VBScript is a deprecated Active Scripting language developed by Microsoft that is modeled on Visual Basic. It allows Microsoft Windows system administrators to generate powerful tools for managing computers without error handling and with subroutines and other advanced programming constructs. It can give the user complete control over many aspects of their computing environment.
New Technology File System (NTFS) is a proprietary journaling file system developed by Microsoft. Starting with Windows NT 3.1, it is the default file system of the Windows NT family. It superseded File Allocation Table (FAT) as the preferred filesystem on Windows and is supported in Linux and BSD as well. NTFS reading and writing support is provided using a free and open-source kernel implementation known as NTFS3 in Linux and the NTFS-3G driver in BSD. By using the convert command, Windows can convert FAT32/16/12 into NTFS without the need to rewrite all files. NTFS uses several files typically hidden from the user to store metadata about other files stored on the drive which can help improve speed and performance when reading data. Unlike FAT and High Performance File System (HPFS), NTFS supports access control lists (ACLs), filesystem encryption, transparent compression, sparse files and file system journaling. NTFS also supports shadow copy to allow backups of a system while it is running, but the functionality of the shadow copies varies between different versions of Windows.
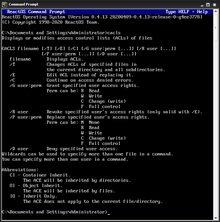
In computer security, an access-control list (ACL) is a list of permissions associated with a system resource. An ACL specifies which users or system processes are granted access to resources, as well as what operations are allowed on given resources. Each entry in a typical ACL specifies a subject and an operation. For instance,
Cabinet is an archive-file format for Microsoft Windows that supports lossless data compression and embedded digital certificates used for maintaining archive integrity. Cabinet files have .cab filename extensions and are recognized by their first four bytes MSCF. Cabinet files were known originally as Diamond files.
The Windows Registry is a hierarchical database that stores low-level settings for the Microsoft Windows operating system and for applications that opt to use the registry. The kernel, device drivers, services, Security Accounts Manager, and user interfaces can all use the registry. The registry also allows access to counters for profiling system performance.

System Restore is a feature in Microsoft Windows that allows the user to revert their computer's state to that of a previous point in time, which can be used to recover from system malfunctions or other problems. First included in Windows Me, it has been included in all following desktop versions of Windows released since, excluding Windows Server. In Windows 10, System Restore is turned off by default and must be enabled by users in order to function. This does not affect personal files such as documents, music, pictures, and videos.

Microsoft ScanDisk is a diagnostic utility program included in MS-DOS and Windows 9x. It checks and repairs file systems errors on a disk drive, while the system starts.

File Manager is a file manager program bundled with releases of OS/2 and Microsoft Windows between 1988 and 1999 and available from 6 April 2018 as an optional download for all modern releases of Windows, including Windows 10.
System File Checker (SFC) is a utility in Microsoft Windows that allows users to scan for and restore corrupted Windows system files.
As the next version of Windows NT after Windows 2000, as well as the successor to Windows Me, Windows XP introduced many new features but it also removed some others.

Microsoft Drive Optimizer is a utility in Microsoft Windows designed to increase data access speed by rearranging files stored on a disk to occupy contiguous storage locations, a technique called defragmentation. Microsoft Drive Optimizer was first officially shipped with Windows XP.
Robocopy is a command-line file transfer utility for Microsoft Windows. Robocopy is functionally more comprehensive than the COPY command and XCOPY, but replaces neither. Created by Kevin Allen and first released as part of the Windows NT 4.0 Resource Kit, it has been a standard feature of Windows since Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008.
The NTFS file system defines various ways to redirect files and folders, e.g., to make a file point to another file or its contents without making a copy of it. The object being pointed to is called the target. Such file is called a hard or symbolic link depending on a way it's stored on the filesystem.
Windows Support Tools is a suite of management, administration and troubleshooting tools for Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 and Windows Server 2003 R2 from Microsoft.
Windows Vista contains a range of new technologies and features that are intended to help network administrators and power users better manage their systems. Notable changes include a complete replacement of both the Windows Setup and the Windows startup processes, completely rewritten deployment mechanisms, new diagnostic and health monitoring tools such as random access memory diagnostic program, support for per-application Remote Desktop sessions, a completely new Task Scheduler, and a range of new Group Policy settings covering many of the features new to Windows Vista. Subsystem for UNIX Applications, which provides a POSIX-compatible environment is also introduced.
Windows Resource Protection is a feature first introduced in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008. It is available in all subsequent Windows operating systems, and replaces Windows File Protection. Windows Resource Protection prevents the replacement of critical system files, registry keys and folders. Protecting these resources prevents system crashes. The way it protects resources differs entirely from the method used by Windows File Protection.
Security descriptors are data structures of security information for securable Windows objects, that is objects that can be identified by a unique name. Security descriptors can be associated with any named objects, including files, folders, shares, registry keys, processes, threads, named pipes, services, job objects and other resources.
SetACL is a freeware utility for manipulating security descriptors on Microsoft Windows. It used to be available under the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) as a command-line utility and as an ActiveX component, but changed to a freeware license in version 3.0.0.0.
In computing, convert is a command-line utility included in the Windows NT operating system line. It is used to convert volumes using the FAT file systems to NTFS.