
Fenwick Island is a coastal resort town in Sussex County, Delaware, United States. According to 2020 census figures, the population of the town is 355, a 2.6% decrease over the last decade. It is part of the Salisbury, Maryland-Delaware Metropolitan Statistical Area. The town is located on Fenwick Island, a barrier spit.

Millville is a town in Sussex County, Delaware, United States. The population in 2020 was 1,825, It is part of the Salisbury, Maryland-Delaware Metropolitan Statistical Area and lies within Baltimore Hundred.

Ocean View is a town in Sussex County, Delaware, United States. The population was 1,882 at the 2010 census, an increase of 87.1% over the previous decade. It is part of the Salisbury, Maryland-Delaware Metropolitan Statistical Area and lies in Baltimore Hundred.

The Intracoastal Waterway (ICW) is a 3,000-mile (4,800 km) inland waterway along the Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico coasts of the United States, running from Massachusetts southward along the Atlantic Seaboard and around the southern tip of Florida, then following the Gulf Coast to Brownsville, Texas. Some sections of the waterway consist of natural inlets, saltwater rivers, bays, and sounds, while others are artificial canals. It provides a navigable route along its length without many of the hazards of travel on the open sea.

Indian River Bay is a body of water in Sussex County, Delaware. It is part of Delaware's inland bay system, along with Little Assawoman Bay and Rehoboth Bay. Fed by the Indian River at its western end, the bay is connected to the Atlantic Ocean to the east via the Indian River Inlet. A natural waterway that shifted up and down a two-mile (3.2 km) stretch of the coast until 1928, the inlet was kept in its current location by dredging between 1928 and 1937, and in 1938 was fixed in place by the construction of jetties. The Charles W. Cullen Bridge, commonly known as the Indian River Inlet Bridge, spans the inlet.

Rehoboth Bay is a body of water in Sussex County, Delaware. It is connected to the Broadkill River by the Lewes and Rehoboth Canal. It is part of Delaware's inland bay system, along with Little Assawoman Bay and Indian River Bay.

The Elk River is a tidal tributary of the Chesapeake Bay on the Eastern Shore of Maryland and on the northern edge of the Delmarva Peninsula. It is about 15 miles (24 km) long. As the most northeastern extension of the Chesapeake Bay estuary, it has served as one entrance to the Chesapeake & Delaware Canal since the 19th century. The canal and river now serve as one boundary of the Elk Neck Peninsula. The river flows through Cecil County, Maryland, with its watershed extending into New Castle County, Delaware and Chester County, Pennsylvania. Elkton, the county seat of Cecil County, is located at its head. Its total watershed area is 143 square miles (370 km2), with 21 square miles (54 km2) of open water, so its watershed is 15% open water. It is south and east of the North East River, and north of the Sassafras River.
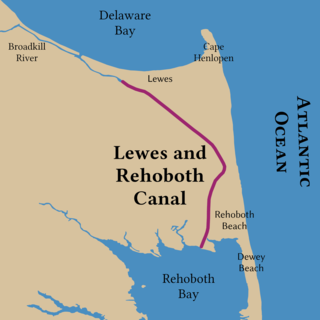
The Lewes and Rehoboth Canal is a canal in Sussex County, Delaware, which connects the Broadkill River and the Delaware Bay to Rehoboth Bay. It forms a portion of the Intracoastal Waterway.

Assawoman Bay, once called Assawoman Sound, is a lagoon that is located between Ocean City, Maryland and mainland Delmarva. The bay is located on the northern end of the city, and the bay on the southern end is called the Isle of Wight Bay. Another bay called Little Assawoman Bay extends into southern Delaware, and is geologically separated from the main estuaries, by a narrow strait locally referred to as "The Ditch" which crosses the Transpeninsular Line. The larger bay is sometimes called "Big Assawoman Bay", to distinguish it from the smaller bay, though this is often meant to be a tongue-in-cheek rendering of the name.

Asturianos is a municipality located in the Sanabria comarca, province of Zamora, Castile and León, Spain.
Rolling Acres is an unincorporated community in Boon Township, Warrick County, in the U.S. state of Indiana.

Mount Olympus is an unincorporated community in Washington Township, Gibson County, Indiana. It was formerly called Ennes. A post office called Ennes operated from 1879 until 1883.
Isle of Wight is an island in Worcester County, Maryland. The island is in Isle of Wight Bay at the mouth of St. Martin River just west of Ocean City on Fenwick Island in eastern Maryland. The Ocean City Expressway crosses the island between the mainland and Fenwick Island.
Nanticoke Wildlife Area is a state wildlife area located in Sussex County, Delaware, along the Nanticoke River and Broad Creek, near to Seaford, Delaware, and Bethel, Delaware. There is a monument commemorating Captain John Smith's journey into the Chesapeake Bay and its tributaries at Phillips Landing along Broad Creek, a tributary of the Nanticoke River in Delaware. It is made up of three large land tracts totaling 4,510 acres (1,825 ha), it is managed by Delaware Department of Natural Resources and Environmental Control (DNREC), Division of Fish and Wildlife. The area also holds one of the few Delmarva fox squirrel populations within Delaware, along with controlled populations in Prime Hook Wildlife Refuge and Assawoman Wildlife Area.

Fenwick Island is a barrier island along the Atlantic Ocean in Delaware and Maryland in the United States. It contains the communities of South Bethany and Fenwick Island in Delaware along with Ocean City, Maryland. Until 1933, it was attached to Assateague Island to the south. That year, a hurricane carved an inlet between the two landforms, which was made permanent. If not for the Assawoman Canal, constructed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers in 1891, the island would be attached to the mainland of Delaware.

The Assawoman Canal is a canal in Sussex County, Delaware. The canal links the Indian River Bay to the north with the Little Assawoman Bay to the south. It is bordered by Bethany Beach and South Bethany to the east and Ocean View to the west. Because of it, Fenwick Island is detached from the Delaware mainland.
Sulphur Springs is an unincorporated community in Crawford County, Indiana, in the United States.
Pigeon is an unincorporated community in Jackson Township, Spencer County, in the U.S. state of Indiana.
Assawoman Wildlife Area is a state wildlife area located in Sussex County, Delaware located near Frankfort, Delaware and Little Assawoman Bay. It is made up of three large tracts of land that total 3,100 acres (1,300 ha) that were originally former farms that were lost due to the Great Depression, and managed by the Delaware Department of Natural Resources and Environmental Control (DNREC). The wildlife areas name came from the nearby Little Assawoman Bay which was originally named Assateague, an Algonkian word meaning "stream or inlet in the middle" before it was changed to another Algonkian name which means "midway fishing stream."













