This article needs additional citations for verification .(January 2024) |
A pressure-balanced valve provides water at nearly constant temperature to a shower or bathtub, despite pressure fluctuations in either the hot or cold supply lines.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(January 2024) |
A pressure-balanced valve provides water at nearly constant temperature to a shower or bathtub, despite pressure fluctuations in either the hot or cold supply lines.
If, for example, someone flushes a toilet while the shower is in use, the fixture suddenly draws a significant amount of cold water from the common supply line, causing a pressure drop. In the absence of a compensating mechanism, the relatively higher pressure in the hot water supply line will cause the shower temperature to rise just as suddenly, possibly reaching an uncomfortable or even dangerous level. Conversely, if someone opens a hot water faucet elsewhere, the relatively higher pressure in the cold water supply line will cause the shower temperature to drop suddenly. This is described in US patent 3674048. [1]
The pressure-balanced shower valve compensates for changes in water pressure. It has a diaphragm or piston inside that reacts to relative changes in either hot or cold water pressure to maintain balanced pressure. As water pressure drops on one supply line, the valve reduces the pressure in the other supply line to match. A side effect of this is that the pressure and flow at the shower head or tub spigot will drop twice as much as if only one supply line had been affected, but without a large temperature change. There are ball bearings in the valves to regulate forces.
The use of pressure-balanced valves can prevent scalding injuries, in particular to the elderly, the infirm, to children and infants. Based on that, some municipalities require by building codes to have it installed.

A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be transformed, by a connecting rod and crank, into rotational force for work. The term "steam engine" is most commonly applied to reciprocating engines as just described, although some authorities have also referred to the steam turbine and devices such as Hero's aeolipile as "steam engines". The essential feature of steam engines is that they are external combustion engines, where the working fluid is separated from the combustion products. The ideal thermodynamic cycle used to analyze this process is called the Rankine cycle. In general usage, the term steam engine can refer to either complete steam plants, such as railway steam locomotives and portable engines, or may refer to the piston or turbine machinery alone, as in the beam engine and stationary steam engine.

A valve is a device or natural object that regulates, directs or controls the flow of a fluid by opening, closing, or partially obstructing various passageways. Valves are technically fittings, but are usually discussed as a separate category. In an open valve, fluid flows in a direction from higher pressure to lower pressure. The word is derived from the Latin valva, the moving part of a door, in turn from volvere, to turn, roll.

Pressure cooking is the process of cooking food with the use of high pressure steam and water or a water-based liquid, inside a sealed vessel called a pressure cooker; the high pressure limits boiling and creates higher temperatures not possible at lower pressures which allow food to be cooked much faster than at normal pressure.

A thermostat is a regulating device component which senses the temperature of a physical system and performs actions so that the system's temperature is maintained near a desired setpoint.

Ice diving is a type of penetration diving where the dive takes place under ice. Because diving under ice places the diver in an overhead environment typically with only a single entry/exit point, it requires special procedures and equipment. Ice diving is done for purposes of recreation, scientific research, public safety and other professional or commercial reasons.

A safety valve is a valve that acts as a fail-safe. An example of safety valve is a pressure relief valve (PRV), which automatically releases a substance from a boiler, pressure vessel, or other system, when the pressure or temperature exceeds preset limits. Pilot-operated relief valves are a specialized type of pressure safety valve. A leak tight, lower cost, single emergency use option would be a rupture disk.

A diving regulator or underwater diving regulator is a pressure regulator that controls the pressure of breathing gas for underwater diving. The most commonly recognised application is to reduce pressurized breathing gas to ambient pressure and deliver it to the diver, but there are also other types of gas pressure regulator used for diving applications. The gas may be air or one of a variety of specially blended breathing gases. The gas may be supplied from a scuba cylinder carried by the diver, in which case it is called a scuba regulator, or via a hose from a compressor or high-pressure storage cylinders at the surface in surface-supplied diving. A gas pressure regulator has one or more valves in series which reduce pressure from the source, and use the downstream pressure as feedback to control the delivered pressure, or the upstream pressure as feedback to prevent excessive flow rates, lowering the pressure at each stage.

A diving air compressor is a breathing air compressor that can provide breathing air directly to a surface-supplied diver, or fill diving cylinders with high-pressure air pure enough to be used as a hyperbaric breathing gas. A low pressure diving air compressor usually has a delivery pressure of up to 30 bar, which is regulated to suit the depth of the dive. A high pressure diving compressor has a delivery pressure which is usually over 150 bar, and is commonly between 200 and 300 bar. The pressure is limited by an overpressure valve which may be adjustable.

A tap is a valve controlling the release of a fluid.

Water heating is a heat transfer process that uses an energy source to heat water above its initial temperature. Typical domestic uses of hot water include cooking, cleaning, bathing, and space heating. In industry, hot water and water heated to steam have many uses.

Icyball is a name given to two early refrigerators, one made by Australian Sir Edward Hallstrom in 1923, and the other design patented by David Forbes Keith of Toronto, and manufactured by American Powel Crosley Jr., who bought the rights to the device. Both devices are unusual in design in that they did not require the use of electricity for cooling. They can run for a day on a cup of kerosene, allowing rural users lacking electricity the benefits of refrigeration.
Moen is an American product line of faucets and other fixtures started by inventor Alfred M. Moen that is now part of the Fortune Brands Innovations company. The Moen subsidiary is headquartered in North Olmsted, Ohio. Moen was originally part of Ravenna Metal Products of Seattle, Washington.
Economizers, or economisers (UK), are mechanical devices intended to reduce energy consumption, or to perform useful function such as preheating a fluid. The term economizer is used for other purposes as well. Boiler, power plant, heating, refrigeration, ventilating, and air conditioning (HVAC) uses are discussed in this article. In simple terms, an economizer is a heat exchanger.
A regenerative heat exchanger, or more commonly a regenerator, is a type of heat exchanger where heat from the hot fluid is intermittently stored in a thermal storage medium before it is transferred to the cold fluid. To accomplish this the hot fluid is brought into contact with the heat storage medium, then the fluid is displaced with the cold fluid, which absorbs the heat.

A thermostatic mixing valve (TMV) is a valve that blends hot water with cold water to ensure constant, safe shower and bath outlet temperatures to prevent scalding.
Automatic balancing valves are utilised in central heating and cooling systems that rely on flow of water through the system. They use the latest flow technology to ensure that the design flow rate is achieved at all times irrespective of any pressure changes within the system.

Tankless water heaters — also called instantaneous, continuous flow, inline, flash, on-demand, or instant-on water heaters — are water heaters that instantly heat water as it flows through the device, and do not retain any water internally except for what is in the heat exchanger coil unless the unit is equipped with an internal buffer tank. Copper heat exchangers are preferred in these units because of their high thermal conductivity and ease of fabrication. However, copper heat exchangers are more susceptible to scale buildup than stainless steel heat exchangers.
Diving hazards are the agents or situations that pose a threat to the underwater diver or their equipment. Divers operate in an environment for which the human body is not well suited. They face special physical and health risks when they go underwater or use high pressure breathing gas. The consequences of diving incidents range from merely annoying to rapidly fatal, and the result often depends on the equipment, skill, response and fitness of the diver and diving team. The classes of hazards include the aquatic environment, the use of breathing equipment in an underwater environment, exposure to a pressurised environment and pressure changes, particularly pressure changes during descent and ascent, and breathing gases at high ambient pressure. Diving equipment other than breathing apparatus is usually reliable, but has been known to fail, and loss of buoyancy control or thermal protection can be a major burden which may lead to more serious problems. There are also hazards of the specific diving environment, and hazards related to access to and egress from the water, which vary from place to place, and may also vary with time. Hazards inherent in the diver include pre-existing physiological and psychological conditions and the personal behaviour and competence of the individual. For those pursuing other activities while diving, there are additional hazards of task loading, of the dive task and of special equipment associated with the task.
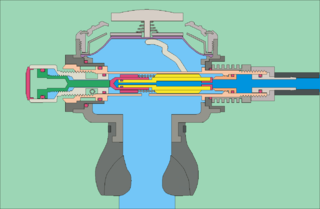
The mechanism of diving regulators is the arrangement of components and function of gas pressure regulators used in the systems which supply breathing gases for underwater diving. Both free-flow and demand regulators use mechanical feedback of the downstream pressure to control the opening of a valve which controls gas flow from the upstream, high-pressure side, to the downstream, low-pressure side of each stage. Flow capacity must be sufficient to allow the downstream pressure to be maintained at maximum demand, and sensitivity must be appropriate to deliver maximum required flow rate with a small variation in downstream pressure, and for a large variation in supply pressure, without instability of flow. Open circuit scuba regulators must also deliver against a variable ambient pressure. They must be robust and reliable, as they are life-support equipment which must function in the relatively hostile seawater environment, and the human interface must be comfortable over periods of several hours.

Human factors in diving equipment design are the influences of the interactions between the user and equipment in the design of diving equipment and diving support equipment. The underwater diver relies on various items of diving and support equipment to stay alive, healthy and reasonably comfortable and to perform planned tasks during a dive.