
The Potomac River is a major river in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States that flows from the Potomac Highlands in West Virginia to the Chesapeake Bay in Maryland. It is 405 miles (652 km) long, with a drainage area of 14,700 square miles (38,000 km2), and is the fourth-largest river along the East Coast of the United States and the 21st-largest in the United States. Over 5 million people live within its watershed.

Jennings Randolph Lake is a reservoir of 952 acres (3.85 km2) located on the North Branch Potomac River in Garrett County, Maryland and Mineral County, West Virginia. It is approximately eight miles upstream of Bloomington, Maryland, and approximately five miles north of Elk Garden, West Virginia.

The Gunpowder River is a 6.8-mile-long (10.9 km) tidal inlet on the western side of the Chesapeake Bay in Maryland, United States. It is formed by the joining of two freshwater rivers, Gunpowder Falls and Little Gunpowder Falls.

Prettyboy Reservoir is a 206.5 km2 (79.7 sq mi) reservoir in northern Baltimore County, Maryland, also known as the Hereford Zone. Even though the reservoir is in the county, the City of Baltimore owns the reservoir and the surrounding land of forested watershed. The reservoir is one of three reservoirs created to supply the Metropolitan Baltimore municipal water system for Baltimore City, Baltimore County and northern Anne Arundel County constructed by the Baltimore City Department of Public Works. Prettyboy Reservoir, along with Loch Raven Reservoir that is downstream of the Gunpowder Falls, provide about 61% of the drinking water for the Baltimore Metropolitan system. For this reason, the Prettyboy is considered a "source water" or drinking water watershed. The reservoir on average contains about 19 billion US gallons (72,000,000 m3) of water.

The Washington Suburban Sanitary Commission is a bi-county political subdivision of the State of Maryland that provides safe drinking water and wastewater treatment for Montgomery and Prince George's Counties in Maryland except for a few cities in both counties that continue to operate their own water facilities.

The Conowingo Dam is a large hydroelectric dam in the lower Susquehanna River near the town of Conowingo, Maryland. The medium-height, masonry gravity dam is one of the largest non-federal hydroelectric dams in the U.S., and the largest dam in the state of Maryland.

Liberty Reservoir is a reservoir west of Baltimore, Maryland; about a mile north of Patapsco Valley State Park's McKeldin area. It is owned by the City of Baltimore Department of Public Works, but is located outside the city, and it divides Baltimore and Carroll Counties.

The Loch Raven Reservoir is a reservoir that provides drinking water for the City of Baltimore and most of Baltimore County, Maryland. It is fed by the Big Gunpowder Falls river, and has a capacity of 23 billion US gallons (87,000,000 m3) of water.

Little Seneca Lake is a reservoir located near the Boyds community in Montgomery County, Maryland.

Rocky Gorge Reservoir is located on the Patuxent River in Howard, Montgomery, and Prince George's counties in Maryland, between Laurel and Burtonsville. The reservoir was created in 1952 by the construction of the T. Howard Duckett Dam on the Patuxent. The dam is visible from Interstate 95 near milemarker 34. Because of its close association with a dam by the name, the reservoir is sometimes called the T. Howard Duckett Reservoir. It has a surface area of 773 acres (313 ha). The reservoir is maintained as a drinking water source by the Washington Suburban Sanitary Commission (WSSC).

Triadelphia Reservoir is located on the Patuxent River, in Howard County and Montgomery County, Maryland near the town of Brookeville.

Broad Creek is a tributary of the lower Susquehanna River located in Harford County, Maryland.

The Savage River Reservoir is a 360 acres (1.5 km2) storage reservoir in northwest Maryland. It was completed in 1952 by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, and is owned and maintained by the Upper Potomac River Commission. The reservoir was formed by the Savage River Dam which impounds the Savage River. The reservoir itself has a maximum capacity of 31,800 acre-feet (39,200,000 m3) and is used for flood control and municipal drinking water supply.
Seneca Dam was the last in a series of dams proposed on the Potomac River in the area of the Great Falls of the Potomac. Apart from small-scale dams intended to divert water for municipal use in the District of Columbia and into the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal, no version of any scheme was ever built. In most cases the proposed reservoir would have extended upriver to Harpers Ferry, West Virginia. The project was part of a program of as many as sixteen major dams in the Potomac watershed, most of which were never built.
The Potomac River basin reservoir projects were U.S. Army Corps of Engineers programs that sought to regulate the flow of the Potomac River to control flooding, to assure a reliable water supply for Washington, D.C., and to provide recreational opportunities. Beginning in 1921 the Corps studied a variety of proposals for an ambitious program of dam construction on the Potomac and its tributaries, which proposed as many as sixteen major dam and reservoir projects. The most ambitious proposals would have created a nearly continuous chain of reservoirs from tidewater to Cumberland, Maryland. The 1938 program was focused on flood control, on the heels of a major flood in 1936. The reformulated 1963 program focused on water supply and quality, mitigating upstream pollution from sewage and coal mine waste.
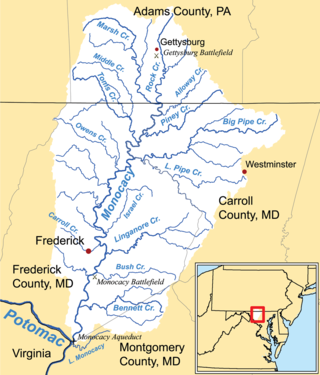
A proposed Union Mills Reservoir represents a half century of efforts by the Commissioners of the Carroll County, Maryland, to build variations on a "dam" or "reservoir" near Union Mills, Maryland, on the Big Pipe Creek, defeated by a petition led by the Carroll County Taxpayers' Committee in the 1970s. The plan may be alive among some county officials but may also be postponed "indefinitely." Land threatened by the reservoir includes the Whittaker Chambers Farm, also known as the Pipe Creek Farm, a National Historic Landmark as well as protected under the Maryland Agricultural Land Preservation Foundation (MALPF).













