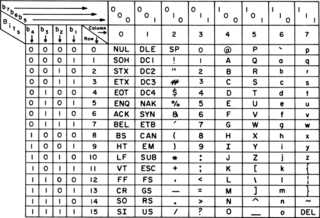
ASCII, an acronym for American Standard Code for Information Interchange, is a character encoding standard for electronic communication. ASCII codes represent text in computers, telecommunications equipment, and other devices. Because of technical limitations of computer systems at the time it was invented, ASCII has just 128 code points, of which only 95 are printable characters, which severely limited its scope. Modern computer systems have evolved to use Unicode, which has millions of code points, but the first 128 of these are the same as the ASCII set.

In computing and electronic systems, binary-coded decimal (BCD) is a class of binary encodings of decimal numbers where each digit is represented by a fixed number of bits, usually four or eight. Sometimes, special bit patterns are used for a sign or other indications.

In computing, plain text is a loose term for data that represent only characters of readable material but not its graphical representation nor other objects. It may also include a limited number of "whitespace" characters that affect simple arrangement of text, such as spaces, line breaks, or tabulation characters. Plain text is different from formatted text, where style information is included; from structured text, where structural parts of the document such as paragraphs, sections, and the like are identified; and from binary files in which some portions must be interpreted as binary objects.
In computer architecture, 8-bit integers or other data units are those that are 8 bits wide. Also, 8-bit central processing unit (CPU) and arithmetic logic unit (ALU) architectures are those that are based on registers or data buses of that size. Memory addresses for 8-bit CPUs are generally larger than 8-bit, usually 16-bit. 8-bit microcomputers are microcomputers that use 8-bit microprocessors.

A power of two is a number of the form 2n where n is an integer, that is, the result of exponentiation with number two as the base and integer n as the exponent.
94 (ninety-four) is the natural number following 93 and preceding 95.
127 is the natural number following 126 and preceding 128. It is also a prime number.

The Aztec Code is a matrix code invented by Andrew Longacre, Jr. and Robert Hussey in 1995. The code was published by AIM, Inc. in 1997. Although the Aztec Code was patented, that patent was officially made public domain. The Aztec Code is also published as ISO/IEC 24778:2008 standard. Named after the resemblance of the central finder pattern to an Aztec pyramid, Aztec Code has the potential to use less space than other matrix barcodes because it does not require a surrounding blank "quiet zone".

Code 128 is a high-density linear barcode symbology defined in ISO/IEC 15417:2007. It is used for alphanumeric or numeric-only barcodes. It can encode all 128 characters of ASCII and, by use of an extension symbol (FNC4), the Latin-1 characters defined in ISO/IEC 8859-1. It generally results in more compact barcodes compared to other methods like Code 39, especially when the texts contain mostly digits. Code 128 was developed by the Computer Identics Corporation in 1981.

In computer architecture, 36-bit integers, memory addresses, or other data units are those that are 36 bits wide. Also, 36-bit central processing unit (CPU) and arithmetic logic unit (ALU) architectures are those that are based on registers, address buses, or data buses of that size. 36-bit computers were popular in the early mainframe computer era from the 1950s through the early 1970s.
129 is the natural number following 128 and preceding 130.
131 is the natural number following 130 and preceding 132.
133 is the natural number following 132 and preceding 134.
Telepen is the name of a barcode symbology designed to encode all 128 ASCII characters without using shift characters for code switching, and only using two different widths for both bars and spaces.. The symbology was devised by George Sims of SB Electronic Systems Ltd. Telepen was originally designed in the UK in 1972.
In computing, a word is the natural unit of data used by a particular processor design. A word is a fixed-sized datum handled as a unit by the instruction set or the hardware of the processor. The number of bits or digits in a word is an important characteristic of any specific processor design or computer architecture.

A Data Matrix is a two-dimensional code consisting of black and white "cells" or dots arranged in either a square or rectangular pattern, also known as a matrix. The information to be encoded can be text or numeric data. Usual data size is from a few bytes up to 1556 bytes. The length of the encoded data depends on the number of cells in the matrix. Error correction codes are often used to increase reliability: even if one or more cells are damaged so it is unreadable, the message can still be read. A Data Matrix symbol can store up to 2,335 alphanumeric characters.
A binary-to-text encoding is encoding of data in plain text. More precisely, it is an encoding of binary data in a sequence of printable characters. These encodings are necessary for transmission of data when the communication channel does not allow binary data or is not 8-bit clean. PGP documentation uses the term "ASCII armor" for binary-to-text encoding when referring to Base64.

Han Xin code is two-dimensional (2D) matrix barcode symbology invented in 2007 by Chinese company The Article Numbering Center of China to break monopoly of QR code. As QR code, Han Xin code consists of black squares and white square spaces arranged in a square grid on a white background. It has four finder patterns and other markers which allow to recognize it with camera-based readers. Han Xin code contains Reed–Solomon error correction with ability to read corrupted images. At this time, it is issued as ISO/IEC 20830:2021.

DotCode is two-dimensional (2D) matrix barcode invented in 2008 by Hand Held Products company to replace outdated Code 128. At this time, it is issued by Association for Automatic Identification and Mobility (AIM) as “ISS DotCode Symbology Specification 4.0”. DotCode consists of sparse black round dots and white spaces on white background. In case of black background round dots, creating barcode, can be white. DotCode was developed to use with high-speed industrial printers where printing accuracy can be low. Because DotCode by the standard does not require complicated elements like continuous lines or special shapes it can be applied with laser engraving or industrial drills.

Rectangular Micro QR Code is two-dimensional (2D) matrix barcode invented and standardized in 2022 by Denso Wave as ISO/IEC 23941. rMQR Code is designed as a rectangular variation of QR code and has the same parameters and applications as original QR code. But rMQR Code is more suitable for the rectangular areas and has difference between width and height up to 19 in R7x139 version. In this way it can be used in places where 1D barcodes are used. rMQR Code can replace Code 128 and Code 39 barcodes with more effective data encoding.











