West Nile fever is an infection by the West Nile virus, which is typically spread by mosquitoes. In about 80% of infections people have few or no symptoms. About 20% of people develop a fever, headache, vomiting, or a rash. In less than 1% of people, encephalitis or meningitis occurs, with associated neck stiffness, confusion, or seizures. Recovery may take weeks to months. The risk of death among those in whom the nervous system is affected is about 10 percent.

Arbovirus is an informal name for any virus that is transmitted by arthropod vectors. The term arbovirus is a portmanteau word. Tibovirus is sometimes used to more specifically describe viruses transmitted by ticks, a superorder within the arthropods. Arboviruses can affect both animals and plants. In humans, symptoms of arbovirus infection generally occur 3–15 days after exposure to the virus and last three or four days. The most common clinical features of infection are fever, headache, and malaise, but encephalitis and viral hemorrhagic fever may also occur.
La Crosse encephalitis is an encephalitis caused by an arbovirus which has a mosquito vector.

Japanese encephalitis (JE) is an infection of the brain caused by the Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV). While most infections result in little or no symptoms, occasional inflammation of the brain occurs. In these cases, symptoms may include headache, vomiting, fever, confusion and seizures. This occurs about 5 to 15 days after infection.
Ross River virus (RRV) is a small encapsulated single-strand RNA Alphavirus endemic to Australia, Papua New Guinea and other islands in the South Pacific. It is responsible for a type of mosquito-borne non-lethal but extremely debilitating tropical disease known as Ross River fever, previously termed "epidemic polyarthritis". There is no known cure, and it can last in the system of the host for up to 20 years. The virus is suspected to be enzootic in populations of various native Australian mammals, and has been found on occasion in horses.
Ross River fever is a mosquito-borne infectious disease caused by infection with the Ross River virus. The illness is typically characterised by flu like symptoms combined with polyarthritis and a rash. The virus is endemic to mainland Australia and Tasmania, the island of New Guinea, Fiji, Samoa, the Cook Islands, New Caledonia and several other islands in the South Pacific. The illness is Queensland's most prolific mosquito-borne disease.

Oropouche fever is a tropical viral infection transmitted by biting midges and mosquitoes from the blood of sloths to humans. This disease is named after the region where it was first discovered and isolated at the Trinidad Regional Virus Laboratory in 1955 by the Oropouche River in Trinidad and Tobago. Oropouche fever is caused by a specific arbovirus, the Oropouche virus (OROV), of the Bunyaviridae family.
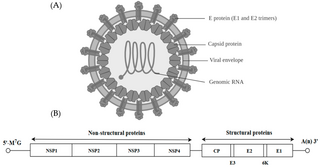
Alphavirus is a genus of RNA viruses, the sole genus in the Togaviridae family. Alphaviruses belong to group IV of the Baltimore classification of viruses, with a positive-sense, single-stranded RNA genome. There are 32 alphaviruses, which infect various vertebrates such as humans, rodents, fish, birds, and larger mammals such as horses, as well as invertebrates. Alphaviruses that could infect both vertebrates and arthropods are referred dual-host alphaviruses, while insect-specific alphaviruses such as Eilat virus and Yada yada virus are restricted to their competent arthropod vector. Transmission between species and individuals occurs mainly via mosquitoes, making the alphaviruses a member of the collection of arboviruses – or arthropod-borne viruses. Alphavirus particles are enveloped, have a 70 nm diameter, tend to be spherical, and have a 40 nm isometric nucleocapsid.
California encephalitis orthobunyavirus type strain California encephalitis virus was discovered in Kern County, California, and causes encephalitis in humans. Encephalitis is an acute inflammation of the brain that can cause minor symptoms, such as headaches, to more severe symptoms such as seizures. Mosquitoes serve as its carrier and for this reason this virus is known as an arbovirus.

Viral encephalitis is inflammation of the brain parenchyma, called encephalitis, by a virus. The different forms of viral encephalitis are called viral encephalitides. It is the most common type of encephalitis and often occurs with viral meningitis. Encephalitic viruses first cause infection and replicate outside of the central nervous system (CNS), most reaching the CNS through the circulatory system and a minority from nerve endings toward the CNS. Once in the brain, the virus and the host's inflammatory response disrupt neural function, leading to illness and complications, many of which frequently are neurological in nature, such as impaired motor skills and altered behavior.
Toscana phlebovirus (TOSV) is an arbovirus belonging to Bunyavirales, an order of negative-stranded, enveloped RNA viruses. The virus can be transmitted to humans by the bite of an infected sandfly of the genus Phlebotomus. Toscana is not normally associated with disease, as indicated by high seroprevalence rates in endemic areas, but in common with other sandfly transmitted viruses such as Naples virus and Sicilian virus, infection may result in Pappataci fever, an illness with mild fever, headache and myalgia. In serious cases that go undiagnosed, acute meningitis, meningoencephalitis and encephalitis may occur. There is no specific treatment for infection, so treatment is supportive, reducing the severity of symptoms until the immune system has cleared the infection.
Mosquito-borne diseases or mosquito-borne illnesses are diseases caused by bacteria, viruses or parasites transmitted by mosquitoes. Nearly 700 million people get a mosquito-borne illness each year resulting in over 725,000 deaths.

Kunjin virus (KUNV) is a zoonotic virus of the family Flaviviridae and the genus Flavivirus. It is a subtype of West Nile virus endemic to Oceania.
Rocio viral encephalitis is an epidemic flaviviral disease of humans first observed in São Paulo State, Brazil, in 1975. Low-level enzootic transmission is likely continuing in the epidemic zone, and with increased deforestation and population expansion, additional epidemics caused by Rocio virus are highly probable. If migratory species of birds are, or become involved in, the virus transmission cycle, the competency of a wide variety of mosquito species for transmitting Rocio virus experimentally suggest that the virus may become more widely distributed. The encephalitis outbreak in the western hemisphere caused by West Nile virus, a related flavivirus, highlights the potential for arboviruses to cause severe problems far from their source enzootic foci.

Usutu virus (USUV) is a flavivirus belonging to the Japanese encephalitis complex, which is an emerging zoonotic arbovirus of concern because of its pathogenicity to humans and its similarity in ecology with other emerging arboviruses such as West Nile virus. It mainly infects Culex mosquitoes and birds; humans form a dead-end host. First identified in South Africa in 1959, the virus has caused outbreaks in birds across Europe since 1996. Nearly 50 cases in humans have been reported as of 2019, mainly in Europe. These are predominantly asymptomatic, but some people experience neurological symptoms.
Tahyna orthobunyavirus ("TAHV") is a viral pathogen of humans classified in the California encephalitis virus (CEV) serogroup of the Orthobunyavirus family in the order Bunyavirales, which is endemic to Europe, Asia, Africa and possibly China.
Cache Valley orthobunyavirus (CVV) is a member of the order Bunyavirales, genus Orthobunyavirus, and serogroup Bunyamwera, which was first isolated in 1956 from Culiseta inornata mosquitos collected in Utah's Cache Valley. CVV is an enveloped arbovirus, nominally 80–120 nm in diameter, whose genome is composed of three single-stranded, negative-sense RNA segments. The large segment of related bunyaviruses is approximately 6800 bases in length and encodes a probable viral polymerase. The middle CVV segment has a 4463-nucleotide sequence and the smallest segment encodes for the nucleocapsid, and a second non-structural protein. CVV has been known to cause outbreaks of spontaneous abortion and congenital malformations in ruminants such as sheep and cattle. CVV rarely infects humans, but when they are infected it has caused encephalitis and multiorgan failure.
Jamestown Canyon encephalitis is an infectious disease caused by the Jamestown Canyon virus, an orthobunyavirus of the California serogroup. It is mainly spread during the summer by different mosquito species in the United States and Canada.
Spondweni virus is an arbovirus, or arthropod-borne virus, which is a member of the family Flaviviridae and the genus Flavivirus. It is part of the Spondweni serogroup which consists of the Sponweni virus and the Zika virus (ZIKV). The Spondweni virus was first isolated in Nigeria in 1952, and ever since, SPONV transmission and activity have been reported throughout Africa. Its primary vector of transmission is the sylvatic mosquito Aedes circumluteolus, though it has been isolated from several different types of mosquito. Transmission of the virus into humans can lead to a viral infection known as Spondweni fever, with symptoms ranging from headache and nausea to myalgia and arthralgia. However, as SPONV is phylogenetically close to the ZIKV, it is commonly misdiagnosed as ZIKV along with other viral illnesses.
Keystone virus is a mosquito-borne virus which can infect mammals. It was first discovered in animals in the Florida area, where it is spread in part by local species of Aedes mosquitoes. In 1964, a case of human infection, producing minor symptoms of a rash and fever, was circumstantially diagnosed. Conclusive laboratory demonstration of the virus in humans was first obtained and reported in 2018.








