
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers. Liquid crystals do not emit light directly but instead use a backlight or reflector to produce images in color or monochrome.
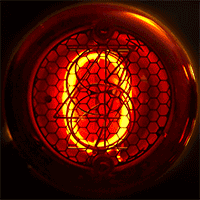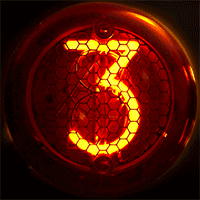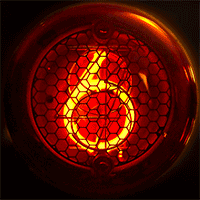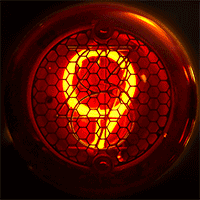
A Nixie tube, or cold cathode display, is an electronic device used for displaying numerals or other information using glow discharge.

A cold cathode is a cathode that is not electrically heated by a filament. A cathode may be considered "cold" if it emits more electrons than can be supplied by thermionic emission alone. It is used in gas-discharge lamps, such as neon lamps, discharge tubes, and some types of vacuum tube. The other type of cathode is a hot cathode, which is heated by electric current passing through a filament. A cold cathode does not necessarily operate at a low temperature: it is often heated to its operating temperature by other methods, such as the current passing from the cathode into the gas.

A flat-panel display (FPD) is an electronic display used to display visual content such as text or images. It is present in consumer, medical, transportation, and industrial equipment.

A display device is an output device for presentation of information in visual or tactile form. When the input information that is supplied has an electrical signal the display is called an electronic display.

A vacuum fluorescent display (VFD) is a display device once commonly used on consumer electronics equipment such as video cassette recorders, car radios, and microwave ovens.

A seven-segment display is a form of electronic display device for displaying decimal numerals that is an alternative to the more complex dot matrix displays.
A fourteen-segment display (FSD) is a type of display based on 14 segments that can be turned on or off to produce letters and numerals. It is an expansion of the more common seven-segment display, having an additional four diagonal and two vertical segments with the middle horizontal segment broken in half. A seven-segment display suffices for numerals and certain letters, but unambiguously rendering the ISO basic Latin alphabet requires more detail. A slight variation is the sixteen-segment display which allows additional legibility in displaying letters or other symbols.

A sixteen-segment display (SISD) is a type of display based on sixteen segments that can be turned on or off to produce a graphic pattern. It is an extension of the more common seven-segment display, adding four diagonal and two vertical segments and splitting the three horizontal segments in half. Other variants include the fourteen-segment display which does not split the top or bottom horizontal segments, and the twenty-two-segment display that allows lower-case characters with descenders.
A thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display is a type of liquid-crystal display that uses thin-film-transistor technology to improve image qualities such as addressability and contrast. A TFT LCD is an active matrix LCD, in contrast to passive matrix LCDs or simple, direct-driven LCDs with a few segments.

Handheld electronic games are interactive electronic games, often miniaturized versions of video games, that are played on portable handheld devices, known as handheld game consoles, whose controls, display and speakers are all part of a single unit. Rather than a general-purpose screen made up of a grid of small pixels, they usually have custom displays designed to play one game. This simplicity means they can be made as small as a smartwatch, and sometimes are. The visual output of these games can range from a few small light bulbs or LED lights to calculator-like alphanumerical screens; later these were mostly displaced by liquid crystal and vacuum fluorescent display screens with detailed images and in the case of VFD games, color. Handhelds' popularity was at its peak from the late 1970s into the early 1990s before declining. They are the precursors to the handheld game console.

An electronic component is any basic discrete electronic device or physical entity part of an electronic system used to affect electrons or their associated fields. Electronic components are mostly industrial products, available in a singular form and are not to be confused with electrical elements, which are conceptual abstractions representing idealized electronic components and elements. A datasheet for an electronic component is a technical document that provides detailed information about the component's specifications, characteristics, and performance.

A digital clock displays the time digitally, as opposed to an analogue clock.

A dot-matrix display is a low-cost electronic digital display device that displays information on machines such as clocks, watches, calculators, and many other devices requiring a simple alphanumeric display device of limited resolution.

The twisted nematic effect (TN-effect) was a major technological breakthrough that made the manufacture of large, thin liquid crystal displays practical and cost competitive. Unlike earlier flat-panel displays, TN-cells did not require a current to flow for operation and used low operating voltages suitable for use with batteries. The introduction of TN-effect displays led to their rapid expansion in the display field, quickly pushing out other common technologies like monolithic LEDs and CRTs for most electronics. By the 1990s, TN-effect LCDs were largely universal in portable electronics, although since then, many applications of LCDs adopted alternatives to the TN-effect such as in-plane switching (IPS) or vertical alignment (VA).
An electronic visual display is a display device that can display images, video, or text that is transmitted electronically. Electronic visual displays include television sets, computer monitors, and digital signage. They are ubiquitous in mobile computing applications like tablet computers, smartphones, and information appliances. Many electronic visual displays are informally referred to as screens.
Electrically operated display devices have developed from electromechanical systems for display of text, up to all-electronic devices capable of full-motion 3D color graphic displays. Electromagnetic devices, using a solenoid coil to control a visible flag or flap, were the earliest type, and were used for text displays such as stock market prices and arrival/departure display times. The cathode ray tube was the workhorse of text and video display technology for several decades until being displaced by plasma, liquid crystal (LCD), and solid-state devices such as thin-film transistors (TFTs), LEDs and OLEDs. With the advent of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs), integrated circuit (IC) chips, microprocessors, and microelectronic devices, many more individual picture elements ("pixels") could be incorporated into one display device, allowing graphic displays and video.
Polarizing organic photovoltaics (ZOPV) is a concept for harvesting energy from Liquid crystal display screens, developed by engineers from UCLA. This concept enables devices to use external light and the LCD screen's backlight using photovoltaic polarizers. Photovoltaic polarizers convert this light into electricity which can be used to power the device. This concept also provides multifunctional capability to devices with LCD screens as they act as photovoltaic devices and as polarisers.













