In property law, title is an intangible construct representing a bundle of rights in (to) a piece of property in which a party may own either a legal interest or equitable interest. The rights in the bundle may be separated and held by different parties. It may also refer to a formal document, such as a deed, that serves as evidence of ownership. Conveyance of the document may be required in order to transfer ownership in the property to another person. Title is distinct from possession, a right that often accompanies ownership but is not necessarily sufficient to prove it. In many cases, possession and title may each be transferred independently of the other. For real property, land registration and recording provide public notice of ownership information.

Tribal sovereignty in the United States is the concept of the inherent authority of indigenous tribes to govern themselves within the borders of the United States.

The Native Hawaiian Government Reorganization Act of 2009 S1011/HR2314 was a bill before the 111th Congress. It is commonly known as the Akaka Bill after Senator Daniel Akaka of Hawaii, who proposed various forms of this bill after 2000.
The Nonintercourse Act is the collective name given to six statutes passed by the Congress in 1790, 1793, 1796, 1799, 1802, and 1834 to set Amerindian boundaries of reservations. The various Acts were also intended to regulate commerce between settlers and the natives. The most notable provisions of the Act regulate the inalienability of aboriginal title in the United States, a continuing source of litigation for almost 200 years. The prohibition on purchases of Indian lands without the approval of the federal government has its origins in the Royal Proclamation of 1763 and the Confederation Congress Proclamation of 1783.
Rice v. Cayetano, 528 U.S. 495 (2000), was a case filed in 1996 by Big Island rancher Harold "Freddy" Rice against the state of Hawaii and argued before the United States Supreme Court. In 2000, the Court ruled that the state could not restrict eligibility to vote in elections for the Board of Trustees of the Office of Hawaiian Affairs to persons of Native Hawaiian descent.
The Alaska Native Regional Corporations were established in 1971 when the United States Congress passed the Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act (ANCSA) which settled land and financial claims made by the Alaska Natives and provided for the establishment of 13 regional corporations to administer those claims.
Colorado River Water Conservation District v. United States, 424 U.S. 800 (1976), was a case in which the Supreme Court of the United States extensively refined the abstention doctrine to prevent duplicative litigation between state and federal courts.

Aboriginal title is a common law doctrine that the land rights of indigenous peoples to customary tenure persist after the assumption of sovereignty under settler colonialism. The requirements of proof for the recognition of aboriginal title, the content of aboriginal title, the methods of extinguishing aboriginal title, and the availability of compensation in the case of extinguishment vary significantly by jurisdiction. Nearly all jurisdictions are in agreement that aboriginal title is inalienable, and that it may be held either individually or collectively.
Indian termination is a phrase describing United States policies relating to Native Americans from the mid-1940s to the mid-1960s. It was shaped by a series of laws and practices with the intent of assimilating Native Americans into mainstream American society. Cultural assimilation of Native Americans was not new; the belief that indigenous people should abandon their traditional lives and become what the government considers "civilized" had been the basis of policy for centuries. What was new, however, was the sense of urgency that, with or without consent, tribes must be terminated and begin to live "as Americans." To that end, Congress set about ending the special relationship between tribes and the federal government.
United States v. Kagama, 118 U.S. 375 (1886), was a United States Supreme Court case that upheld the constitutionality of the Major Crimes Act of 1885. This Congressional act gave the federal courts jurisdiction in certain Indian-on-Indian crimes, even if they were committed on an Indian reservation. Kagama, a Yurok Native American (Indian) accused of murder, was selected as a test case by the Department of Justice to test the constitutionality of the Act.
Hodel v. Irving, 481 U.S. 704 (1987), is a case in which the U.S. Supreme Court held that a statute ordering the escheat of fractional interests in real property which had been bequeathed to members of the Oglala Sioux tribe was an unconstitutional taking which required just compensation.
Menominee Tribe v. United States, 391 U.S. 404 (1968), is a case in which the Supreme Court ruled that the Menominee Indian Tribe kept their historical hunting and fishing rights even after the federal government ceased to recognize the tribe. It was a landmark decision in Native American case law.

The United States was the first jurisdiction to acknowledge the common law doctrine of aboriginal title. Native American tribes and nations establish aboriginal title by actual, continuous, and exclusive use and occupancy for a "long time." Individuals may also establish aboriginal title, if their ancestors held title as individuals. Unlike other jurisdictions, the content of aboriginal title is not limited to historical or traditional land uses. Aboriginal title may not be alienated, except to the federal government or with the approval of Congress. Aboriginal title is distinct from the lands Native Americans own in fee simple and occupy under federal trust.
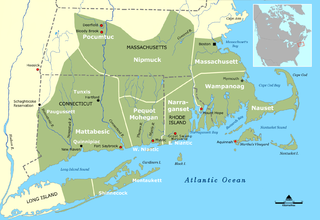
The Narragansett land claim was one of the first litigations of aboriginal title in the United States in the wake of the U.S. Supreme Court's landmark Oneida Indian Nation of New York v. County of Oneida (1974), or Oneida I, decision. The Narragansett claimed a few thousand acres of land in and around Charlestown, Rhode Island, challenging a variety of early 19th century land transfers as violations of the Nonintercourse Act, suing both the state and private land owners.
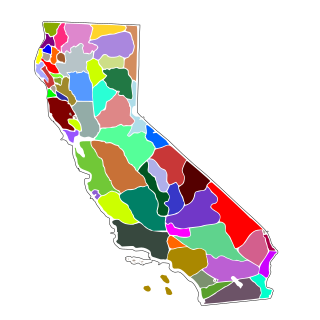
Aboriginal title in California refers to the aboriginal title land rights of the indigenous peoples of California. The state is unique in that no Native American tribe in California is the counterparty to a ratified federal treaty. Therefore, all the Indian reservations in the state were created by federal statute or executive order.
Aboriginal land title in New Mexico is unique among aboriginal title in the United States. Congressional legislation was passed to define such title after the United States acquired this territory following war with Mexico (1846-1848). But the Supreme Court of the New Mexico Territory and the United States Supreme Court held that the Nonintercourse Act did not restrict the alienability of Pueblo lands.
The McCarran Amendment, 43 U.S.C. § 666 (1952) is a federal law enacted by the United States Congress in 1952 which waives the United States' sovereign immunity in suits concerning ownership or management of water rights. It amended Chapter 15 of Title 43 of the United States Code. The McCarran Amendment gives others the right to join in such a lawsuit as a defendant. Prior to the Amendment, sovereign immunity kept the United States from being joined in any suits. The Amendment enabled suits concerning federal water rights to be tried in state courts.
Idaho v. Coeur d'Alene Tribe of Idaho, 521 U.S. 261 (1997), was a United States Supreme Court case in which the Court held that the Coeur d'Alene Tribe could not maintain an action against the state of Idaho to press its claim to Lake Coeur d'Alene due to the state's Eleventh Amendment immunity from suit, notwithstanding the exception recognized in Ex parte Young. The case was an important precedent for aboriginal title in the United States and sovereign immunity in the United States.
Idaho v. United States, 533 U.S. 262 (2001), was a United States Supreme Court case in which the Court held that the United States, not the state of Idaho, held title to lands submerged under Lake Coeur d'Alene and the St. Joe River, and that the land was held in trust for the Coeur d'Alene Tribe as part of its reservation, and in recognition of the importance of traditional tribal uses of these areas for basic food and other needs.
United States v. Creek Nation, 295 U.S. 103 (1935), was a United States Supreme Court case in which the Court held that the compensation for land taken from the Creek Nation by the United States was the value of the land at the time of the taking, plus interest.







