Joubert syndrome is a rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder that affects the cerebellum, an area of the brain that controls balance and coordination.

Obesity hypoventilation syndrome (OHS) is a condition in which severely overweight people fail to breathe rapidly or deeply enough, resulting in low oxygen levels and high blood carbon dioxide (CO2) levels. The syndrome is often associated with obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), which causes periods of absent or reduced breathing in sleep, resulting in many partial awakenings during the night and sleepiness during the day. The disease puts strain on the heart, which may lead to heart failure and leg swelling.

Tietze syndrome is a benign inflammation of one or more of the costal cartilages. It was first described in 1921 by German surgeon Alexander Tietze and was subsequently named after him. The condition is characterized by tenderness and painful swelling of the anterior (front) chest wall at the costochondral, sternocostal, or sternoclavicular junctions. Tietze syndrome affects the true ribs and has a predilection for the 2nd and 3rd ribs, commonly affecting only a single joint.

Bronchiectasis is a disease in which there is permanent enlargement of parts of the airways of the lung. Symptoms typically include a chronic cough with mucus production. Other symptoms include shortness of breath, coughing up blood, and chest pain. Wheezing and nail clubbing may also occur. Those with the disease often get lung infections.

Mucopolysaccharidoses are a group of metabolic disorders caused by the absence or malfunctioning of lysosomal enzymes needed to break down molecules called glycosaminoglycans (GAGs). These long chains of sugar carbohydrates occur within the cells that help build bone, cartilage, tendons, corneas, skin and connective tissue. GAGs are also found in the fluids that lubricate joints.
Multisystem developmental disorder (MSDD) is a term used by Stanley Greenspan to describe children under age 3 who exhibit signs of impaired communication as in autism, but with strong emotional attachments atypical of autism. It is described in the DC:0-3R manual as an optional diagnosis for children under two years of age.

Pectus excavatum is a structural deformity of the anterior thoracic wall in which the sternum and rib cage are shaped abnormally. This produces a caved-in or sunken appearance of the chest. It can either be present at birth or develop after puberty.
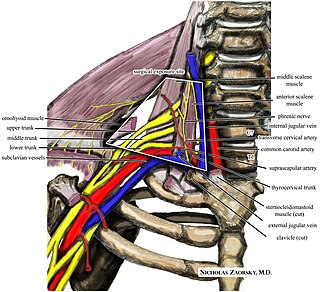
Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a condition in which there is compression of the nerves, arteries, or veins in the superior thoracic aperture, the passageway from the lower neck to the armpit, also known as the thoracic outlet. There are three main types: neurogenic, venous, and arterial. The neurogenic type is the most common and presents with pain, weakness, paraesthesia, and occasionally loss of muscle at the base of the thumb. The venous type results in swelling, pain, and possibly a bluish coloration of the arm. The arterial type results in pain, coldness, and pallor of the arm.

Central hypoventilation syndrome (CHS) is a sleep-related breathing disorder that causes ineffective breathing, apnea, or respiratory arrest during sleep. CHS can either be congenital (CCHS) or acquired (ACHS) later in life. The condition can be fatal if untreated. CCHS was once known as Ondine's curse.

Pectus carinatum, also called pigeon chest, is a malformation of the chest characterized by a protrusion of the sternum and ribs. It is distinct from the related malformation pectus excavatum.

Morquio syndrome, also known as mucopolysaccharidosis type IV (MPS IV), is a rare metabolic disorder in which the body cannot process certain types of sugar molecules called glycosaminoglycans (AKA GAGs, or mucopolysaccharides). In Morquio syndrome, the specific GAG which builds up in the body is called keratan sulfate. This birth defect, which is autosomal recessive, is a type of lysosomal storage disorder. The buildup of GAGs in different parts of the body causes symptoms in many different organ systems. In the US, the incidence rate for Morquio syndrome is estimated at between 1 in 200,000 and 1 in 300,000 live births.

Flail chest is a life-threatening medical condition that occurs when a segment of the rib cage breaks due to trauma and becomes detached from the rest of the chest wall. Two of the symptoms of flail chest are chest pain and shortness of breath.

Alström syndrome (AS), also called Alström–Hallgren syndrome, is a very rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder characterised by childhood obesity and multiple organ dysfunction. Symptoms include early-onset type 2 diabetes, cone-rod dystrophy resulting in blindness, sensorineural hearing loss and dilated cardiomyopathy. Endocrine disorders typically also occur, such as hypergonadotrophic hypogonadism and hypothyroidism, as well as acanthosis nigricans resulting from hyperinsulinemia. Developmental delay is seen in almost half of people with Alström syndrome.

Pierre Robin sequence is a congenital defect observed in humans which is characterized by facial abnormalities. The three main features are micrognathia, which causes glossoptosis, which in turn causes breathing problems due to obstruction of the upper airway. A wide, U-shaped cleft palate is commonly also present. PRS is not merely a syndrome, but rather it is a sequence—a series of specific developmental malformations which can be attributed to a single cause.

A pulmonary contusion, also known as lung contusion, is a bruise of the lung, caused by chest trauma. As a result of damage to capillaries, blood and other fluids accumulate in the lung tissue. The excess fluid interferes with gas exchange, potentially leading to inadequate oxygen levels (hypoxia). Unlike pulmonary laceration, another type of lung injury, pulmonary contusion does not involve a cut or tear of the lung tissue.
Pulmonary hygiene, formerly referred to as pulmonary toilet, is a set of methods used to clear mucus and secretions from the airways. The word pulmonary refers to the lungs. The word toilet, related to the French toilette, refers to body care and hygiene; this root is used in words such as toiletry that also relate to cleansing.
Central sleep apnea (CSA) or central sleep apnea syndrome (CSAS) is a sleep-related disorder in which the effort to breathe is diminished or absent, typically for 10 to 30 seconds either intermittently or in cycles, and is usually associated with a reduction in blood oxygen saturation. CSA is usually due to an instability in the body's feedback mechanisms that control respiration. Central sleep apnea can also be an indicator of Arnold–Chiari malformation.
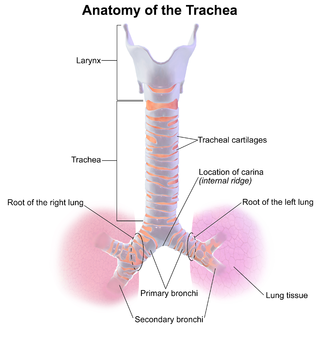
Tracheobronchomalacia (TBM) is a condition characterized by flaccidity of the tracheal support cartilage which leads to tracheal collapse. This condition can also affect the bronchi. There are two forms of this condition: primary TBM and secondary TBM. Primary TBM is congenital and starts as early as birth. It is mainly linked to genetic causes. Secondary TBM is acquired and starts in adulthood. It is mainly developed after an accident or chronic inflammation.
Chest pain in children is the pain felt in the chest by infants, children and adolescents. In most cases the pain is not associated with the heart. It is primarily identified by the observance or report of pain by the infant, child or adolescent by reports of distress by parents or caregivers. Chest pain is not uncommon in children. Many children are seen in ambulatory clinics, emergency departments and hospitals and cardiology clinics. Most often there is a benign cause for the pain for most children. Some have conditions that are serious and possibly life-threatening. Chest pain in pediatric patients requires careful physical examination and a detailed history that would indicate the possibility of a serious cause. Studies of pediatric chest pain are sparse. It has been difficult to create evidence-based guidelines for evaluation.

Slipping rib syndrome (SRS) is a condition in which the interchondral ligaments are weakened or disrupted and have increased laxity, causing the costal cartilage tips to subluxate. This results in pain or discomfort due to pinched or irritated intercostal nerves, straining of the intercostal muscles, and inflammation. The condition affects the 8th, 9th, and 10th ribs, referred to as the false ribs, with the 10th rib most commonly affected.