
A pump is a device that moves fluids, or sometimes slurries, by mechanical action, typically converted from electrical energy into hydraulic energy.

A valve is a device or natural object that regulates, directs or controls the flow of a fluid by opening, closing, or partially obstructing various passageways. Valves are technically fittings, but are usually discussed as a separate category. In an open valve, fluid flows in a direction from higher pressure to lower pressure. The word is derived from the Latin valva, the moving part of a door, in turn from volvere, to turn, roll.

Aqua-Lung was the first open-circuit, self-contained underwater breathing apparatus to achieve worldwide popularity and commercial success. This class of equipment is now commonly referred to as a twin-hose diving regulator, or demand valve. The Aqua-Lung was invented in France during the winter of 1942–1943 by two Frenchmen: engineer Émile Gagnan and Jacques Cousteau, who was a Naval Lieutenant. It allowed Cousteau and Gagnan to film and explore underwater more easily.
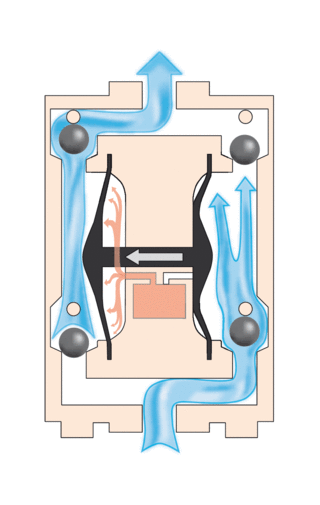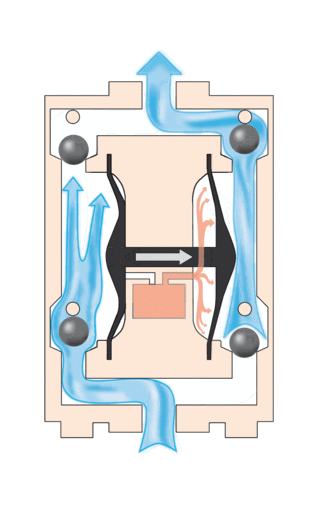
A diaphragm pump is a positive displacement pump that uses a combination of the reciprocating action of a rubber, thermoplastic or teflon diaphragm and suitable valves on either side of the diaphragm (check valve, butterfly valves, flap valves, or any other form of shut-off valves) to pump a fluid.

A flush toilet is a toilet that disposes of human waste by using the force of water to flush it through a drainpipe to another location for treatment, either nearby or at a communal facility, thus maintaining a separation between humans and their waste. Flush toilets can be designed for sitting or squatting, in the case of squat toilets. Most modern sewage treatment systems are also designed to process specially designed toilet paper. The opposite of a flush toilet is a dry toilet, which uses no water for flushing.

A water gun is a type of toy gun designed to shoot jets of water. Similar to water balloons, the primary purpose of the toy is to soak another person in a recreational game such as water fight.

A check valve, non-return valve, reflux valve, retention valve, foot valve, or one-way valve is a valve that normally allows fluid to flow through it in only one direction.
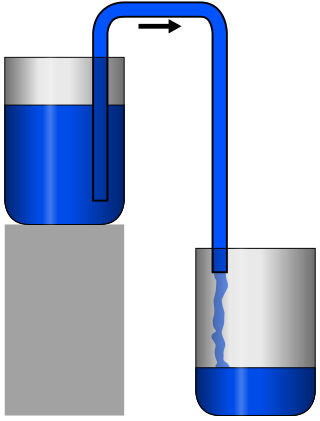
A siphon is any of a wide variety of devices that involve the flow of liquids through tubes. In a narrower sense, the word refers particularly to a tube in an inverted "U" shape, which causes a liquid to flow upward, above the surface of a reservoir, with no pump, but powered by the fall of the liquid as it flows down the tube under the pull of gravity, then discharging at a level lower than the surface of the reservoir from which it came.

A diving regulator is a pressure regulator that controls the pressure of breathing gas for diving. The most commonly recognised application is to reduce pressurized breathing gas to ambient pressure and deliver it to the diver, but there are also other types of gas pressure regulator used for diving applications. The gas may be air or one of a variety of specially blended breathing gases. The gas may be supplied from a scuba cylinder carried by the diver, in which case it is called a scuba regulator, or via a hose from a compressor or high-pressure storage cylinders at the surface in surface-supplied diving. A gas pressure regulator has one or more valves in series which reduce pressure from the source, and use the downstream pressure as feedback to control the delivered pressure, or the upstream pressure as feedback to prevent excessive flow rates, lowering the pressure at each stage.

Main components found on a typical steam locomotive include:
A ballcock is a mechanism or machine for filling water tanks, such as those found in flush toilets, while avoiding overflow and backflow. The modern ballcock was invented by José Antonio de Alzate y Ramírez, a Mexican priest and scientist, who described the device in 1790 in the Gaceta de Literatura Méxicana. The ballcock device was patented in 1797 for use in steam engines by Edmund Cartwright.

A solenoid valve is an electromechanically operated valve.

An irrigation sprinkler is a device used to irrigate (water) agricultural crops, lawns, landscapes, golf courses, and other areas. They are also used for cooling and for the control of airborne dust. Sprinkler irrigation is the method of applying water in a controlled manner in way similar to rainfall. The water is distributed through a network that may consist of pumps, valves, pipes, and sprinklers.
In internal combustion engines with carburetors, a choke valve or choke modifies the air pressure in the intake manifold, thereby altering the air–fuel ratio entering the engine. Choke valves are generally used in naturally aspirated engines to supply a richer fuel mixture when starting the engine. Most choke valves in engines are butterfly valves mounted upstream of the carburetor jet to produce a higher partial vacuum, which increases the fuel draw.
Sloan Valve Company is a privately owned American company specializing in plumbing valves and fixtures.
A pressure carburetor is a type of fuel metering system manufactured by the Bendix Corporation for piston aircraft engines, starting in the 1940s. It is recognized as an early type of throttle-body fuel injection and was developed to prevent fuel starvation during inverted flight.

Of the three types of carburetors used on large, high-performance aircraft engines manufactured in the United States during World War II, the Bendix-Stromberg pressure carburetor was the one most commonly found. The other two carburetor types were manufactured by Chandler Groves and Chandler Evans Control Systems (CECO). Both of these types of carburetors had a relatively large number of internal parts, and in the case of the Holley Carburetor, there were complications in its "variable venturi" design.

A booster pump is a machine which increases the pressure of a fluid. It may be used with liquids or gases, and the construction details vary depending on the fluid. A gas booster is similar to a gas compressor, but generally a simpler mechanism which often has only a single stage of compression, and is used to increase pressure of a gas already above ambient pressure. Two-stage boosters are also made. Boosters may be used for increasing gas pressure, transferring high pressure gas, charging gas cylinders and scavenging.
A toilet plume is the dispersal of microscopic particles as a result of flushing a toilet. Normal use of a toilet by healthy individuals is considered unlikely to be a major health risk. However this dynamic changes if an individual is fighting an illness and currently shedding out a virulent pathogen in their urine, feces or vomitus. There is indirect evidence that specific pathogens such as norovirus or SARS coronavirus could potentially be spread by toilet aerosols, but as of 2015, no direct experimental studies had clearly demonstrated or refuted actual disease transmission from toilet aerosols. It has been hypothesized that dispersal of pathogens may be reduced by closing the toilet lid before flushing, and by using toilets with lower flush energy.
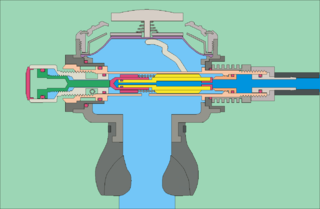
The mechanism of diving regulators is the arrangement of components and function of gas pressure regulators used in the systems which supply breathing gases for underwater diving. Both free-flow and demand regulators use mechanical feedback of the downstream pressure to control the opening of a valve which controls gas flow from the upstream, high-pressure side, to the downstream, low-pressure side of each stage. Flow capacity must be sufficient to allow the downstream pressure to be maintained at maximum demand, and sensitivity must be appropriate to deliver maximum required flow rate with a small variation in downstream pressure, and for a large variation in supply pressure, without instability of flow. Open circuit scuba regulators must also deliver against a variable ambient pressure. They must be robust and reliable, as they are life-support equipment which must function in the relatively hostile seawater environment, and the human interface must be comfortable over periods of several hours.















