
The foot is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws and/or nails.

A joint or articulation is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole. They are constructed to allow for different degrees and types of movement. Some joints, such as the knee, elbow, and shoulder, are self-lubricating, almost frictionless, and are able to withstand compression and maintain heavy loads while still executing smooth and precise movements. Other joints such as sutures between the bones of the skull permit very little movement in order to protect the brain and the sense organs. The connection between a tooth and the jawbone is also called a joint, and is described as a fibrous joint known as a gomphosis. Joints are classified both structurally and functionally.

In anatomy, a sesamoid bone is a bone embedded within a tendon or a muscle. Its name is derived from the Greek word for 'sesame seed', indicating the small size of most sesamoids. Often, these bones form in response to strain, or can be present as a normal variant. The patella is the largest sesamoid bone in the body. Sesamoids act like pulleys, providing a smooth surface for tendons to slide over, increasing the tendon's ability to transmit muscular forces.

A bunion, also known as hallux valgus, is a deformity of the MTP joint connecting the big toe to the foot. The big toe often bends towards the other toes and the joint becomes red and painful. The onset of bunions is typically gradual. Complications may include bursitis or arthritis.
Ulnar collateral ligament reconstruction, colloquially known as Tommy John surgery, is a surgical graft procedure where the ulnar collateral ligament in the medial elbow is replaced with either a tendon from elsewhere in the patient's body, or with one from a deceased donor. The procedure is common among collegiate and professional athletes in several sports, particularly in baseball. The surgery is performed to restore optimal function for repetitive elbow movements or specifically throwing ability, often extending the careers of professional athletes. In many athletes, the surgery is done more than once during their careers.
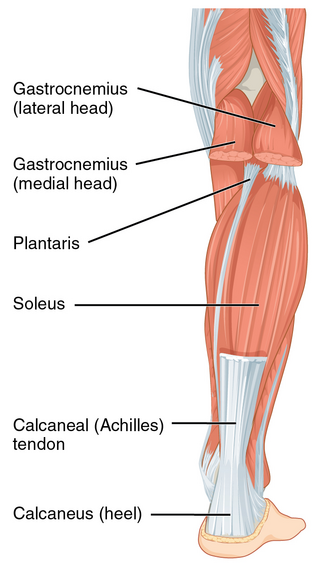
The Achilles tendon or heel cord, also known as the calcaneal tendon, is a tendon at the back of the lower leg, and is the thickest in the human body. It serves to attach the plantaris, gastrocnemius (calf) and soleus muscles to the calcaneus (heel) bone. These muscles, acting via the tendon, cause plantar flexion of the foot at the ankle joint, and flexion at the knee.

Diseases of the foot generally are not limited, that is they are related to or manifest elsewhere in the body. However, the foot is often the first place some of these diseases or a sign or symptom of others appear. This is because of the foot's distance from the central circulation, the heart and its constant exposure to pressures from the ground and the weight of the body.
Navicular syndrome, often called navicular disease, is a syndrome of lameness problems in horses. It most commonly describes an inflammation or degeneration of the navicular bone and its surrounding tissues, usually on the front feet. It can lead to significant and even disabling lameness.
Bone spavin is a bony growth within the lower hock joint of horses or cattle. It is caused by osteoarthritis, and the degree of lameness that results can be serious enough to end a horse's competitive career.
Tendinitis/tendonitis is inflammation of a tendon, often involving torn collagen fibers. A bowed tendon is a horseman's term for a tendon after a horse has sustained an injury that causes swelling in one or more tendons creating a "bowed" appearance.

Equine conformation evaluates a horse's bone structure, musculature, and its body proportions in relation to each other. Undesirable conformation can limit the ability to perform a specific task. Although there are several faults with universal disadvantages, a horse's conformation is usually judged by what its intended use may be. Thus "form to function" is one of the first set of traits considered in judging conformation. A horse with poor form for a Grand Prix show jumper could have excellent conformation for a World Champion cutting horse, or to be a champion draft horse. Every horse has good and bad points of its conformation and many horses excel even with conformation faults.

Ringbone is exostosis in the pastern or coffin joint of a horse. In severe cases, the growth can encircle the bones, giving ringbone its name. It has been suggested by some authors that such a colloquial term, whilst commonly used, might be misleading and that it would be better to refer to this condition as osteoarthritis of the inter-phalangeal joints in ungulates.

The pastern is a part of the leg of a horse between the fetlock and the top of the hoof. It incorporates the long pastern bone and the short pastern bone, which are held together by two sets of paired ligaments to form the pastern joint. Anatomically homologous to the two largest bones found in the human finger, the pastern was famously mis-defined by Samuel Johnson in his dictionary as "the knee of a horse". When a lady asked Johnson how this had happened, he gave the much-quoted reply: "Ignorance, madam, pure ignorance."

An accessory navicular bone is an accessory bone of the foot that occasionally develops abnormally in front of the ankle towards the inside of the foot. This bone may be present in approximately 2-21% of the general population and is usually asymptomatic. When it is symptomatic, surgery may be necessary.

The skeletal system of the horse is a skeletal system of a horse that has three major functions in the body. It protects vital organs, provides framework, and supports soft parts of the body. Horses typically have 205 bones. The pelvic limb typically contains 19 bones, while the thoracic limb contains 20 bones.
Lameness is an abnormal gait or stance of an animal that is the result of dysfunction of the locomotor system. In the horse, it is most commonly caused by pain, but can be due to neurologic or mechanical dysfunction. Lameness is a common veterinary problem in racehorses, sport horses, and pleasure horses. It is one of the most costly health problems for the equine industry, both monetarily for the cost of diagnosis and treatment, and for the cost of time off resulting in loss-of-use.

The limbs of the horse are structures made of dozens of bones, joints, muscles, tendons, and ligaments that support the weight of the equine body. They include two apparatuses: the suspensory apparatus, which carries much of the weight, prevents overextension of the joint and absorbs shock, and the stay apparatus, which locks major joints in the limbs, allowing horses to remain standing while relaxed or asleep. The limbs play a major part in the movement of the horse, with the legs performing the functions of absorbing impact, bearing weight, and providing thrust. In general, the majority of the weight is borne by the front legs, while the rear legs provide propulsion. The hooves are also important structures, providing support, traction and shock absorption, and containing structures that provide blood flow through the lower leg. As the horse developed as a cursorial animal, with a primary defense mechanism of running over hard ground, its legs evolved to the long, sturdy, light-weight, one-toed form seen today.
Running injuries affect about half of runners annually. The frequencies of various RRI depend on the type of running, such as speed and mileage. Some injuries are acute, caused by sudden overstress, such as side stitch, strains, and sprains. Many of the common injuries that affect runners are chronic, developing over longer periods as the result of overuse. Common overuse injuries include shin splints, stress fractures, Achilles tendinitis, Iliotibial band syndrome, Patellofemoral pain, and plantar fasciitis.
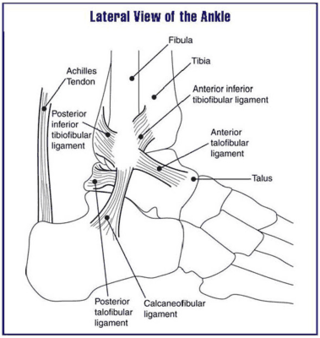
Ankle problems occur frequently, having symptoms of pain or discomfort in the ankles.
In the skeleton of humans and other animals, a tubercle, tuberosity or apophysis is a protrusion or eminence that serves as an attachment for skeletal muscles. The muscles attach by tendons, where the enthesis is the connective tissue between the tendon and bone. A tuberosity is generally a larger tubercle.














