
Molybdenum disulfide is an inorganic compound composed of molybdenum and sulfur. Its chemical formula is MoS
2.
Molybdenum trioxide describes a family of inorganic compounds with the formula MoO3(H2O)n where n = 0, 1, 2. The anhydrous compound is produced on the largest scale of any molybdenum compound since it is the main intermediate produced when molybdenum ores are purified. The anhydrous oxide is a precursor to molybdenum metal, an important alloying agent. It is also an important industrial catalyst. It is a yellow solid, although impure samples can appear blue or green.
In chemistry, an arsenide is a compound of arsenic with a less electronegative element or elements. Many metals form binary compounds containing arsenic, and these are called arsenides. They exist with many stoichiometries, and in this respect arsenides are similar to phosphides.

Boron arsenide is a chemical compound involving boron and arsenic, usually with a chemical formula BAs. Other boron arsenide compounds are known, such as the subarsenide B12As2. Chemical synthesis of cubic BAs is very challenging and its single crystal forms usually have defects.

Yttrium arsenide is an inorganic compound of yttrium and arsenic with the chemical formula YAs. It can be prepared by reacting yttrium and arsenic at high temperature. Some literature has done research on the eutectic system of it and zinc arsenide.
Molybdenum dioxide is the chemical compound with the formula MoO2. It is a violet-colored solid and is a metallic conductor. The mineralogical form of this compound is called tugarinovite, and is only very rarely found.

In chemistry, a molybdate is a compound containing an oxyanion with molybdenum in its highest oxidation state of 6: O−−Mo(=O)2−O−. Molybdenum can form a very large range of such oxyanions, which can be discrete structures or polymeric extended structures, although the latter are only found in the solid state. The larger oxyanions are members of group of compounds termed polyoxometalates, and because they contain only one type of metal atom are often called isopolymetalates. The discrete molybdenum oxyanions range in size from the simplest MoO2−
4, found in potassium molybdate up to extremely large structures found in isopoly-molybdenum blues that contain for example 154 Mo atoms. The behaviour of molybdenum is different from the other elements in group 6. Chromium only forms the chromates, CrO2−
4, Cr
2O2−
7, Cr
3O2−
10 and Cr
4O2−
13 ions which are all based on tetrahedral chromium. Tungsten is similar to molybdenum and forms many tungstates containing 6 coordinate tungsten.
In chemistry, molybdenum bronze is a generic name for certain mixed oxides of molybdenum with the generic formula A
xMo
yO
z where A may be hydrogen, an alkali metal cation (such as Li+, Na+, K+), and Tl+. These compounds form deeply coloured plate-like crystals with a metallic sheen, hence their name. These bronzes derive their metallic character from partially occupied 4d bands. The oxidation states in K0.28MoO3 are K+1, O2−, and Mo+5.72. MoO3 is an insulator, with an unfilled 4d band.
Lithium molybdenum purple bronze is a chemical compound with formula Li
0.9Mo
6O
17, that is, a mixed oxide of molybdenum and lithium. It can be obtained as flat crystals with a purple-red color and metallic sheen.
The selenide iodides are chemical compounds that contain both selenide ions (Se2−) and iodide ions (I−) and one or metal atoms. They are in the class of mixed anion compounds or chalcogenide halides.
Arsenidosilicates are chemical compounds that contain anions with arsenic bonded to silicon. They are in the category of tetrelarsenides, pnictidosilicates, or tetrelpnictides. They can be classed as Zintl phases or intermetallics. They are analogous to the nitridosilicates, phosphidosilicates, arsenidogermanates, and arsenidostannates. They are distinct from arsenate silicates which have oxygen connected with arsenic and silicon, or arsenatosilicates with arsenate groups sharing oxygen with silicate.
Arsenidogermanates are chemical compounds that contain anions with arsenic bonded to germanium. They are in the category of tetrelarsenides, pnictidogermanates, or tetrelpnictides.
Arsenidostanates are chemical compounds that contain anions with arsenic bonded to tin. They are in the category of tetrelarsenides, pnictidostancates, or tetrelpnictides.
Arsenide bromides or bromide arsenides are compounds containing anions composed of bromide (Br−) and arsenide (As3−). They can be considered as mixed anion compounds. They are in the category of pnictidehalides. Related compounds include the arsenide chlorides, arsenide iodides, phosphide bromides, and antimonide bromides.
Arsenide iodides or iodide arsenides are compounds containing anions composed of iodide (I−) and arsenide (As3−). They can be considered as mixed anion compounds. They are in the category of pnictidehalides. Related compounds include the arsenide chlorides, arsenide bromides, phosphide iodides, and antimonide iodides.
Antimonide iodides or iodide antimonides are compounds containing anions composed of iodide (I−) and antimonide (Sb3−). They can be considered as mixed anion compounds. They are in the category of pnictide halides. Related compounds include the antimonide chlorides, antimonide bromides, phosphide iodides, and arsenide iodides.

Europium compounds are compounds formed by the lanthanide metal europium (Eu). In these compounds, europium generally exhibits the +3 oxidation state, such as EuCl3, Eu(NO3)3 and Eu(CH3COO)3. Compounds with europium in the +2 oxidation state are also known. The +2 ion of europium is the most stable divalent ion of lanthanide metals in aqueous solution. Many europium compounds fluoresce under ultraviolet light due to the excitation of electrons to higher energy levels. Lipophilic europium complexes often feature acetylacetonate-like ligands, e.g., Eufod.
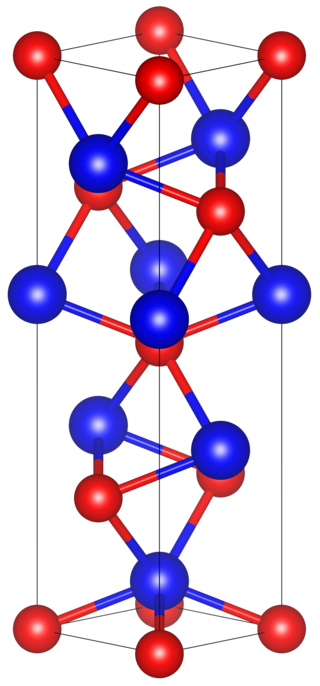
Tantalum arsenide is a compound of tantalum and arsenic with the formula TaAs. It is notable as being the first topological Weyl semimetal that was identified and characterized by ARPES.
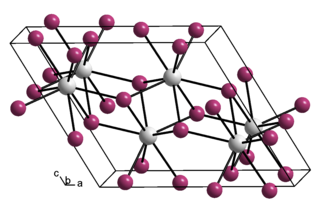
Tungsten diarsenide is an arsenide of tungsten with the chemical formula WAs2. Other tungsten arsenides include tungsten triarsenide (WAs3) and ditungsten triarsenide (W2As3).
Palladium diarsenide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula PdAs2. It is one of the arsenides of palladium.







