Related Research Articles

In molecular biology, RNA polymerase, is an enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template.

A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA molecules from nucleoside triphosphates, the molecular precursors of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to create two identical DNA duplexes from a single original DNA duplex. During this process, DNA polymerase "reads" the existing DNA strands to create two new strands that match the existing ones. These enzymes catalyze the chemical reaction

DNA polymerase III holoenzyme is the primary enzyme complex involved in prokaryotic DNA replication. It was discovered by Thomas Kornberg and Malcolm Gefter in 1970. The complex has high processivity and, specifically referring to the replication of the E.coli genome, works in conjunction with four other DNA polymerases. Being the primary holoenzyme involved in replication activity, the DNA Pol III holoenzyme also has proofreading capabilities that corrects replication mistakes by means of exonuclease activity reading 3'→5' and synthesizing 5'→3'. DNA Pol III is a component of the replisome, which is located at the replication fork.
dnaQ is the gene encoding the ε subunit of DNA polymerase III in Escherichia coli. The ε subunit is one of three core proteins in the DNA polymerase complex. It functions as a 3’→5’ DNA directed proofreading exonuclease that removes incorrectly incorporated bases during replication. dnaQ may also be referred to as mutD.

RNA polymerase II is a multiprotein complex that transcribes DNA into precursors of messenger RNA (mRNA) and most small nuclear RNA (snRNA) and microRNA. It is one of the three RNAP enzymes found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. A 550 kDa complex of 12 subunits, RNAP II is the most studied type of RNA polymerase. A wide range of transcription factors are required for it to bind to upstream gene promoters and begin transcription.

DNA polymerase II is a prokaryotic DNA-Dependent DNA polymerase encoded by the PolB gene.

A DNA clamp, also known as a sliding clamp or β-clamp, is a protein complex that serves as a processivity-promoting factor in DNA replication. As a critical component of the DNA polymerase III holoenzyme, the clamp protein binds DNA polymerase and prevents this enzyme from dissociating from the template DNA strand. The clamp-polymerase protein–protein interactions are stronger and more specific than the direct interactions between the polymerase and the template DNA strand; because one of the rate-limiting steps in the DNA synthesis reaction is the association of the polymerase with the DNA template, the presence of the sliding clamp dramatically increases the number of nucleotides that the polymerase can add to the growing strand per association event. The presence of the DNA clamp can increase the rate of DNA synthesis up to 1,000-fold compared with a nonprocessive polymerase.

The gene polymerase delta 1 (POLD1) encodes the large, POLD1/p125, catalytic subunit of the DNA polymerase delta (Polδ) complex. The Polδ enzyme is responsible for synthesizing the lagging strand of DNA, and has also been implicated in some activities at the leading strand. The POLD1/p125 subunit encodes both DNA polymerizing and exonuclease domains, which provide the protein an important second function in proofreading to ensure replication accuracy during DNA synthesis, and in a number of types of replication-linked DNA repair following DNA damage. Germline mutations impairing activity of POLD1 have been implicated in several types of hereditary cancer, in some sporadic cancers, and in a developmental syndrome of premature aging, Mandibular hypoplasia, Deafness, and Progeroid features and Lipodystrophy. Studies of POLD1 emphasize the importance of maintaining genomic stability to limit tumorigenesis. It is currently unclear whether the enhanced tumorigenesis associated with POLD1 defects is the result of increased base substitutions or due to fork collapse and production of DNA double strand breaks (DSBs). Recent reviews have addressed important functions of POLD1 and Polδ.

DNA polymerase delta subunit 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the POLD2 gene. It is a component of the DNA polymerase delta complex.
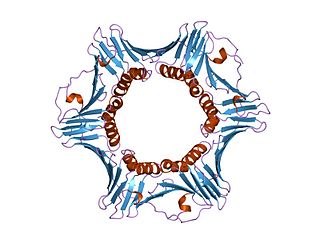
DNA polymerase delta subunit 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the POLD3 gene. It is a component of the DNA polymerase delta complex.

Polymerase delta-interacting protein 2 also known as Polymerase delta-interacting protein of 38 kDa (PDIP38) is encoded by the POLDIP2 gene in humans.

Polymerase delta-interacting protein 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the POLDIP3 gene.

DNA polymerase eta, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the POLH gene.
The term proofreading is used in genetics to refer to the error-correcting processes, first proposed by John Hopfield and Jacques Ninio, involved in DNA replication, immune system specificity, enzyme-substrate recognition among many other processes that require enhanced specificity. The proofreading mechanisms of Hopfield and Ninio are non-equilibrium active processes that consume ATP to enhance specificity of various biochemical reactions.

DNA polymerase delta subunit 4, also known as DNA polymerase delta subunit p12, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the POLD4 gene. It is a component of the DNA polymerase delta complex.

In molecular biology, the δ (delta) subunit of DNA polymerase III is encoded by the holA gene in E. coli and other bacteria. Along with the γ, δ', χ, and ψ subunits that make up the core polymerase, and the β accessory proteins, the δ subunit is responsible for the high speed and processivity of polIII.

In E. coli and other bacteria, holC is a gene that encodes the chi subunit of DNA polymerase III.
In E. coli and other bacteria, holD is a gene that encodes the psi subunit of DNA polymerase III.
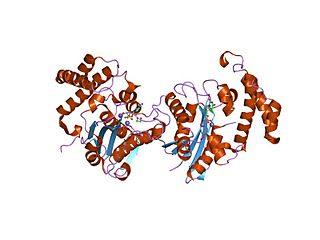
In E. coli and other bacteria, holE is a gene that encodes the theta subunit of DNA polymerase III.
DNA polymerase may refer to:
References
| This molecular biology article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |