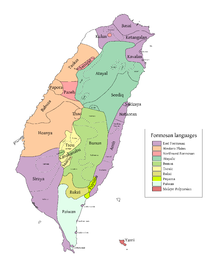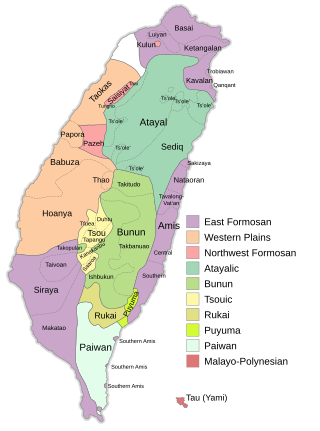
The Formosan languages are a geographic grouping comprising the languages of the indigenous peoples of Taiwan, all of which are Austronesian. They do not form a single subfamily of Austronesian but rather nine separate subfamilies. The Taiwanese indigenous peoples recognized by the government are about 2.3% of the island's population. However, only 35% speak their ancestral language, due to centuries of language shift. Of the approximately 26 languages of the Taiwanese indigenous peoples, at least ten are extinct, another four are moribund, and all others are to some degree endangered.

Hsinchu County is a county in north-western Taiwan. The population of the county is mainly Hakka; with a Taiwanese aboriginal minority in the southeastern part of the county. Zhubei is the county capital, where the government office and county office is located. A portion of the Hsinchu Science Park is located in Hsinchu County.
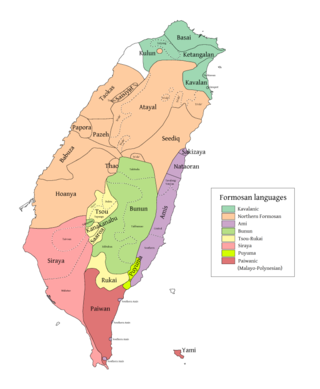
Basay was a Formosan language spoken around modern-day Taipei in northern Taiwan by the Basay, Qauqaut, and Trobiawan peoples. Trobiawan, Linaw, and Qauqaut were other dialects.
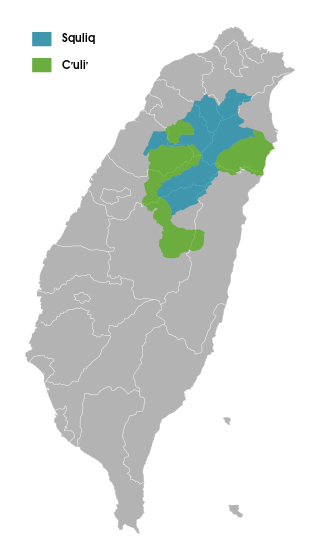
The Atayal language is spoken by the Atayal people of Taiwan. Squliq and C’uli’ (Ts’ole’) are two major dialects. Mayrinax and Pa’kuali’, two subdialects of C’uli’, are unique among Atayal dialects in having male and female register distinctions in their vocabulary.

Kavalan was formerly spoken in the Northeast coast area of Taiwan by the Kavalan people (噶瑪蘭). It is an East Formosan language of the Austronesian family.

The languages of Taiwan consist of several varieties of languages under the families of Austronesian languages and Sino-Tibetan languages. The Formosan languages, a branch of Austronesian languages, have been spoken by the Taiwanese indigenous peoples for thousands of years. Owing to the wide internal variety of the Formosan languages, research on historical linguistics recognizes Taiwan as the Urheimat (homeland) of the whole Austronesian languages family. In the last 400 years, several waves of Han emigrations brought several different Sinitic languages into Taiwan. These languages include Taiwanese Hokkien, Hakka, and Mandarin, which have become the major languages spoken in present-day Taiwan.
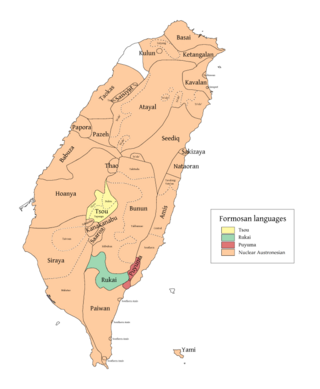
Tsou is a divergent Austronesian language spoken by the Tsou people of Taiwan. Tsou is a threatened language; however, this status is uncertain. Its speakers are located in the west-central mountains southeast of the Chiayi/Alishan area in Taiwan.

Rukai is a Formosan language spoken by the Rukai people in Taiwan. It is a member of the Austronesian language family. The Rukai language comprises six dialects, which are Budai, Labuan, Maga, Mantauran, Tanan and Tona. The number of speakers of the six Rukai dialects is estimated to be about 10,000. Some of them are monolingual. There are varying degrees of mutual intelligibility among the Rukai dialects. Rukai is notable for its distinct grammatical voice system among the Formosan languages.
Pazeh and Kaxabu are dialects of an extinct language of the Pazeh and Kaxabu, neighboring Taiwanese indigenous peoples. The language was Formosan, of the Austronesian language family. The last remaining native speaker of the Pazeh dialect died in 2010.
Kanakanavu is a Southern Tsouic language spoken by the Kanakanavu people, an indigenous people of Taiwan. It is a Formosan language of the Austronesian family.

Saaroa or Lhaʼalua is a Southern Tsouic language is spoken by the Saaroa (Hla'alua) people, an indigenous people of Taiwan. It is a Formosan language of the Austronesian family.

The Qauqaut were a Taiwanese aboriginal people who lived primarily in the town of Su-ao in Yilan County. They spoke the Basay language, which is a Kavalanic language. According to Japanese anthropologist Inō Kanori, the Qauqaut people had been assimilated by the Kavalan people by early 20th century. The Qauqaut people are not recognised by the government of Taiwan.

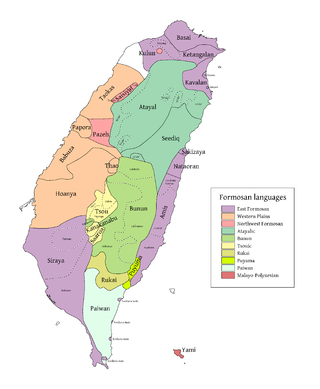
The Tsouic languages are three Formosan languages, Tsou proper and the Southern languages Kanakanavu and Saaroa. The Southern Tsouic languages of Kanakanavu and Saaroa have the smallest phonemic inventories out of all the Formosan languages, with each language having only 13 consonants and 4 vowels. These two languages are highly endangered, as many Southern Tsouic speakers are shifting to Bunun and Mandarin Chinese.
The Atayalic languages are a group of Formosan languages spoken in northern Taiwan. Robert Blust considers them to form a primary branch within the Austronesian language family, However, Paul Jen-kuei Li groups them into the Northern Formosan branch, which includes the Northwestern Formosan languages.

The East Formosan languages consist of various Formosan languages scattered across Taiwan, including Kavalan, Amis, and the extinct Siraya language. This grouping is supported by both Robert Blust and Paul Jen-kuei Li. Li considers the Siraya-speaking area in the southwestern plains of Taiwan to be the most likely homeland of the East Formosan speakers, where they then spread to the eastern coast of Taiwan and gradually migrated to the area of modern-day Taipei.

The Northern Formosan languages is a proposed grouping of Formosan languages that includes the Atayalic languages, the Western Plains languages, and the Northwest Formosan languages.
This article describes the personal pronoun systems of various Austronesian languages.

Luilang, or ambiguously Ketagalan, was a Formosan language spoken south of modern-day Taipei in northern Taiwan by one of several peoples that have been called Ketagalan. The language probably went extinct in the mid-20th century and it is very poorly attested.

Kulon is an extinct language of the Taiwanese aboriginal people that belonged to the Austronesian language family. Very little data is available for Kulon; the primary source is the 60 pages of Tsuchida (1985). Li (2008) follows Tsuchida in linking Kulon with Saisiyat, while Blust (1999) proposes it was more closely related to Pazeh
The writing systems of the Formosan languages are Latin-based alphabets. Currently, 16 languages have been regulated. The alphabet was made official in 2005.