
Erosion is the action of surface processes that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is distinct from weathering which involves no movement. Removal of rock or soil as clastic sediment is referred to as physical or mechanical erosion; this contrasts with chemical erosion, where soil or rock material is removed from an area by dissolution. Eroded sediment or solutes may be transported just a few millimetres, or for thousands of kilometres.

A glacier is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as crevasses and seracs, as it slowly flows and deforms under stresses induced by its weight. As it moves, it abrades rock and debris from its substrate to create landforms such as cirques, moraines, or fjords. Although a glacier may flow into a body of water, it forms only on land and is distinct from the much thinner sea ice and lake ice that form on the surface of bodies of water.

Landslides, also known as landslips, are several forms of mass wasting that may include a wide range of ground movements, such as rockfalls, mudflows, shallow or deep-seated slope failures and debris flows. Landslides occur in a variety of environments, characterized by either steep or gentle slope gradients, from mountain ranges to coastal cliffs or even underwater, in which case they are called submarine landslides.

A jökulhlaup is a type of glacial outburst flood. It is an Icelandic term that has been adopted in glaciological terminology in many languages. It originally referred to the well-known subglacial outburst floods from Vatnajökull, Iceland, which are triggered by geothermal heating and occasionally by a volcanic subglacial eruption, but it is now used to describe any large and abrupt release of water from a subglacial or proglacial lake/reservoir.

Downhill creep, also known as soil creep or commonly just creep, is a type of creep characterized by the slow, downward progression of rock and soil down a low grade slope; it can also refer to slow deformation of such materials as a result of prolonged pressure and stress. Creep may appear to an observer to be continuous, but it really is the sum of numerous minute, discrete movements of slope material caused by the force of gravity. Friction, being the primary force to resist gravity, is produced when one body of material slides past another offering a mechanical resistance between the two which acts to hold objects in place. As slope on a hill increases, the gravitational force that is perpendicular to the slope decreases and results in less friction between the material that could cause the slope to slide.

Glacial motion is the motion of glaciers, which can be likened to rivers of ice. It has played an important role in sculpting many landscapes. Most lakes in the world occupy basins scoured out by glaciers. Glacial motion can be fast or slow, but is typically around 25 centimetres per day (9.8 in/d).

An ice stream is a region of fast-moving ice within an ice sheet. It is a type of glacier, a body of ice that moves under its own weight. They can move upwards of 1,000 metres (3,300 ft) a year, and can be up to 50 kilometres (31 mi) in width, and hundreds of kilometers in length. They tend to be about 2 km (1.2 mi) deep at the thickest, and constitute the majority of the ice that leaves the sheet. In Antarctica, the ice streams account for approximately 90% of the sheet's mass loss per year, and approximately 50% of the mass loss in Greenland.
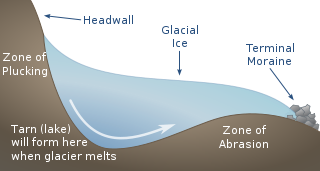
Plucking, also referred to as quarrying, is a glacial phenomenon that is responsible for the weathering and erosion of pieces of bedrock, especially large "joint blocks". This occurs in a type of glacier called a "valley glacier". As a glacier moves down a valley, friction causes the basal ice of the glacier to melt and infiltrate joints (cracks) in the bedrock. The freezing and thawing action of the ice enlarges, widens, or causes further cracks in the bedrock as it changes volume across the ice/water phase transition, gradually loosening the rock between the joints. This produces large pieces of rock called joint blocks. Eventually these joint blocks come loose and become trapped in the glacier.

Meltwater is water released by the melting of snow or ice, including glacial ice, tabular icebergs and ice shelves over oceans. Meltwater is often found during early spring when snow packs and frozen rivers melt with rising temperatures, and in the ablation zone of glaciers where the rate of snow cover is reducing. Meltwater can be produced during volcanic eruptions, in a similar way in which the more dangerous lahars form. It can also be produced by the heat generated by the flow itself.
A subaqueous fan is a fan-shaped deposit formed beneath water, that is commonly related to glaciers and crater lakes.
There have been known various classifications of landslides. Broad definitions include forms of mass movement that narrower definitions exclude. For example, the McGraw-Hill Encyclopedia of Science and Technology distinguishes the following types of landslides:
Fluvioglacial landforms or glaciofluvial landforms are those that result from the associated erosion and deposition of sediments caused by glacial meltwater. Glaciers contain suspended sediment loads, much of which is initially picked up from the underlying landmass. Landforms are shaped by glacial erosion through processes such as glacial quarrying, abrasion, and meltwater. Glacial meltwater contributes to the erosion of bedrock through both mechanical and chemical processes. Fluvio-glacial processes can occur on the surface and within the glacier. The deposits that happen within the glacier are revealed after the entire glacier melts or partially retreats. Fluvio-glacial landforms and erosional surfaces include: outwash plains, kames, kame terraces, kettle holes, eskers, varves, and proglacial lakes.

An earthflow is a downslope viscous flow of fine-grained materials that have been saturated with water and moves under the pull of gravity. It is an intermediate type of mass wasting that is between downhill creep and mudflow. The types of materials that are susceptible to earthflows are clay, fine sand and silt, and fine-grained pyroclastic material.

A supraglacial lake is any pond of liquid water on the top of a glacier. Although these pools are ephemeral, they may reach kilometers in diameter and be several meters deep. They may last for months or even decades at a time, but can empty in the course of hours.

Ice sheet dynamics describe the motion within large bodies of ice such as those currently on Greenland and Antarctica. Ice motion is dominated by the movement of glaciers, whose gravity-driven activity is controlled by two main variable factors: the temperature and the strength of their bases. A number of processes alter these two factors, resulting in cyclic surges of activity interspersed with longer periods of inactivity, on both hourly and centennial time scales. Ice-sheet dynamics are of interest in modelling future sea level rise.

A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually a freshwater stream, flowing on the earth's land surface or inside caves towards another waterbody at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, sea, bay, lake, wetland, or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground or becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of water. Small rivers can be referred to by names such as creek, brook, and rivulet. There are no official definitions for the generic term river as applied to geographic features, although in some countries or communities, a stream is defined by its size. Many names for small rivers are specific to geographic location; examples are "run" in some parts of the United States, "burn" in Scotland and Northeast England, and "beck" in Northern England. Sometimes a river is defined as being larger than a creek, but not always; the language is vague.

A bedrock river is a river that has little to no alluvium mantling the bedrock over which it flows. However, most bedrock rivers are not pure forms; they are a combination of a bedrock channel and an alluvial channel. The way one can distinguish between bedrock rivers and alluvial rivers is through the extent of sediment cover.

Overdeepening is a characteristic of basins and valleys eroded by glaciers. An overdeepened valley profile is often eroded to depths which are hundreds of metres below the lowest continuous surface line along a valley or watercourse. This phenomenon is observed under modern day glaciers, in salt-water fjords and fresh-water lakes remaining after glaciers melt, as well as in tunnel valleys which are partially or totally filled with sediment. When the channel produced by a glacier is filled with debris, the subsurface geomorphic structure is found to be erosionally cut into bedrock and subsequently filled by sediments. These overdeepened cuts into bedrock structures can reach a depth of several hundred metres below the valley floor.
Subglacial streams are conduits of glacial meltwater that flow at the base of glaciers and ice caps. Meltwater from the glacial surface travels downward throughout the glacier, forming an englacial drainage system consisting of a network of passages that eventually reach the bedrock below, where they form subglacial streams. Subglacial streams form a system of tunnels and interlinked cavities and conduits, with water flowing under extreme pressures from the ice above; as a result, flow direction is determined by the pressure gradient from the ice and the topography of the bed rather than gravity. Subglacial streams form a dynamic system that is responsive to changing conditions, and the system can change significantly in response to seasonal variation in meltwater and temperature. Water from subglacial streams is routed towards the glacial terminus, where it exits the glacier. Discharge from subglacial streams can have a significant impact on local, and in some cases global, environmental and geological conditions. Sediments, nutrients, and organic matter contained in the meltwater can all influence downstream and marine conditions. Climate change may have a significant impact on subglacial stream systems, increasing the volume of meltwater entering subglacial drainage systems and influencing their hydrology.

A glacier stream is a channelized area that is formed by a glacier in which liquid water accumulates and flows. Glacial streams are also commonly referred to as "glacier stream" or/and "glacial meltwater stream". The movement of the water is influenced and directed by gravity and the melting of ice. The melting of ice forms different types of glacial streams such as supraglacial, englacial, subglacial and proglacial streams. Water enters supraglacial streams that sit at the top of the glacier via filtering through snow in the accumulation zone and forming slush pools at the FIRN zone. The water accumulates on top of the glacier in supraglacial lakes and into supraglacial stream channels. The meltwater then flows through various different streams either entering inside the glacier into englacial channels or under the glacier into subglacial channels. Finally, the water leaves the glacier through proglacial streams or lakes. Proglacial streams do not only act as the terminus point but can also receive meltwater. Glacial streams can play a significant role in energy exchange and in the transport of meltwater and sediment.















