Haemophilia, or hemophilia, is a mostly inherited genetic disorder that impairs the body's ability to make blood clots, a process needed to stop bleeding. This results in people bleeding for a longer time after an injury, easy bruising, and an increased risk of bleeding inside joints or the brain. Those with a mild case of the disease may have symptoms only after an accident or during surgery. Bleeding into a joint can result in permanent damage while bleeding in the brain can result in long term headaches, seizures, or a decreased level of consciousness.
Haemophilia A is a blood clotting disorder caused by a genetic deficiency in clotting factor VIII, thereby resulting in significant susceptibility to bleeding, both internally and externally. This condition occurs almost exclusively in males born to carrier mothers due to X-linked recessive inheritance. Nevertheless, rare isolated cases do emerge from de novo (spontaneous) mutations.

Haemophilia B, also spelled hemophilia B, is a blood clotting disorder causing easy bruising and bleeding due to an inherited mutation of the gene for factor IX, and resulting in a deficiency of factor IX. It is less common than factor VIII deficiency.

Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot. It potentially results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair. The mechanism of coagulation involves activation, adhesion and aggregation of platelets, as well as deposition and maturation of fibrin.

Von Willebrand disease (VWD) is the most common hereditary blood-clotting disorder in humans. An acquired form can sometimes result from other medical conditions. It arises from a deficiency in the quality or quantity of von Willebrand factor (VWF), a multimeric protein that is required for platelet adhesion. It is known to affect several breeds of dogs as well as humans. The three forms of VWD are hereditary, acquired, and pseudo or platelet type. The three types of hereditary VWD are VWD type 1, VWD type 2, and VWD type 3. Type 2 contains various subtypes. Platelet type VWD is also an inherited condition.

The prothrombin time (PT) – along with its derived measures of prothrombin ratio (PR) and international normalized ratio (INR) – is an assay for evaluating the extrinsic pathway and common pathway of coagulation. This blood test is also called protime INR and PT/INR. They are used to determine the clotting tendency of blood, in such things as the measure of warfarin dosage, liver damage, and vitamin K status. PT measures the following coagulation factors: I (fibrinogen), II (prothrombin), V (proaccelerin), VII (proconvertin), and X.

Von Willebrand factor (VWF) is a blood glycoprotein that promotes hemostasis, specifically, platelet adhesion. It is deficient and/or defective in von Willebrand disease and is involved in many other diseases, including thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, Heyde's syndrome, and possibly hemolytic–uremic syndrome. Increased plasma levels in many cardiovascular, neoplastic, metabolic, and connective tissue diseases are presumed to arise from adverse changes to the endothelium, and may predict an increased risk of thrombosis.

In medicine (hematology), bleeding diathesis is an unusual susceptibility to bleed (hemorrhage) mostly due to hypocoagulability, in turn caused by a coagulopathy. Therefore, this may result in the reduction of platelets being produced and leads to excessive bleeding. Several types of coagulopathy are distinguished, ranging from mild to lethal. Coagulopathy can be caused by thinning of the skin, such that the skin is weakened and is bruised easily and frequently without any trauma or injury to the body. Also, coagulopathy can be contributed by impaired wound healing or impaired clot formation.

The partial thromboplastin time (PTT), also known as the activated partial thromboplastin time, is a blood test that characterizes coagulation of the blood. A historical name for this measure is the kaolin-cephalin clotting time (KCCT), reflecting kaolin and cephalin as materials historically used in the test. Apart from detecting abnormalities in blood clotting, partial thromboplastin time is also used to monitor the treatment effect of heparin, a widely prescribed drug that reduces blood's tendency to clot.
Mixing studies are tests performed on blood plasma of patients or test subjects to distinguish factor deficiencies from factor inhibitors, such as lupus anticoagulant, or specific factor inhibitors, such as antibodies directed against factor VIII. The basic purpose of these tests is to determine the cause of prolongation of Prothrombin Time (PT), Partial Thromboplastin Time, or sometimes of thrombin time (TT). Mixing studies take advantage of the fact that factor levels that are 50 percent of normal should give a normal Prothrombin time (PT) or Partial thromboplastin time (PTT) result. Factor deficient plasmas are used in mixing studies. Plasma with known factor deficiencies are commercially available but are very expensive, so they are often prepared in the laboratory and can then be used for mixing experiments.
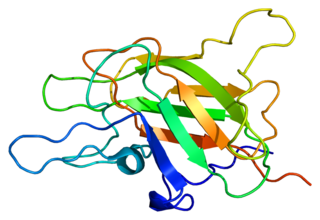
Factor V is a protein of the coagulation system, rarely referred to as proaccelerin or labile factor. In contrast to most other coagulation factors, it is not enzymatically active but functions as a cofactor. Deficiency leads to predisposition for hemorrhage, while some mutations predispose for thrombosis.

Factor XI or plasma thromboplastin antecedent is the zymogen form of factor XIa, one of the enzymes of the coagulation cascade. Like many other coagulation factors, it is a serine protease. In humans, Factor XI is encoded by the F11 gene.

Coagulopathy is a condition in which the blood's ability to coagulate is impaired. This condition can cause a tendency toward prolonged or excessive bleeding, which may occur spontaneously or following an injury or medical and dental procedures.
Congenital afibrinogenemia is a rare, genetically inherited blood fibrinogen disorder in which the blood does not clot normally due to the lack of fibrinogen, a blood protein necessary for coagulation. This disorder is autosomal recessive, meaning that two unaffected parents can have a child with the disorder. The lack of fibrinogen expresses itself with excessive and, at times, uncontrollable bleeding.

Factor VII deficiency is a bleeding disorder characterized by a lack in the production of Factor VII (FVII) (proconvertin), a protein that causes blood to clot in the coagulation cascade. After a trauma factor VII initiates the process of coagulation in conjunction with tissue factor in the extrinsic pathway.
The fibrinolysis system is responsible for removing blood clots. Hyperfibrinolysis describes a situation with markedly enhanced fibrinolytic activity, resulting in increased, sometimes catastrophic bleeding. Hyperfibrinolysis can be caused by acquired or congenital reasons. Among the congenital conditions for hyperfibrinolysis, deficiency of alpha-2-antiplasmin or plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 (PAI-1) are very rare. The affected individuals show a hemophilia-like bleeding phenotype. Acquired hyperfibrinolysis is found in liver disease, in patients with severe trauma, during major surgical procedures, and other conditions. A special situation with temporarily enhanced fibrinolysis is thrombolytic therapy with drugs which activate plasminogen, e.g. for use in acute ischemic events or in patients with stroke. In patients with severe trauma, hyperfibrinolysis is associated with poor outcome. Moreover, hyperfibrinolysis may be associated with blood brain barrier impairment, a plasmin-dependent effect due to an increased generation of bradykinin.
Moroctocog alfa is a recombinant antihemophilic factor genetically engineered from Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell line. Chemically it is a glycoprotein. It is manufactured by Genetics Institute, Inc. and used to control and prevent hemorrhagic bleeding and prophylaxis associated with surgery or to reduce the number of spontaneous bleeding episodes in patients with hemophilia A. It is partially a recombinant coagulation factor VIII since it has an amino acid sequence which compares to the 90 + 80 kDa form of factor VIII (BDDrFVIII). It also has posttranslational modifications which are similar to those of the plasma-derived molecule. It can not prevent hemorrhagic bleeding associated with von Willebrand's disease since it is not a von Willebrand factor.
Factor XII deficiency is a deficiency in the production of factor XII (FXII), a plasma glycoprotein and clotting factor that participates in the coagulation cascade and activates factor XI. FXII appears to be not essential for blood clotting, as individuals with this condition are usually asymptomatic and form blood clots in vivo. FXII deficiency tends to be identified during presurgical laboratory screening for bleeding disorders.
Congenital hypofibrinogenemia is a rare disorder in which one of the three genes responsible for producing fibrinogen, a critical blood clotting factor, is unable to make a functional fibrinogen glycoprotein because of an inherited mutation. In consequence, liver cells, the normal site of fibrinogen production, make small amounts of this critical coagulation protein, blood levels of fibrinogen are low, and individuals with the disorder may develop a coagulopathy, i.e. a diathesis or propensity to experience episodes of abnormal bleeding. However, individuals with congenital hypofibrinogenemia may also have episodes of abnormal blood clot formation, i.e. thrombosis. This seemingly paradoxical propensity to develop thrombosis in a disorder causing a decrease in a critical protein for blood clotting may be due to the function of fibrin to promote the lysis or disintegration of blood clots. Lower levels of fibrin may reduce the lysis of early fibrin strand depositions and thereby allow these depositions to develop into clots.
Acquired haemophilia A (AHA) is a rare but potentially life-threatening bleeding disorder characterized by autoantibodies directed against coagulation factor VIII. These autoantibodies constitute the most common spontaneous inhibitor to any coagulation factor and may induce spontaneous bleeding in patients with no previous history of a bleeding disorder.