had osteopenia. Unlike osteoporosis, osteopenia does not usually cause symptoms, and losing bone density in itself does not cause pain.

Bone density, or bone mineral density, is the amount of bone mineral in bone tissue. The concept is of mass of mineral per volume of bone, although clinically it is measured by proxy according to optical density per square centimetre of bone surface upon imaging. Bone density measurement is used in clinical medicine as an indirect indicator of osteoporosis and fracture risk. It is measured by a procedure called densitometry, often performed in the radiology or nuclear medicine departments of hospitals or clinics. The measurement is painless and non-invasive and involves low radiation exposure. Measurements are most commonly made over the lumbar spine and over the upper part of the hip. The forearm may be scanned if the hip and lumbar spine are not accessible.

Ibandronic acid is a bisphosphonate medication used in the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis and metastasis-associated skeletal fractures in people with cancer. It may also be used to treat hypercalcemia. It is typically formulated as its sodium salt ibandronate sodium.

Denosumab is a human monoclonal antibody for the treatment of osteoporosis, treatment-induced bone loss, metastases to bone, and giant cell tumor of bone.
Senile osteoporosis has been recently recognized as a geriatric syndrome with a particular pathophysiology. There are different classification of osteoporosis: primary, in which bone loss is a result of aging and secondary, in which bone loss occurs from various clinical and lifestyle factors. Primary, or involuntary osteoporosis, can further be classified into Type I or Type II. Type I refers to postmenopausal osteoporosis and is caused by the deficiency of estrogen. While senile osteoporosis is categorized as an involuntary, Type II, and primary osteoporosis, which affects both men and women over the age of 70 years. It is accompanied by vitamin D deficiency, body's failure to absorb calcium, and increased parathyroid hormone.
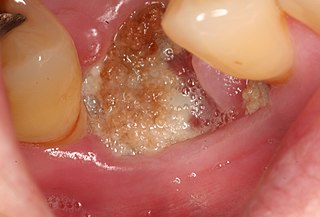
Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw is progressive death of the jawbone in a person exposed to a medication known to increase the risk of disease, in the absence of a previous radiation treatment. It may lead to surgical complication in the form of impaired wound healing following oral and maxillofacial surgery, periodontal surgery, or endodontic therapy.
FRAX is a diagnostic tool used to evaluate the 10-year probability of bone fracture risk. It was developed by the University of Sheffield. FRAX integrates clinical risk factors and bone mineral density at the femoral neck to calculate the 10-year probability of hip fracture and the 10-year probability of a major osteoporotic fracture. The models used to develop the FRAX diagnostic tool were derived from studying patient populations in North America, Europe, Latin America, Asia and Australia.
The trabecular bone score is a measure of bone texture correlated with bone microarchitecture and a marker for the risk of osteoporosis. Introduced in 2008, its main projected use is alongside measures of bone density in better predicting fracture risk in people with metabolic bone problems.
Eldecalcitol is a drug used in Japan for the treatment of osteoporosis. It is an analog of vitamin D. Osteoporosis is a common bone disease among the older generation, with an estimated prevalence of over 200 million people. This condition often results in bone fractures due to abnormally low bone mass density, and is a leading cause of disability, especially among developed countries with longer average life spans. Osteoporosis is more common in women than with men.