
Anesthesia or anaesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia, paralysis, amnesia, and unconsciousness. An individual under the effects of anesthetic drugs is referred to as being anesthetized.

Anesthesiology, anaesthesiology, or anaesthesia is the medical specialty concerned with the total perioperative care of patients before, during and after surgery. It encompasses anesthesia, intensive care medicine, critical emergency medicine, and pain medicine. A physician specialized in anesthesiology is called an anesthesiologist, anaesthesiologist, or anaesthetist, depending on the country. In some countries the terms are synonymous, while in other countries they refer to different positions and anesthetist is only used for non-physicians, such as nurse anesthetists.
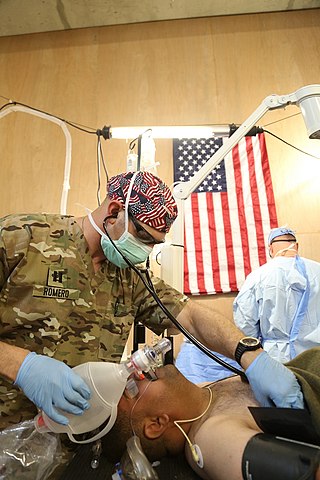
A nurse anesthetist is an advanced practice nurse who administers anesthesia for surgery or other medical procedures. They are involved in the administration of anesthesia in a majority of countries, with varying levels of autonomy.

A Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist (CRNA) is a type of advanced practice nurse who administers anesthesia in the United States. CRNAs account for approximately half of the anesthesia providers in the United States and are the main providers (80%) of anesthesia in rural America. Historically, nurse anesthetists have been providing anesthesia care to patients for over 150 years since the American Civil War and the CRNA credential came into existence in 1956. CRNA schools issue a doctorate of nursing anesthesia degree to nurses who have completed a program in anesthesia, which is roughly 3 years in length.
A medical specialty is a branch of medical practice that is focused on a defined group of patients, diseases, skills, or philosophy. Examples include those branches of medicine that deal exclusively with children (paediatrics), cancer (oncology), laboratory medicine (pathology), or primary care. After completing medical school or other basic training, physicians or surgeons and other clinicians usually further their medical education in a specific specialty of medicine by completing a multiple-year residency to become a specialist.
The California Society of Anesthesiologists (CSA), Inc., is a component society of the American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc., in the state of California.
The ASA physical status classification system is a system for assessing the fitness of patients before surgery. In 1963 the American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) adopted the five-category physical status classification system; a sixth category was later added. These are:
- Healthy person.
- Mild systemic disease.
- Severe systemic disease.
- Severe systemic disease that is a constant threat to life.
- A moribund person who is not expected to survive without the operation.
- A declared brain-dead person whose organs are being removed for donor purposes.
In the United States, anesthesia can be administered by physician anesthesiologists, an anesthesiologist assistant, or nurse anesthetist.
Cardiothoracic anesthesiology is a subspeciality of the medical practice of anesthesiology, devoted to the preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative care of adult and pediatric patients undergoing cardiothoracic surgery and related invasive procedures.
Geriatric anesthesia is the branch of medicine that studies anesthesia approach in elderly.
The American Association of Nurse Anesthesiologists (AANA) is the professional association of nurse Anesthesiologists in the United States. The organization states that it has a membership of more than 59,000, includes Certified Registered Nurse Anesthesiologist (CRNA) and student (SRNA) members. The organization represents approximately 90 percent of CRNAs in the United States. The AANA headquarters is currently located in Park Ridge, Illinois, a suburb of Chicago.
Neurosurgical anesthesiology, neuroanesthesiology, or neurological anesthesiology is a subspecialty of anesthesiology devoted to the total perioperative care of patients before, during, and after neurological surgeries, including surgeries of the central (CNS) and peripheral nervous systems (PNS). The field has undergone extensive development since the 1960s correlating with the ability to measure intracranial pressure (ICP), cerebral blood flow (CBF), and cerebral metabolic rate (CMR).
The American Dental Society of Anesthesiology (ADSA) is an American professional association established in 1953 and based in Chicago.
Certified anesthesiologist assistants (CAAs) are highly trained master’s degree level non-physician anesthesia care providers. CAAs are integral members of the anesthesia care team as described by the American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA). This designation must be disambiguated from the Certified Clinical Anesthesia Assistant (CCAA) designation conferred by the Canadian Society of Respiratory Therapists. All CAAs possess a baccalaureate degree, and complete an intensive didactic and clinical program at a postgraduate level. CAAs are trained in the delivery and maintenance of all types of anesthesia care as well as advanced patient monitoring techniques. The goal of CAA education is to guide the transformation of student applicants into competent clinicians.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to anesthesia:

The American Osteopathic Board of Anesthesiology (AOBA) is an organization that provides board certification to qualified Doctors of Osteopathic Medicine (D.O.) and physicians who specialize in the administration of anesthetic agents and perioperative medicine (anesthesiologists). The board is one of 16 medical specialty certifying boards of the American Osteopathic Association Bureau of Osteopathic Specialists approved by the American Osteopathic Association (AOA), and was established in 1956.
John Adriani was an American anesthesiologist and director of anesthesiology at Charity Hospital in New Orleans. He was president of the American Board of Anesthesiology (ABA) and he received a Distinguished Service Award from the American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA). He was an early supporter of physician involvement in nurse anesthetist training.
Obstetric anesthesia or obstetric anesthesiology, also known as ob-gyn anesthesia or ob-gyn anesthesiology, is a sub-specialty of anesthesiology that provides peripartum pain relief (analgesia) for labor and anesthesia for cesarean deliveries ('C-sections').

James Tayloe Gwathmey, M.D. was an American physician and the first president of the American Association of Anesthetics. A pioneer of early anesthetic devices for medical use, he co-authored the first comprehensive textbook on the subject of medical anesthetics, titled Anesthesia, which was published in 1914. For this and other contributions to anesthesiology, which included innovations in administering anesthetics to war wounded and in obstetrics, Gwathmey was hailed at the time of his death as the "Father of Modern Anesthesia."
Jerrold H. Levy is an American critical care physician and cardiac anesthesiologist at Duke University Medical Center who currently serves as the co-director of Duke's Cardiothoracic Intensive Care Unit. He is most noted for his research in surgical hemostasis, coagulopathy in the critically ill, shock, anaphylaxis, and developing purified and recombinant therapeutic approaches to treat bleeding. He has authored over 400 publications, including scientific manuscripts, review articles, editorials, books, and book chapters. Additionally, he has authored a number of websites aimed at providing medical information to healthcare professionals through his website, DocMD.






