
A kelpie, or water kelpie, is a shape-shifting spirit inhabiting lochs in Irish and Scottish folklore. It is usually described as a grey or white horse-like creature, able to adopt human form. Some accounts state that the kelpie retains its hooves when appearing as a human, leading to its association with the Christian idea of Satan as alluded to by Robert Burns in his 1786 poem "Address to the Devil".
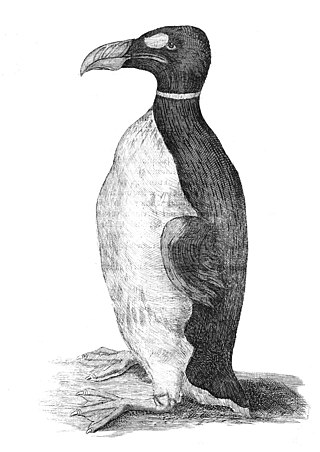
The boobrie is a mythological shapeshifting entity inhabiting the lochs of the west coast of Scotland. It commonly adopts the appearance of a gigantic water bird resembling a cormorant or great northern diver, but it can also materialise in the form of various other mythological creatures such as a water bull.

The cat-sìth, in Irish cat sí, is a fairy creature from Celtic mythology, said to resemble a large black cat with a white spot on its chest. Legend has it that the spectral cat haunts the Scottish Highlands. The legends surrounding this creature are more common in Scottish folklore, but a few occur in Irish. Some common folklore suggested that the cat-sìth was not a fairy, but a witch that could transform into a cat nine times.

The nuckelavee or nuckalavee is a horse-like demon from Orcadian folklore that combines equine and human elements. British folklorist Katharine Briggs called it "the nastiest" of all the demons of Scotland's Northern Isles. The nuckelavee's breath was thought to wilt crops and sicken livestock, and the creature was held responsible for droughts and epidemics on land despite being predominantly a sea-dweller.

A fuath is a class of malevolent spirits in Scottish Highland folklore, especially water spirits.
A bodach is a trickster or bogeyman figure in Gaelic folklore and mythology. The bodach "old man" is paired with the cailleach "hag, old woman" in Irish legend.

The Sword of Light or Claidheamh Soluis is a trope object that appears in a number of Irish and Scottish Gaelic folktales. The "Quest for sword of light" formula is catalogued as motif H1337.

The each-uisge is a water spirit in Irish and Scottish folklore, spelled as the each-uisce in Ireland and cabbyl-ushtey on the Isle of Man. It usually takes the form of a horse, and is similar to the kelpie but far more vicious.
The glaistig is a ghost from Scottish mythology, a type of fuath. It is also known as maighdean uaine, and may appear as a woman of beauty or monstrous mien, as a half-woman and half-goat similar to a faun or satyr, or in the shape of a goat. The lower goat half of her hybrid form is usually disguised by a long, flowing green robe or dress, and the woman often appears grey with long yellow hair.
Fenodyree in the folklore of the Isle of Man, is a hairy supernatural creature, a sort of sprite or fairy, often carrying out chores to help humans, like the brownies of the larger areas of Scotland and England.

Popular Tales of the West Highlands is a four-volume collection of fairy tales, collected and published by John Francis Campbell, and often translated from Gaelic. Alexander Carmichael was one of the main contributors. The collection in four volumes was first published in 1860–62 in Edinburgh. A new edition appeared under the auspices of the Islay Association in 1890–93. Campbell dedicated the work in 1860 to the son of my Chief, the Marquess of Lorne.
How Ian Dìreach got the Blue Falcon is a Scottish fairy tale, collected by John Francis Campbell in Popular Tales of the West Highlands. He recorded it from a quarryman in Knockderry, Roseneath, named Angus Campbell.

Glashtyn is a legendary creature from Manx folklore.

The Sea-Maiden is a Scottish fairy tale collected by John Francis Campbell in Popular Tales of the West Highlands, listing his informant as John Mackenzie, fisherman, near Inverary. Joseph Jacobs included it in Celtic Fairy Tales.
Garb mac Stairn is a character in late prose narratives and poetry (duan) of the Ulster cycle; and claims Scandinavian origins, or is represented as a giant from the Eastlands.
The water bull, also known as tarbh-uisge in Scottish Gaelic, is a mythological Scottish creature similar to the Manx tarroo ushtey. Generally regarded as a nocturnal resident of moorland lochs, it is usually more amiable than its equine counterpart the water horse, but has similar amphibious and shapeshifting abilities.
In Scottish folklore, the beithir is a large snakelike creature or dragon.
Fachin, fachan or fachen is a monster or giant described by John Francis Campbell in Popular Tales of the West Highlands as having a single eye, a single hand, and a single leg.










