The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involuntary) functions, ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor centers, and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep wake cycle.
Articles related to anatomy include:
Pronator quadratus is a square-shaped muscle on the distal forearm that acts to pronate the hand.

The brainstem is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is continuous with the thalamus of the diencephalon through the tentorial notch, and sometimes the diencephalon is included in the brainstem.
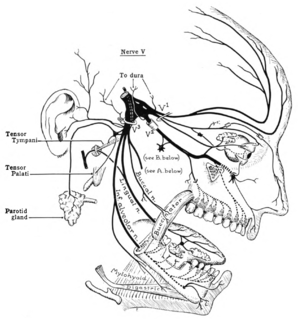
In neuroanatomy, the trigeminal nerve, also known as the fifth cranial nerve, cranial nerve V, or simply CN V, is a cranial nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing; it is the most complex of the cranial nerves. Its name ("trigeminal", from Latin tri- 'three', and -geminus 'twin') derives from each of the two nerves (one on each side of the pons) having three major branches: the ophthalmic nerve (V1), the maxillary nerve (V2), and the mandibular nerve (V3). The ophthalmic and maxillary nerves are purely sensory, whereas the mandibular nerve supplies motor as well as sensory (or "cutaneous") functions. Adding to the complexity of this nerve is that autonomic nerve fibers as well as special sensory fibers (taste) are contained within it.

The internal capsule is a white matter structure situated in the inferomedial part of each cerebral hemisphere of the brain. It carries information past the basal ganglia, separating the caudate nucleus and the thalamus from the putamen and the globus pallidus. The internal capsule contains both ascending and descending axons, going to and coming from the cerebral cortex. It also separates the caudate nucleus and the putamen in the dorsal striatum, a brain region involved in motor and reward pathways.

The spinothalamic tract is a part of the anterolateral system or the ventrolateral system, a sensory pathway to the thalamus. From the ventral posterolateral nucleus in the thalamus, sensory information is relayed upward to the somatosensory cortex of the postcentral gyrus.

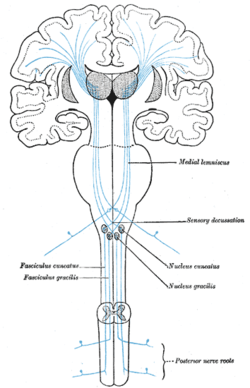
The dorsal column–medial lemniscus pathway (DCML) is a sensory pathway of the central nervous system that conveys sensations of fine touch, vibration, two-point discrimination, and proprioception (position) from the skin and joints. It transmits information from the body to the primary somatosensory cortex in the postcentral gyrus of the parietal lobe of the brain. The pathway receives information from sensory receptors throughout the body, and carries this in nerve tracts in the white matter of the dorsal column of the spinal cord to the medulla, where it is continued in the medial lemniscus, on to the thalamus and relayed from there through the internal capsule and transmitted to the somatosensory cortex. The name dorsal-column medial lemniscus comes from the two structures that carry the sensory information: the dorsal columns of the spinal cord, and the medial lemniscus in the brainstem.

In neuroanatomy, the medial lemniscus, also known as Reil's band or Reil's ribbon, is a large ascending bundle of heavily myelinated axons that decussate (cross) in the brainstem, specifically in the medulla oblongata. The medial lemniscus is formed by the crossings of the internal arcuate fibers. The internal arcuate fibers are composed of axons of nucleus gracilis and nucleus cuneatus. The axons of the nucleus gracilis and nucleus cuneatus in the medial lemniscus have cell bodies that lie contralaterally.
Stereognosis is the ability to perceive and recognize the form of an object in the absence of visual and auditory information, by using tactile information to provide cues from texture, size, spatial properties, and temperature, etc. In humans, this sense, along with tactile spatial acuity, vibration perception, texture discrimination and proprioception, is mediated by the dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway of the central nervous system. Stereognosis tests determine whether or not the parietal lobe of the brain is intact. Typically, these tests involved having the patient identify common objects placed in their hand without any visual cues. Stereognosis is a higher cerebral associative cortical function.

The posterior grey column of the spinal cord is one of the three grey columns of the spinal cord. It receives several types of sensory information from the body, including fine touch, proprioception, and vibration. This information is sent from receptors of the skin, bones, and joints through sensory neurons whose cell bodies lie in the dorsal root ganglion.

The spinocerebellar tract is a nerve tract originating in the spinal cord and terminating in the same side (ipsilateral) of the cerebellum.

The dorsal root of spinal nerve is one of two "roots" which emerge from the spinal cord. It emerges directly from the spinal cord, and travels to the dorsal root ganglion. Nerve fibres with the ventral root then combine to form a spinal nerve. The dorsal root transmits sensory information, forming the afferent sensory root of a spinal nerve.

The accessory cuneate nucleus is located lateral to the cuneate nucleus in the medulla oblongata at the level of the sensory decussation.
The dorsal longitudinal fasciculus (DLF) is a white matter fiber tract located within the brain stem, specifically in the dorsal brainstem tegmentum. The DLF travels through the periaqueductal gray matter. The tract is composed of a diffuse brainstem pathway located in the periventricular gray matter comprising ascending visceral sensory axons and descending hypothalamic axons.

In neuroanatomy, the internal arcuate fibers or internal arcuate tract are the axons of second-order sensory neurons that compose the gracile and cuneate nuclei of the medulla oblongata. These second-order neurons begin in the gracile and cuneate nuclei in the medulla. They receive input from first-order sensory neurons, which provide sensation to many areas of the body and have cell bodies in the dorsal root ganglia of the dorsal root of the spinal nerves. Upon decussation from one side of the medulla to the other, also known as the sensory decussation, they are then called the medial lemniscus.
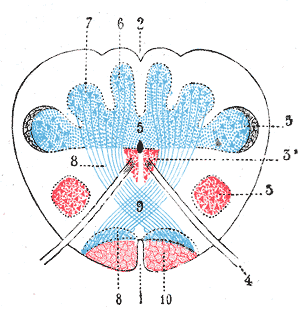
In neuroanatomy, the dorsal column nuclei are a pair of nuclei in the dorsal columns in the brainstem. The name refers collectively to the cuneate nucleus and gracile nucleus, which are present at the bottom of the medulla oblongata. Both nuclei contain second-order neurons of the dorsal column–medial lemniscus pathway, which carries fine touch and proprioceptive information from the body to the brain. Fibres reach the thalamus.

The posterior spinal artery arises from the vertebral artery in 25% of humans or the posterior inferior cerebellar artery in 75% of humans, adjacent to the medulla oblongata. It supplies the grey and white posterior columns of the spinal cord.

The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the spinal cord, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system (CNS). In humans, the spinal cord begins at the occipital bone, passing through the foramen magnum and then enters the spinal canal at the beginning of the cervical vertebrae. The spinal cord extends down to between the first and second lumbar vertebrae, where it ends. The enclosing bony vertebral column protects the relatively shorter spinal cord. It is around 45 cm (18 in) long in adult men and around 43 cm (17 in) long in adult women. The diameter of the spinal cord ranges from 13 mm in the cervical and lumbar regions to 6.4 mm in the thoracic area.