Kanaka Dasa (1509–1609) was a Haridasa saint and philosopher of Dvaita Vedanta, also known as Daasashreshta Kanakadasa from present-day Karnataka, India. He was a follower of Madhvacharya's Dvaita philosophy and a disciple of Vyasatirtha. He was a composer of Carnatic music, poet, reformer and musician. He is known for his keertanas and ugabhoga, and his compositions in the Kannada language for Carnatic music. Like other Haridasas, he used simple Kannada and native metrical forms for his compositions.

Belagavi district, formerly also known as Belgaum district, is a district in the state of Karnataka, India. The district is known as the sugar bowl of Karnataka with 150,000 hectares being used for commercial production. It has overtaken Mandya district in sugarcane production over the last decade. The city of Belgaum (Belagavi) is the district headquarters in Belagavi district. It houses the Second legislative building, where the Karnataka Legislature hold session once a year. The district is famous for its native sweet, Kunda. According to the 2011 Census of India, it has a population of 4,779,661, of which 24.03% live in urban areas, making it the second most populous district in Karnataka, after Bangalore Urban. The district has an area of 13,415 km2 (5,180 sq mi) making it the largest district in Karnataka, and is bounded by Kolhapur District and Sangli district of Maharashtra state on the west and north, on the northeast by Bijapur district, on the east by Bagalkot district, on the southeast by Gadag district, on the south by Dharwad and Uttara Kannada districts, and on the southwest by the state of Goa.

North Karnataka is a geographical region in Deccan plateau from 300 to 730 metres elevation that constitutes the region of the Karnataka state in India and the region consists of 14 districts. It is drained by the Krishna River and its tributaries the Bhima, Ghataprabha, Malaprabha, and Tungabhadra. North Karnataka lies within the Deccan thorn scrub forests ecoregion, which extends north into eastern Maharashtra.

Dharwad or Dharawada is an administrative district of the state of Karnataka in southern India. The administrative headquarters of the district is the city of Dharwad, also known as Dharwar. Dharwad is located 425 km northwest of Bangalore and 421 km southeast of Pune, on the main highway between Chennai and Pune, the National Highway 4 (NH4).

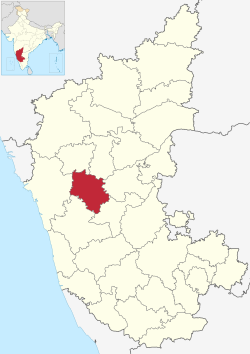
Haveri is a city in Karnataka, India. It is the administrative headquarters of Haveri district. Haveri is famous for its cardamom garlands and Byadagi red chillies. Around 25 km away, there is a place called Bada, which is the birthplace of the poet Kanakadasa.
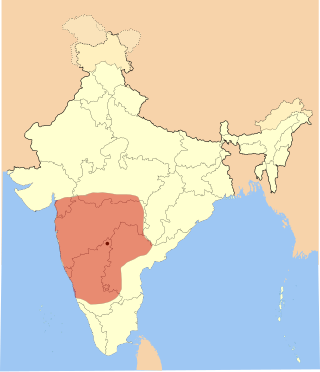
The Western Chalukya Empire ruled most of the western Deccan, South India, between the 10th and 12th centuries. This Kannada-speaking dynasty is sometimes called the Kalyani Chalukya after its regal capital at Kalyani, today's Basavakalyan in the modern Bidar district of Karnataka state, and alternatively the Later Chalukya from its theoretical relationship to the 6th-century Chalukya dynasty of Badami. The dynasty is called Western Chalukyas to differentiate from the contemporaneous Eastern Chalukyas of Vengi, a separate dynasty. Before the rise of these Chalukyas, the Rashtrakuta Empire of Manyakheta controlled most of the Deccan Plateau and Central India for over two centuries. In 973, seeing confusion in the Rashtrakuta empire after a successful invasion of their capital by the ruler of the Paramara dynasty of Malwa, Tailapa II, a feudatory of the Rashtrakuta dynasty ruling from Bijapur region defeated his overlords and made Manyakheta his capital. The dynasty quickly rose to power and grew into an empire under Someshvara I who moved the capital to Kalyani.
Bankapura is a panchayat town in Haveri district in the state of Karnataka, India. It is in Shiggaon taluk, is just 2.5 km from the Pune-Bangalore national highway NH-4, 22 km from Haveri town. Bankapura is about 45 km from Hubli-Dharwad. An historical site, Bankapura is famous for the Nagareshwara temple, Bankapura fort, The Bankapura Peacock Sanctuary. Baada, the birthplace of Kanakadasa is near to Bankapura.

Gadag-Betageri is a city municipal council in Gadag district in the state of Karnataka, India. It is the administrative headquarters of Gadag District. The original city of Gadag and its sister city Betageri have a combined city administration. The municipality of Gadag-Betageri has a population of 172,813 and an area of 54.0956 km2 (20.8864 sq mi). Kanaginahal of Gadag is the birthplace of the first co-operative society in Asia. The temples of Veera Narayana and Trikuteshwara are places of religious and historic importance.
Hirekeruru is a panchayat town in Haveri district in the Indian state of Karnataka. The name "the village of the big pond". The name is pronounced as "Hee ray kay roor".
Shiggaavi is a municipal town in Haveri district in the Indian state of Karnataka.

Karnataka, the sixth largest state in India, has been ranked as the third most popular state in the country for tourism in 2014. It is home to 507 of the 3600 centrally protected monuments in India, second only to Uttar Pradesh. The State Directorate of Archaeology and Museums protects an additional 752 monuments and another 25,000 monuments are yet to receive protection.
Religion in Karnataka has played a very important role in shaping modern Indian religions and philosophy.

Temples of North Karnataka
Galaganath is a small village located near Haveri, in the Haveri District, Karnataka. Located here is the famous Galageshwar Shiva Temple built during the rule of the Western Chalukyas. This large temple faces east and is situated along the Tungabhadra River. The rivers Tunga and Varada join at Galaganath.
Chaudayyadanapur is a small village in Ranebennur taluk of Haveri District in Karnataka state of India. All facets of Indian civilisation are exemplified in an exquisite Mukteshwara temple, with the highest degree of refinement.
Shigli is a city located in the Shirhatti taluk of Gadag district in Karnataka. It is situated 52 kilometres (32 mi) to the south of district headquarters Gadag, 26 km (16 mi) from Shirhatti, and 382 km (237 mi) from state capital Bangalore. Shigli's pin code is 582210, and the postal head office is Shigli.
Rattihalli is a new taluk in the southern state of Karnataka, India. It is located in the Haveri district in Karnataka. It is around 26 km from Ranebennur and around 16 km from Hirekerur. The Veerabhadreshwara Car festival is very famous in Rattihalli.

Kadamba architecture was a style of temple architecture founded by Mayurasharma in the 4th century AD in Karnataka, India. Kadambas created new style of architecture which was the basis of the Hoysalas style of architecture, developed original school of sculpture, was the forerunner of series of South Indian sculptors. Many temples at Aihole, Badami and Hampi are built in Kadamba style.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Karnataka:
Aremallapur is a village in the southern state of Karnataka, India. It is located in the Ranebennur taluk of Haveri district in Karnataka.