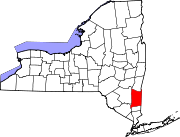
Dutchess County is a county in the U.S. state of New York. As of the 2020 census, the population was 295,911. The county seat is the city of Poughkeepsie. The county was created in 1683, one of New York's first twelve counties, and later organized in 1713. The county is part of the Hudson Valley region of the state.

The Mohicans are an Eastern Algonquian Native American tribe that historically spoke an Algonquian language. As part of the Eastern Algonquian family of tribes, they are related to the neighboring Lenape, whose indigenous territory was to the south as far as the Atlantic coast. The Mohican lived in the upper tidal Hudson River Valley, including the confluence of the Mohawk River and into western New England centered on the upper Housatonic River watershed. After 1680, due to conflicts with the powerful Mohawk to the west during the Beaver Wars, many were driven southeastward across the present-day Massachusetts western border and the Taconic Mountains to Berkshire County around Stockbridge, Massachusetts.

Clermont is a town in Columbia County, New York, United States. The population was 2,058 at the 2020 census. The name of the town is French for "Clear Mountain", in reference to the mountain views in the town.

Wappinger is a town in Dutchess County, New York, United States. The town is located in the Hudson River Valley region, on the eastern bank of the Hudson River. The population was 28,216 at the 2020 census. The name is derived from the Wappinger Native Americans who inhabited the area. Wappinger comprises three-fourths of the incorporated village of Wappingers Falls, several unincorporated hamlets such as Chelsea, Diddell, Hughsonville, Middlebush, Myers Corners, New Hackensack, and Swartwoutville, and a number of neighborhoods.

Germantown is a town in Columbia County, New York, United States. The population was 1,936 at the 2020 census, down slightly from 1,954 in 2010. Germantown is located in the south-western part of the county along the east side of the Hudson River.

Red Hook is a village in Dutchess County, New York, United States. The population was 1,975 at the 2020 census. It is part of the Poughkeepsie–Newburgh–Middletown, NY Metropolitan Statistical Area as well as the larger New York–Newark–Bridgeport, NY-NJ-CT-PA Combined Statistical Area. The name is derived from the Dutch "Roode Hoeck" – hoeck meaning peninsula, and roode meaning red – a reference to the vibrant reds in the area's fall foliage.

Red Hook is a town in Dutchess County, New York, United States. The population was 9,953 at the time of the 2020 census, down from 11,319 in 2010. The name is supposedly derived from the red foliage on trees on a small strip of land on the Hudson River The town contains two villages, Red Hook and Tivoli. The town is in the northwest part of Dutchess County.

Rhinebeck is a village in the town of Rhinebeck in Dutchess County, New York, United States. The population was 2,657 at the 2010 census. It is part of the Poughkeepsie–Newburgh–Middletown, NY Metropolitan Statistical Area as well as the larger New York–Newark–Connecticut.

New York State Route 9G (NY 9G) is a state highway in the Hudson Valley of New York in the United States. It runs north from U.S. Route 9 (US 9) at Poughkeepsie, starting out as Violet Avenue, then follows the Hudson River mostly along the eastern side of the US 9 to Rhinebeck, where the two routes cross just north of the village. From this point onward, NY 9G runs on the western side of US 9, closer to the Hudson River, to Hudson. It ends at another junction with US 9 in the city. NY 9G initially extended from Rhinebeck to Hudson when it was assigned as part of the 1930 renumbering of state highways in New York. It was extended to its current length in the late 1930s, supplanting New York State Route 9F, an alternate route of US 9 between Poughkeepsie and Rhinebeck.

New York State Route 308 (NY 308) is a short state highway, 6.19 miles (9.96 km) in length, located entirely in northern Dutchess County, in the U.S. state of New York. It is a major collector road through a mostly rural area, serving primarily as a shortcut for traffic from the two main north–south routes in the area, U.S. Route 9 (US 9) and NY 9G, to get to NY 199 and the Taconic State Parkway. The western end of NY 308 is located within Rhinebeck's historic district, a 2.6-square-mile (6.7 km2) historic district comprising 272 historical structures. The highway passes near the Dutchess County Fairgrounds, several historical landmarks, and briefly parallels the Landsman Kill.
The Moravian mission at Shekomeko was founded in 1740 by Christian Henry Rauch to convert the Mahican Indians in eastern New York.
Shekomeko was a historic hamlet in the southwestern part of the town of North East, New York, United States) in present-day Dutchess County. It was a village of the Mahican people. They lived by a stream which Anglo-Americans later named Shekomeko Creek, after their village. Shekomeko comes from Mahikanneuw and means "people of the place of eels ["linear fish"], from "shaxk" - linear, straight; "amek" = fish; = locative suffix "ink", + ethnonymial locative suffix "oik" - Shaxkaminkoik > Shekomeko.

The Hudson River Historic District, also known as Hudson River Heritage Historic District, is the largest Federally designated district on the mainland of the contiguous United States. It covers an area of 22,205 acres extending inland roughly a mile (1.6 km) from the east bank of the Hudson River between Staatsburg and Germantown in Dutchess and Columbia counties in the U.S. state of New York. This area includes the riverfront sections of the towns of Clermont, Red Hook, Rhinebeck and part of Hyde Park. This strip includes in their entirety the hamlets of Annandale, Barrytown, Rhinecliff and the village of Tivoli. Bard College and two protected areas, Margaret Lewis Norrie State Park and Tivoli Bays Unique Area, are also within the district.

Barrytown is a hamlet within the town of Red Hook in Dutchess County, New York, United States. It is within the Hudson River Historic District, a National Historic Landmark, and contains four notable Hudson River Valley estates: Edgewater, Massena, Rokeby, and Sylvania.

New York State Route 402 (NY 402) was a state highway located within the village of Tivoli in Dutchess County, New York, in the United States. It was assigned in the early 1930s and served as a connector between NY 9G and what was once a ferry landing on the Hudson River west of the village. Although the ferry service linking Tivoli and the village of Saugerties was shut down in the 1940s, NY 402 continued to exist until 1980. On April 1 of that year, ownership and maintenance of the highway was transferred to Dutchess County as part of a highway maintenance swap between the county and the state of New York. The highway became part of an extended County Route 78 (CR 78), which had begun at the junction of NY 9G and NY 402 prior to the swap.
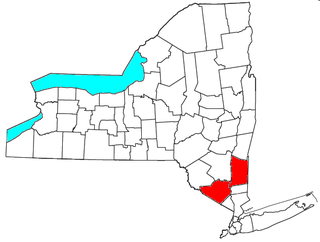
The Kiryas Joel-Poughkeepsie-Newburgh, NY Metropolitan Statistical Area, as defined by the United States Office of Management and Budget, is an area consisting of two counties in New York's Hudson Valley, with the municipalities of Kiryas Joel, Poughkeepsie, and Newburgh as its principal cities. As of the 2020 census, the MSA had a population of 679,221. The area was centered on the urban area of Poughkeepsie-Newburgh. Prior to July 2023, it was known as the Poughkeepsie-Newburgh-Middletown, NY Metropolitan Statistical Area; whereupon it was renamed to its current name, to reflect population changes among its largest municipalities.

The Watts De Peyster Fireman's Hall is located on Broadway in the village of Tivoli, New York. John Watts De Peyster, a resident, paid for it and gave it to the village for its fire department in 1898. It is a brick "storefront" firehouse, a type of fire station more commonly seen in cities at the time than small rural villages like Tivoli.

The Roeliff Jansen Kill is a major tributary to the Hudson River. Roeliff Jansen Kill was the traditional boundary between the Native American Mahican and Wappinger tribes.

The Saw Kill is a 14.3-mile-long (23.0 km) tributary of the Hudson River, called the Metambesem by the Algonquin people of the area and sometimes called Sawkill Creek today. It rises in the town of Milan and drains a 22-square-mile (57 km2) area of northwestern Dutchess County, New York, that includes most of the town of Red Hook to the west and part of Rhinebeck to Red Hook's south.
Robert Reginald Livingston Jr., was an American politician and farmer from New York.