
A fossil fuel power station is a thermal power station which burns a fossil fuel, such as coal or natural gas, to produce electricity. Fossil fuel power stations have machinery to convert the heat energy of combustion into mechanical energy, which then operates an electrical generator. The prime mover may be a steam turbine, a gas turbine or, in small plants, a reciprocating gas engine. All plants use the energy extracted from the expansion of a hot gas, either steam or combustion gases. Although different energy conversion methods exist, all thermal power station conversion methods have their efficiency limited by the Carnot efficiency and therefore produce waste heat.

Coal pollution mitigation, sometimes labeled as clean coal, is a series of systems and technologies that seek to mitigate health and environmental impact of burning coal for energy. Burning coal releases harmful substances, including mercury, lead, sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and carbon dioxide (CO2), contributing to air pollution, acid rain, and greenhouse gas emissions. Methods include flue-gas desulfurization, selective catalytic reduction, electrostatic precipitators, and fly ash reduction focusing on reducing the emissions of these harmful substances. These measures aim to reduce coal's impact on human health and the environment.
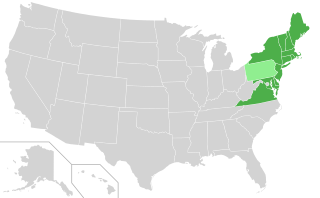
The Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI, pronounced "Reggie") is the first mandatory market-based program to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by the United States. RGGI is a cooperative effort among the states of Connecticut, Delaware, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Rhode Island, Vermont, and Virginia to cap and reduce carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from the power sector. RGGI compliance obligations apply to fossil-fueled power plants 25 megawatts (MW) and larger within the 11-state region. Pennsylvania's participation in the RGGI cooperative was ruled unconstitutional on November 1, 2023. North Carolina's entrance into RGGI has been blocked by the enactment of the state's fiscal year 2023-25 budget.

The Capitol Power Plant is a fossil-fuel burning power plant which provides steam and chilled water for the United States Capitol, the Supreme Court, the Library of Congress and 19 other buildings in the Capitol Complex. Located at 25 E St SE in southeast Washington, D.C., the CPP was the only coal-burning power plant in the District of Columbia, and it now it mostly uses natural gas. The plant has been serving the Capitol since 1910, and is under the administration of the Architect of the Capitol.

Edward Scott Pruitt is an American attorney, lobbyist and Republican politician from the state of Oklahoma. He served as the 14th Administrator of the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) from February 17, 2017, to July 9, 2018, during the Donald Trump presidency, resigning while under at least 14 federal investigations. Pruitt denies the scientific consensus on climate change.

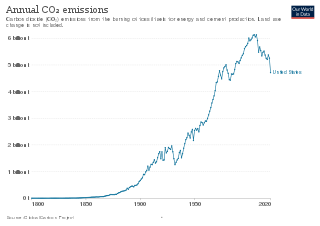
The United States produced 5.2 billion metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 2020, the second largest in the world after greenhouse gas emissions by China and among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per person. In 2019 China is estimated to have emitted 27% of world GHG, followed by the United States with 11%, then India with 6.6%. In total the United States has emitted a quarter of world GHG, more than any other country. Annual emissions are over 15 tons per person and, amongst the top eight emitters, is the highest country by greenhouse gas emissions per person. However, the IEA estimates that the richest decile in the US emits over 55 tonnes of CO2 per capita each year. Because coal-fired power stations are gradually shutting down, in the 2010s emissions from electricity generation fell to second place behind transportation which is now the largest single source. In 2020, 27% of the GHG emissions of the United States were from transportation, 25% from electricity, 24% from industry, 13% from commercial and residential buildings and 11% from agriculture. In 2021, the electric power sector was the second largest source of U.S. greenhouse gas emissions, accounting for 25% of the U.S. total. These greenhouse gas emissions are contributing to climate change in the United States, as well as worldwide.
The Emissions & Generation Resource Integrated Database (eGRID) is a comprehensive source of data on the environmental characteristics of almost all electric power generated in the United States. eGRID is issued by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
United States vehicle emission standards are set through a combination of legislative mandates enacted by Congress through Clean Air Act (CAA) amendments from 1970 onwards, and executive regulations managed nationally by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), and more recently along with the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA). These standard cover common motor vehicle air pollution, including carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate emissions, and newer versions have incorporated fuel economy standards.

Coal generated about 19.5% of the electricity at utility-scale facilities in the United States in 2022, down from 38.6% in 2014 and 51% in 2001. In 2021, coal supplied 9.5 quadrillion British thermal units (2,800 TWh) of primary energy to electric power plants, which made up 90% of coal's contribution to U.S. energy supply. Utilities buy more than 90% of the coal consumed in the United States. There were over 200 coal powered units across the United States in 2022. Coal plants have been closing since the 2010s due to cheaper and cleaner natural gas and renewables. Due to measures such as scrubbers air pollution from the plants kills far fewer people nowadays, but deaths in 2020 from PM 2.5 have been estimated at 1600. Environmentalists say that political action is needed to close them faster, to also reduce greenhouse gas emissions by the United States and better limit climate change.
The environmental policy of the United States is a federal governmental action to regulate activities that have an environmental impact in the United States. The goal of environmental policy is to protect the environment for future generations while interfering as little as possible with the efficiency of commerce or the liberty of the people and to limit inequity in who is burdened with environmental costs. As his first official act bringing in the 1970s, President Richard Nixon signed the U.S. National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) into law on New Years Day, 1970. Also in the same year, America began celebrating Earth Day, which has been called "the big bang of U.S. environmental politics, launching the country on a sweeping social learning curve about ecological management never before experienced or attempted in any other nation." NEPA established a comprehensive US national environmental policy and created the requirement to prepare an environmental impact statement for “major federal actions significantly affecting the quality of the environment.” Author and consultant Charles H. Eccleston has called NEPA the world's “environmental Magna Carta”.
New Energy for America was a plan led by Barack Obama and Joe Biden beginning in 2008 to invest in renewable energy sources, reduce reliance on foreign oil, address global warming issues, and create jobs for Americans. The main objective of the New Energy for America plan was to implement clean energy sources in the United States to switch from nonrenewable resources to renewable resources. The plan led by the Obama Administration aimed to implement short-term solutions to provide immediate relief from pain at the pump, and mid- to- long-term solutions to provide a New Energy for America plan. The goals of the clean energy plan hoped to: invest in renewable technologies that will boost domestic manufacturing and increase homegrown energy, invest in training for workers of clean technologies, strengthen the middle class, and help the economy.

The Clean Air Act (CAA) is the United States' primary federal air quality law, intended to reduce and control air pollution nationwide. Initially enacted in 1963 and amended many times since, it is one of the United States' first and most influential modern environmental laws.
The climate change policy of the United States has major impacts on global climate change and global climate change mitigation. This is because the United States is the second largest emitter of greenhouse gasses in the world after China, and is among the countries with the highest greenhouse gas emissions per person in the world. In total, the United States has emitted over a trillion metric tons of greenhouse gasses, more than any country in the world.
The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) began regulating greenhouse gases (GHGs) under the Clean Air Act from mobile and stationary sources of air pollution for the first time on January 2, 2011. Standards for mobile sources have been established pursuant to Section 202 of the CAA, and GHGs from stationary sources are currently controlled under the authority of Part C of Title I of the Act. The basis for regulations was upheld in the United States Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia in June 2012.

Energy Tax Prevention Act, also known as H.R. 910, was a 2011 bill in the United States House of Representatives to prohibit the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) from regulating greenhouse gases to address climate change. On April 7, 2011, the bill passed the House by a vote of 255 to 172. The bill died in January 2013 with the ending of the Congressional session.
In the United States, the war on coal is a phrase used by the coal industry and its supporters to describe what they claim was an effort by the Obama administration to impose stringent regulations on coal power in the United States and thereby make such power uneconomical. Proponents of this phrase also often identify the Environmental Protection Agency as one of the chief entities waging this putative war, although Michael Grunwald has claimed that the war on coal, although real, does not primarily happen at the national level but at the state and local level, and that the "boots on the ground" in the war are lawyers from the Sierra Club's Beyond Coal campaign. During Obama's tenure, the Obama administration denied that they were waging a war on coal, noting the possibility of upgrading older power plants with more efficient turbines, and also pointing to the possibility of carbon sequestration techniques.

The environmental policy of the Donald Trump administration represented a shift from the policy priorities and goals of the preceding Barack Obama administration. Where President Obama's environmental agenda prioritized the reduction of carbon emissions through the use of renewable energy with the goal of conserving the environment for future generations, the Trump administration policy was for the US to attain energy independence based on fossil fuel use and to rescind many environmental regulations. By the end of Trump's term, his administration had rolled back 98 environmental rules and regulations, leaving an additional 14 rollbacks still in progress. As of early 2021, the Biden administration was making a public accounting of regulatory decisions under the Trump administration that had been influenced by politics rather than science.
Fossil fuel regulations are part of the energy policy in the United States and have gained major significance with the nation's strong dependence on fossil fuel-based energy. Regulatory processes are established at the federal and state level due to the immense economic, socio-political and environmental impact of fossil fuel extraction and production. Over 80% of the United States' energy comes from fossil fuels such as coal, natural gas, and oil. The Bush administration was marked by the Energy Policy Act of 2005, which provided a monetary incentive for renewable energy adoption and addressed the issue of climate change. The Obama administration was made up of advocates for renewable energy and natural gas, while Donald Trump built his campaign on promises to revive the coal industry.

Andrew R. Wheeler is an American attorney who served as the 15th administrator of the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) from 2019 to 2021. He served as the deputy administrator from April to July 2018, and served as the acting administrator from July 2018 to February 2019. He has been a senior advisor to Governor of Virginia Glenn Youngkin since March 2022. He previously worked in the law firm Faegre Baker Daniels, representing coal magnate Robert E. Murray and lobbying against the Obama Administration's environmental regulations. Wheeler served as chief counsel to the United States Senate Committee on Environment and Public Works and to the chairman U.S. senator James Inhofe, prominent for his rejection of climate change. Wheeler is a critic of limits on greenhouse gas emissions and the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.
West Virginia v. Environmental Protection Agency, 597 U.S. ___ (2022), is a landmark decision of the U.S. Supreme Court relating to the Clean Air Act, and the extent to which the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) can regulate carbon dioxide emissions related to climate change.















