Antioxidants are compounds that inhibit oxidation, a chemical reaction that can produce free radicals. Autoxidation leads to degradation of organic compounds, including living matter. Antioxidants are frequently added to industrial products, such as polymers, fuels, and lubricants, to extend their usable lifetimes. Food are also treated with antioxidants to forestall spoilage, in particular the rancidification of oils and fats. In cells, antioxidants such as glutathione, mycothiol or bacillithiol, and enzyme systems like superoxide dismutase, can prevent damage from oxidative stress.
Drug metabolism is the metabolic breakdown of drugs by living organisms, usually through specialized enzymatic systems. More generally, xenobiotic metabolism is the set of metabolic pathways that modify the chemical structure of xenobiotics, which are compounds foreign to an organism's normal biochemistry, such as any drug or poison. These pathways are a form of biotransformation present in all major groups of organisms and are considered to be of ancient origin. These reactions often act to detoxify poisonous compounds. The study of drug metabolism is called pharmacokinetics.

Punicalagin (Pyuni-cala-jen) is an ellagitannin, a type of phenolic compound. It is found as alpha and beta isomers in pomegranates, Terminalia catappa, Terminalia myriocarpa, and in Combretum molle, the velvet bushwillow, a plant species found in South Africa. These three genera are all Myrtales and the last two are both Combretaceae.

Terminalia chebula, commonly known as black- or chebulic myrobalan, is a species of Terminalia, native to South Asia from India and Nepal east to southwest China (Yunnan), and south to Sri Lanka, Malaysia, and Vietnam.
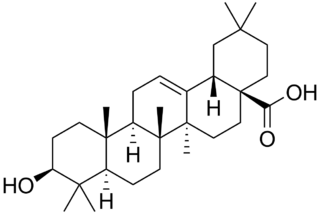
Oleanolic acid or oleanic acid is a naturally occurring pentacyclic triterpenoid related to betulinic acid. It is widely distributed in food and plants where it exists as a free acid or as an aglycone of triterpenoid saponins.

Cornus officinalis, the Japanese cornel or Japanese cornelian cherry, is a species of flowering plant in the dogwood family Cornaceae. Despite its name, it is native to China and Korea as well as Japan. It is not to be confused with C. mas, which is also known as the Cornelian cherry. It is not closely related to the true cherries of the genus Prunus.

Chebulinic acid is an ellagitannin found in the seeds of Euphoria longana, in the fruits of Terminalia chebula or in the leaves of T. macroptera.
A hydrolysable tannin or pyrogallol-type tannin is a type of tannin that, on heating with hydrochloric or sulfuric acids, yields gallic or ellagic acids.

Quercus infectoria or the Aleppo oak is a species of oak well known for producing galls that have been traditionally used for centuries in Asia medicinally while also used in softening leather and in making black dye and ink.
Tergallic acids are trimers of gallic acid, often found naturally in the form of glycosides. Tergallic acid O- or C-glucosides that can be found in acorns of several Quercus (oak) species. The dehydrated tergallic acid C-glucoside and tergallic acid O-glucoside can be characterised in the acorns of Quercus macrocarpa. Dehydrated tergallic-C-glucoside can be found in the cork from Quercus suber.
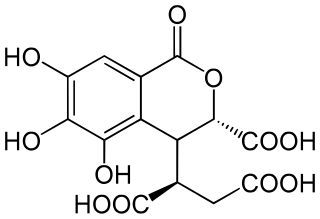
Chebulic acid is a phenolic compound isolated from the ripe fruits of Terminalia chebula.

Punicalin is an ellagitannin. It can be found in Punica granatum (pomegranate) or in the leaves of Terminalia catappa, a plant used to treat dermatitis and hepatitis. It is also reported in Combretum glutinosum, all three species being Myrtales, the two last being Combretaceae.

The pomegranate ellagitannins, which include punicalagin isomers, are ellagitannins found in the sarcotestas, rind (peel), bark or heartwood of pomegranates.
Maximilian Nierenstein was a professor of biochemistry at the University of Bristol.
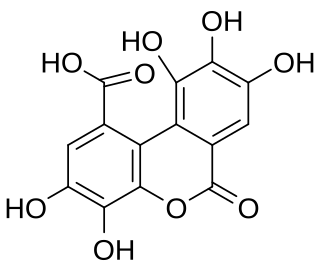
Luteic acid is a natural phenol found in numerous fruits. It is a monolactonized tergalloyl group. Maximilian Nierenstein showed in 1945 that luteic acid was a molecule present in the myrobalanitannin, a tannin found in the fruit of Terminalia chebula and is an intermediary compound in the synthesis of ellagic acid. It can form from hexahydroxydiphenic acid. It is also present in the structure of the tannins alnusiin and bicornin.

Geraniin is a dehydroellagitannin found in geraniums. It is found for instance in Geranium thunbergii, which is one of the most popular folk medicines and also an official antidiarrheic drug in Japan. It can also be found in the rind of Nephelium lappaceum (rambutan).

Cucurbitacin E is a biochemical compound from the family of cucurbitacins. These are found in plants which are member of the family Cucurbitaceae, most of them coming from traditional Chinese medicinal plants, but also in other plants such as pumpkins and gourds.

Tellimagrandin I is an ellagitannin found in plants, such as Cornus canadensis, Eucalyptus globulus, Melaleuca styphelioides, Rosa rugosa, and walnut. It is composed of two galloyl and one hexahydroxydiphenyl groups bound to a glucose residue. It differs from Tellimagrandin II only by a hydroxyl group instead of a third galloyl group. It is also structurally similar to punigluconin and pedunculagin, two more ellagitannin monomers.

Chuquiraga spinosa, common name huamanpinta in Spanish, is a species of flowering plant of the family Asteraceae. Native to Perú and Bolivia, it is used in traditional medicine for its anti-inflammatory properties.














