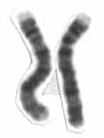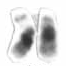
Chromosome 21 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. Chromosome 21 is both the smallest human autosome and chromosome, with 45 million base pairs representing about 1.5 percent of the total DNA in cells. Most people have two copies of chromosome 21, while those with three copies of chromosome 21 have Down syndrome, also called "trisomy 21".

Chromosome 1 is the designation for the largest human chromosome. Humans have two copies of chromosome 1, as they do with all of the autosomes, which are the non-sex chromosomes. Chromosome 1 spans about 249 million nucleotide base pairs, which are the basic units of information for DNA. It represents about 8% of the total DNA in human cells.
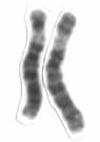
Chromosome 6 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 6 spans more than 172 million base pairs and represents between 5.5 and 6% of the total DNA in cells. It contains the major histocompatibility complex, which contains over 100 genes related to the immune response, and plays a vital role in organ transplantation.
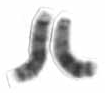
Chromosome 13 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 13 spans about 113 million base pairs and represents between 3.5 and 4% of the total DNA in cells.
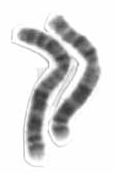
Chromosome 2 is one of the twenty-three pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 2 is the second-largest human chromosome, spanning more than 242 million base pairs and representing almost eight percent of the total DNA in human cells.
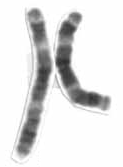
Chromosome 3 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 3 spans 201 million base pairs and represents about 6.5 percent of the total DNA in cells.
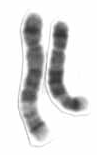
Chromosome 5 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 5 spans about 182 million base pairs and represents almost 6% of the total DNA in cells. Chromosome 5 is the 5th largest human chromosome, yet has one of the lowest gene densities. This is partially explained by numerous gene-poor regions that display a remarkable degree of non-coding and syntenic conservation with non-mammalian vertebrates, suggesting they are functionally constrained.
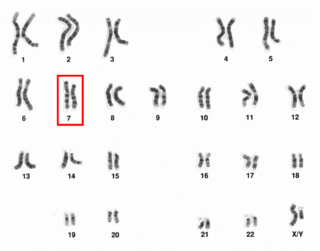
Chromosome 7 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans, who normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 7 spans about 160 million base pairs and represents between 5 and 5.5 percent of the total DNA in cells.
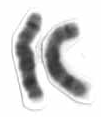
Chromosome 8 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 8 spans about 146 million base pairs and represents between 4.5 and 5.0% of the total DNA in cells.
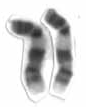
Chromosome 9 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. Humans normally have two copies of this chromosome, as they normally do with all chromosomes. Chromosome 9 spans about 150 million base pairs of nucleic acids and represents between 4.0 and 4.5% of the total DNA in cells.

Chromosome 10 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 10 spans about 134 million base pairs and represents between 4 and 4.5 percent of the total DNA in cells.
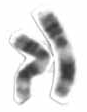
Chromosome 11 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. Humans normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 11 spans about 135 million base pairs and represents between 4 and 4.5 percent of the total DNA in cells. The shorter arm is termed 11p while the longer arm is 11q. At about 21.5 genes per megabase, chromosome 11 is one of the most gene-rich, and disease-rich, chromosomes in the human genome.
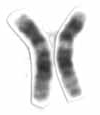
Chromosome 12 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 12 spans about 133 million base pairs and represents between 4 and 4.5 percent of the total DNA in cells.
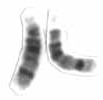
Chromosome 14 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 14 spans about 101 million base pairs and represents between 3 and 3.5% of the total DNA in cells.

Chromosome 15 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 15 spans about 99.7 million base pairs and represents between 3% and 3.5% of the total DNA in cells. Chromosome 15 is an acrocentric chromosome, with a very small short arm, which contains few protein coding genes among its 19 million base pairs. It has a larger long arm that is gene rich, spanning about 83 million base pairs.
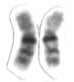
Chromosome 16 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 16 spans about 96 million base pairs and represents just under 3% of the total DNA in cells.
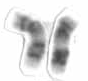
Chromosome 17 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 17 spans more than 84 million base pairs and represents between 2.5 and 3% of the total DNA in cells.

Chromosome 18 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 18 spans about 80 million base pairs and represents about 2.5 percent of the total DNA in cells.

Chromosome 19 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 19 spans more than 61.7 million base pairs, the building material of DNA. It is considered the most gene-rich chromosome containing roughly 1,500 genes, despite accounting for only 2 percent of the human genome.

Chromosome 20 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. Chromosome 20 spans around 66 million base pairs and represents between 2 and 2.5 percent of the total DNA in cells. Chromosome 20 was fully sequenced in 2001 and was reported to contain over 59 million base pairs. Since then, due to sequencing improvements and fixes, the length of chromosome 20 has been updated to just over 66 million base pairs.