
Riboflavin, also known as vitamin B2, is a vitamin found in food and sold as a dietary supplement. It is essential to the formation of two major coenzymes, flavin mononucleotide and flavin adenine dinucleotide. These coenzymes are involved in energy metabolism, cellular respiration, and antibody production, as well as normal growth and development. The coenzymes are also required for the metabolism of niacin, vitamin B6, and folate. Riboflavin is prescribed to treat corneal thinning, and taken orally, may reduce the incidence of migraine headaches in adults.

Vitamin C is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits, berries and vegetables. It is also a generic prescription medication and in some countries is sold as a non-prescription dietary supplement. As a therapy, it is used to prevent and treat scurvy, a disease caused by vitamin C deficiency.

Vitamin K is a family of structurally similar, fat-soluble vitamers found in foods and marketed as dietary supplements. The human body requires vitamin K for post-synthesis modification of certain proteins that are required for blood coagulation or for controlling binding of calcium in bones and other tissues. The complete synthesis involves final modification of these so-called "Gla proteins" by the enzyme gamma-glutamyl carboxylase that uses vitamin K as a cofactor.

Pantothenic acid (vitamin B5) is a B vitamin and an essential nutrient. All animals need pantothenic acid in order to synthesize coenzyme A (CoA)—essential for metabolizing fatty acid—and to synthesize and metabolize proteins, carbohydrates, and fats.

Vitamin B6 is one of the B vitamins, and thus an essential nutrient. The term refers to a group of six chemically similar compounds, i.e., "vitamers", which can be interconverted in biological systems. Its active form, pyridoxal 5′-phosphate, serves as a coenzyme in more than 140 enzyme reactions in amino acid, glucose, and lipid metabolism.

Retinol, also called vitamin A1, is a fat-soluble vitamin in the vitamin A family that is found in food and used as a dietary supplement. Retinol or other forms of vitamin A are needed for vision, cellular development, maintenance of skin and mucous membranes, immune function and reproductive development. Dietary sources include fish, dairy products, and meat. As a supplement it is used to treat and prevent vitamin A deficiency, especially that which results in xerophthalmia. It is taken by mouth or by injection into a muscle. As an ingredient in skin-care products, it is used to reduce wrinkles and other effects of skin aging.
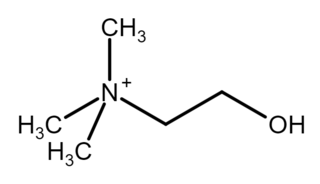
Choline is an essential nutrient for humans and many other animals, which was formerly classified as a B vitamin . It is a structural part of phospholipids and a methyl donor in metabolic one-carbon chemistry. The compound is related to trimethylglycine in the latter respect. It is a cation with the chemical formula [(CH3)3NCH2CH2OH]+. Choline forms various salts, for example choline chloride and choline bitartrate.

Cholecalciferol, also known as vitamin D3 and colecalciferol, is a type of vitamin D that is made by the skin when exposed to sunlight; it is found in some foods and can be taken as a dietary supplement.
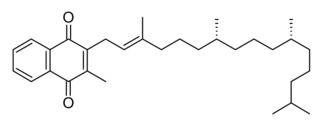
Phytomenadione, also known as vitamin K1 or phylloquinone, is a vitamin found in food and used as a dietary supplement. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.

Menatetrenone (INN), also known as menaquinone-4 (MK-4), is one of the nine forms of vitamin K2.
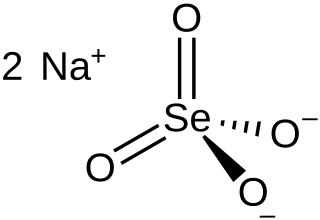
Sodium selenate is the inorganic compound with the formula Na
2SeO
4, not to be confused with sodium selenite. It exists as the anhydrous salt, the heptahydrate, and the decahydrate. These are white, water-soluble solids. The decahydrate is a common ingredient in multivitamins and livestock feed as a source of selenium. The anhydrous salt is used in the production of some glass. Although the selenates are much more toxic, many physical properties of sodium selenate and sodium sulfate are similar.

In enzymology, a NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (quinone) (EC 1.6.5.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Vitamin K deficiency results from insufficient dietary vitamin K1 or vitamin K2 or both.
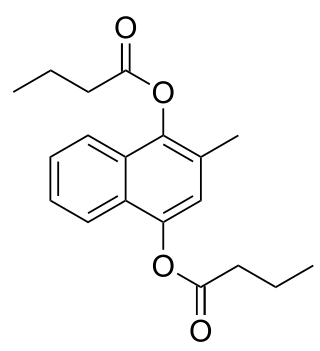
Menadiol is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(COH)2(CH)(CH3). It is formally a derivative of p-hydroquinone. The name vitamin K4 can refer to:

Naphthoquinones constitute a class of organic compounds structurally related to naphthalene. Two isomers are common for the parent naphthoquinones:

Vitamin K2 or menaquinone (MK) is one of three types of vitamin K, the other two being vitamin K1 (phylloquinone) and K3 (menadione). K2 is both a tissue and bacterial product (derived from vitamin K1 in both cases) and is usually found in animal products or fermented foods.

Vitamin B3, colloquially referred to as niacin, is a vitamin family that includes three forms, or vitamers: niacin (nicotinic acid), nicotinamide (niacinamide), and nicotinamide riboside. All three forms of vitamin B3 are converted within the body to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD). NAD is required for human life and people are unable to make it within their bodies without either vitamin B3 or tryptophan. Nicotinamide riboside was identified as a form of vitamin B3 in 2004.

Nivalenol (NIV) is a mycotoxin of the trichothecene group. In nature it is mainly found in fungi of the Fusarium species. The Fusarium species belongs to the most prevalent mycotoxin producing fungi in the temperate regions of the northern hemisphere, therefore making them a considerable risk for the food crop production industry.

4-Amino-2-methyl-1-naphthol is a menadione analog. Its water-soluble hydrochloride (HCl) salt is often called vitamin K5. The HCl salt has been used as a medicine for vitamin K deficiency under tradenames such as Synkamin, which was sold by Parke-Davis, but has since been discontinued.
Megavitamin-B6 syndrome is a collection of symptoms that can result from chronic supplementation, or acute overdose, of vitamin B6. While it is also known as hypervitaminosis B6, vitamin B6 toxicity and vitamin B6 excess, megavitamin-b6 syndrome is the name used in the ICD-10.




















