Related Research Articles

Celeron is a discontinued series of low-end IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor models targeted at low-cost personal computers, manufactured by Intel. The first Celeron-branded CPU was introduced on April 15, 1998, and was based on the Pentium II.
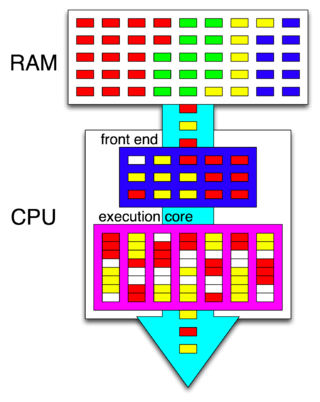
Hyper-threading is Intel's proprietary simultaneous multithreading (SMT) implementation used to improve parallelization of computations performed on x86 microprocessors. It was introduced on Xeon server processors in February 2002 and on Pentium 4 desktop processors in November 2002. Since then, Intel has included this technology in Itanium, Atom, and Core 'i' Series CPUs, among others.

Xeon is a brand of x86 microprocessors designed, manufactured, and marketed by Intel, targeted at the non-consumer workstation, server, and embedded markets. It was introduced in June 1998. Xeon processors are based on the same architecture as regular desktop-grade CPUs, but have advanced features such as support for error correction code (ECC) memory, higher core counts, more PCI Express lanes, support for larger amounts of RAM, larger cache memory and extra provision for enterprise-grade reliability, availability and serviceability (RAS) features responsible for handling hardware exceptions through the Machine Check Architecture (MCA). They are often capable of safely continuing execution where a normal processor cannot due to these extra RAS features, depending on the type and severity of the machine-check exception (MCE). Some also support multi-socket systems with two, four, or eight sockets through use of the Ultra Path Interconnect (UPI) bus, which replaced the older QuickPath Interconnect (QPI) bus.

The land grid array (LGA) is a type of surface-mount packaging for integrated circuits (ICs) that is notable for having the pins on the socket — as opposed to pins on the integrated circuit, known as a pin grid array (PGA). An LGA can be electrically connected to a printed circuit board (PCB) either by the use of a socket or by soldering directly to the board.
The Intel Core microarchitecture is a multi-core processor microarchitecture launched by Intel in mid-2006. It is a major evolution over the Yonah, the previous iteration of the P6 microarchitecture series which started in 1995 with Pentium Pro. It also replaced the NetBurst microarchitecture, which suffered from high power consumption and heat intensity due to an inefficient pipeline designed for high clock rate. In early 2004 the new version of NetBurst (Prescott) needed very high power to reach the clocks it needed for competitive performance, making it unsuitable for the shift to dual/multi-core CPUs. On May 7, 2004 Intel confirmed the cancellation of the next NetBurst, Tejas and Jayhawk. Intel had been developing Merom, the 64-bit evolution of the Pentium M, since 2001, and decided to expand it to all market segments, replacing NetBurst in desktop computers and servers. It inherited from Pentium M the choice of a short and efficient pipeline, delivering superior performance despite not reaching the high clocks of NetBurst.

Pentium is a discontinued series of x86 architecture-compatible microprocessors produced by Intel. The original Pentium was first released on March 22, 1993. The name "Pentium" is originally derived from the Greek word pente (πεντε), meaning "five", a reference to the prior numeric naming convention of Intel's 80x86 processors (8086–80486), with the Latin ending -ium since the processor would otherwise have been named 80586 using that convention.

Sandy Bridge is the codename for Intel's 32 nm microarchitecture used in the second generation of the Intel Core processors. The Sandy Bridge microarchitecture is the successor to Nehalem and Westmere microarchitecture. Intel demonstrated an A1 stepping Sandy Bridge processor in 2009 during Intel Developer Forum (IDF), and released first products based on the architecture in January 2011 under the Core brand.

Haswell is the codename for a processor microarchitecture developed by Intel as the "fourth-generation core" successor to the Ivy Bridge. Intel officially announced CPUs based on this microarchitecture on June 4, 2013, at Computex Taipei 2013, while a working Haswell chip was demonstrated at the 2011 Intel Developer Forum. Haswell was the last generation of Intel processor to have socketed processors on mobile. With Haswell, which uses a 22 nm process, Intel also introduced low-power processors designed for convertible or "hybrid" ultrabooks, designated by the "U" suffix. Haswell began shipping to manufacturers and OEMs in mid-2013, with its desktop chips officially launched in September 2013.

LGA 1156, also known as Socket H or H1, is an Intel desktop CPU socket. Its incompatible successor is LGA 1155.

Arrandale is the code name for a family of mobile Intel processors, sold as mobile Intel Core i3, i5 and i7 as well as Celeron and Pentium. It is closely related to the desktop Clarkdale processor; both use dual-core dies based on the Westmere 32 nm die shrink of the Nehalem microarchitecture, and have integrated Graphics as well as PCI Express and DMI links.

Intel Core is a line of multi-core central processing units (CPUs) for midrange, embedded, workstation, high-end and enthusiast computer markets marketed by Intel Corporation. These processors displaced the existing mid- to high-end Pentium processors at the time of their introduction, moving the Pentium to the entry level. Identical or more capable versions of Core processors are also sold as Xeon processors for the server and workstation markets.
Clarkdale is the codename for Intel's first-generation Core i5, i3 and Pentium dual-core desktop processors. It is closely related to the mobile Arrandale processor; both use dual-core dies based on the 32 nm Westmere microarchitecture and have integrated Graphics, PCI Express and DMI links built-in.

Intel Graphics Technology (GT) is the collective name for a series of integrated graphics processors (IGPs) produced by Intel that are manufactured on the same package or die as the central processing unit (CPU). It was first introduced in 2010 as Intel HD Graphics and renamed in 2017 as Intel UHD Graphics.

Socket G1, also known as rPGA 988A, is a CPU socket introduced by Intel in 2009 for the mobile variants of the first-generation Intel Core processors. It is the successor to Socket P, and the mobile counterpart to LGA 1156 and LGA 1366.

Broadwell is the fifth generation of the Intel Core processor. It is Intel's codename for the 14 nanometer die shrink of its Haswell microarchitecture. It is a "tick" in Intel's tick–tock principle as the next step in semiconductor fabrication. Like some of the previous tick-tock iterations, Broadwell did not completely replace the full range of CPUs from the previous microarchitecture (Haswell), as there were no low-end desktop CPUs based on Broadwell.

Kaby Lake is Intel's codename for its seventh generation Core microprocessor family announced on August 30, 2016. Like the preceding Skylake, Kaby Lake is produced using a 14 nanometer manufacturing process technology. Breaking with Intel's previous "tick–tock" manufacturing and design model, Kaby Lake represents the optimized step of the newer process–architecture–optimization model. Kaby Lake began shipping to manufacturers and OEMs in the second quarter of 2016, with its desktop chips officially launched in January 2017.

Coffee Lake is Intel's codename for its eighth-generation Core microprocessor family, announced on September 25, 2017. It is manufactured using Intel's second 14 nm process node refinement. Desktop Coffee Lake processors introduced i5 and i7 CPUs featuring six cores and Core i3 CPUs with four cores and no hyperthreading.
Comet Lake is Intel's codename for its 10th generation Core processors. They are manufactured using Intel's third 14 nm Skylake process revision, succeeding the Whiskey Lake U-series mobile processor and Coffee Lake desktop processor families. Intel announced low-power mobile Comet Lake-U CPUs on August 21, 2019, H-series mobile CPUs on April 2, 2020, desktop Comet Lake-S CPUs April 30, 2020, and Xeon W-1200 series workstation CPUs on May 13, 2020. Comet Lake processors and Ice Lake 10 nm processors are together branded as the Intel "10th Generation Core" family. Intel officially launched Comet Lake-Refresh CPUs on the same day as 11th Gen Core Rocket Lake launch. The low-power mobile Comet Lake-U Core and Celeron 5205U CPUs were discontinued on July 7, 2021.
References
- ↑ Parallel Computing: On the Road to Exascale . Netherlands, IOS Press, 2016. 373.