The pyramidal tracts include both the corticobulbar tract and the corticospinal tract. These are aggregations of efferent nerve fibers from the upper motor neurons that travel from the cerebral cortex and terminate either in the brainstem (corticobulbar) or spinal cord (corticospinal) and are involved in the control of motor functions of the body.

Onuf's nucleus is a distinct group of neurons located in the ventral part of the anterior horn of the sacral region of the human spinal cord involved in the maintenance of micturition and defecatory continence, as well as muscular contraction during orgasm. It contains motor neurons, and is the origin of the pudendal nerve. The sacral region of the spinal cord is the fourth segment of vertebrae in the spinal cord which consists of the vertebrae 26-30. While working in New York City in 1899, Bronislaw Onuf-Onufrowicz discovered this group of unique cells and originally identified it as “Group X.” “Group X” was considered distinct by Onufrowicz because the cells were different in size from the surrounding neurons in the anterolateral group, suggesting that they were independent.

An upper motor neuron lesion Is an injury or abnormality that occurs in the neural pathway above the anterior horn cell of the spinal cord or motor nuclei of the cranial nerves. Conversely, a lower motor neuron lesion affects nerve fibers traveling from the anterior horn of the spinal cord or the cranial motor nuclei to the relevant muscle(s).

A fasciculation, or muscle twitch, is a spontaneous, involuntary muscle contraction and relaxation, involving fine muscle fibers. They are common, with as many as 70% of people experiencing them. They can be benign, or associated with more serious conditions. When no cause or pathology is identified, they are diagnosed as benign fasciculation syndrome.

Upper motor neurons (UMNs) is a term introduced by William Gowers in 1886. They are found in the cerebral cortex and brainstem and carry information down to activate interneurons and lower motor neurons, which in turn directly signal muscles to contract or relax. UMNs represent the major origin point for voluntary somatic movement.
Lower motor neurons (LMNs) are motor neurons located in either the anterior grey column, anterior nerve roots or the cranial nerve nuclei of the brainstem and cranial nerves with motor function. Many voluntary movements rely on spinal lower motor neurons, which innervate skeletal muscle fibers and act as a link between upper motor neurons and muscles. Cranial nerve lower motor neurons also control some voluntary movements of the eyes, face and tongue, and contribute to chewing, swallowing and vocalization. Damage to the lower motor neurons can lead to flaccid paralysis, absent deep tendon reflexes and muscle atrophy.

The facial motor nucleus is a collection of neurons in the brainstem that belong to the facial nerve. These lower motor neurons innervate the muscles of facial expression and the stapedius.

The lateral corticospinal tract is the largest part of the corticospinal tract. It extends throughout the entire length of the spinal cord, and on transverse section appears as an oval area in front of the posterior column and medial to the posterior spinocerebellar tract.

The anterior corticospinal tract is a small bundle of descending fibers that connect the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord. Descending tracts are pathways by which motor signals are sent from upper motor neurons in the brain to lower motor neurons which then directly innervate muscle to produce movement. The anterior corticospinal tract is usually small, varying inversely in size with the lateral corticospinal tract, which is the main part of the corticospinal tract.
Alpha (α) motor neurons (also called alpha motoneurons), are large, multipolar lower motor neurons of the brainstem and spinal cord. They innervate extrafusal muscle fibers of skeletal muscle and are directly responsible for initiating their contraction. Alpha motor neurons are distinct from gamma motor neurons, which innervate intrafusal muscle fibers of muscle spindles.
Hyporeflexia is the reduction or absence of normal bodily reflexes (areflexia). It can be detected through the use of a reflex hammer and is the opposite of hyperreflexia.

Progressive muscular atrophy (PMA), also called Duchenne–Aran disease and Duchenne–Aran muscular atrophy, is a disorder characterised by the degeneration of lower motor neurons, resulting in generalised, progressive loss of muscle function.
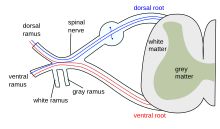
A nerve root is the initial segment of a nerve leaving the central nervous system. Nerve roots can be classified as:
Progressive bulbar palsy (PBP) is a medical condition. It belongs to a group of disorders known as motor neuron diseases. PBP is a disease that attacks the nerves supplying the bulbar muscles. These disorders are characterized by the degeneration of motor neurons in the cerebral cortex, spinal cord, brain stem, and pyramidal tracts. This specifically involves the glossopharyngeal nerve (IX), vagus nerve (X), and hypoglossal nerve (XII).
Bulbar palsy refers to a range of different signs and symptoms linked to impairment of function of the glossopharyngeal nerve, the vagus nerve, the accessory nerve, and the hypoglossal nerve. It is caused by a lower motor neuron lesion in the medulla oblongata, or from lesions to these nerves outside the brainstem, and also botulism. This may be caused by any of a number of genetic, vascular, degenerative, inflammatory, and other underlying conditions. It can be differentiated from pseudobulbar palsy. When there is airway obstruction, intubation is used.

Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neurone disease (MND) or Lou Gehrig's disease in the United States, is a rare but terminal neurodegenerative disorder that results in the progressive loss of both upper and lower motor neurons that normally control voluntary muscle contraction. ALS is the most common form of the motor neuron diseases. ALS often presents in its early stages with gradual muscle stiffness, twitches, weakness, and wasting. Motor neuron loss typically continues until the abilities to eat, speak, move, and, lastly, breathe are all lost. While only 15% of people with ALS also fully develop frontotemporal dementia, an estimated 50% face at least some minor difficulties with thinking and behavior. Depending on which of the aforementioned symptoms develops first, ALS is classified as limb-onset or bulbar-onset.

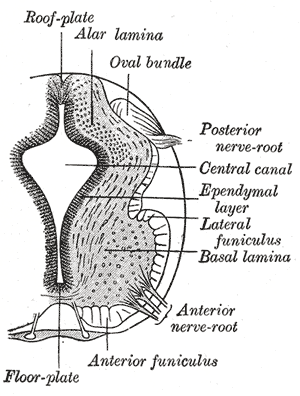
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue that extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone) of vertebrate animals. The center of the spinal cord is hollow and contains a structure called the central canal, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The spinal cord is also covered by meninges and enclosed by the neural arches. Together, the brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system.
Multifocal motor neuropathy (MMN) is a progressively worsening condition where muscles in the extremities gradually weaken. The disorder, a pure motor neuropathy syndrome, is sometimes mistaken for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) because of the similarity in the clinical picture, especially if muscle fasciculations are present. MMN is thought to be autoimmune. It was first described in the mid-1980s.

Monomelic amyotrophy (MMA) is a rare motor neuron disease first described in 1959 in Japan. Its symptoms usually appear about two years after adolescent growth spurt and is significantly more common in males, with an average age of onset between 15 and 25 years. MMA is reported most frequently in Asia but has a global distribution. It is typically marked by insidious onset of muscle atrophy of an upper limb, which plateaus after two to five years from which it neither improves nor worsens. There is no pain or sensory loss associated with MMA. MMA is not believed to be hereditary.
Facial onset sensory and motor neuronopathy, often abbreviated FOSMN, is a rare disorder of the nervous system in which sensory and motor nerves of the face and limbs progressively degenerate over a period of months to years. This degenerative process, the cause of which is unknown, eventually results in sensory and motor symptoms — the former consisting mainly of paresthesia followed by numbness, and the latter in muscle weakness, atrophy, and eventual paralysis. FOSM is characterized by sensory and motor loss beginning in the face and spreading to involve an increasingly larger area including the scalp, upper arms and trunk. The muscles or respiration and swallowing are commonly affected. In many ways, it is reminiscent of the much better known condition amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, with which it is closely related. There is no cure; treatment is supportive. Life expectancy may be shortened by respiratory complications arising from weakness of the muscles that aid breathing and swallowing. It was first described in four patients by Vucic and colleagues working at the Massachusetts General Hospital in the United States; subsequent reports from the United Kingdom, Europe and Asia point to a global incidence of the disease. It is thought to be exceptionally rare, with only approximately 100 individuals described to date in the medical literature.