
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environments and are an example of an ecotone. Estuaries are subject both to marine influences such as tides, waves, and the influx of saline water, and to fluvial influences such as flows of freshwater and sediment. The mixing of seawater and freshwater provides high levels of nutrients both in the water column and in sediment, making estuaries among the most productive natural habitats in the world.

Georgetown County is a county located in the U.S. state of South Carolina. As of the 2020 census, the population was 63,404. Its county seat is Georgetown. The county was founded in 1769. It is named for George III of the United Kingdom.

The National Estuarine Research Reserve System is a network of 30 protected areas established by partnerships between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and coastal states. The reserves represent different biogeographic regions of the United States. The National Estuarine Research Reserve System protects more than 1.3 million acres of coastal and estuarine habitats for long-term research, water-quality monitoring, education, and coastal stewardship.

The Waccamaw River is a river, approximately 140 miles (225 km) long, in southeastern North Carolina and eastern South Carolina in the United States. It drains an area of approximately 1,110 square miles (2886 km2) in the coastal plain along the eastern border between the two states into the Atlantic Ocean. Along its upper course, it is a slow-moving, blackwater river surrounded by vast wetlands, passable only by shallow-draft watercraft such as canoe. Along its lower course, it is lined by sandy banks and old plantation houses, providing an important navigation channel with a unique geography, flowing roughly parallel to the coast.

Coos Bay is an estuary where the Coos River enters the Pacific Ocean, the estuary is approximately 12 miles long and up to two miles wide. It is the largest estuary completely within Oregon state lines. The Coos Bay watershed covers an area of about 600 square miles and is located in northern Coos County, Oregon, in the United States. The Coos River, which begins in the Oregon Coast Range, enters the bay from the east. From Coos River, the bay forms a sharp loop northward before arching back to the south and out to the Pacific Ocean. Haynes Inlet enters the top of this loop. South Slough branches off from the bay directly before its entrance into the Pacific Ocean. The bay was formed when sea levels rose over 20,000 years ago at the end of the Last Glacial Maximum, flooding the mouth of the Coos River. Coos Bay is Oregon's most important coastal industrial center and international shipping port, with close ties to San Francisco, the Columbia River, Puget Sound and other major ports of the Pacific rim.

The Matanzas River is a body of water in St. Johns and Flagler counties in the U.S. state of Florida. It is a narrow saltwater bar-bounded estuary sheltered from the Atlantic Ocean by Anastasia Island. The river is part of the Atlantic Intracoastal Waterway.

Winyah Bay is a coastal estuary that is the confluence of the Waccamaw River, the Pee Dee River, the Black River, and the Sampit River in Georgetown County, in eastern South Carolina. Its name comes from the Winyaw, who inhabited the region during the eighteenth century. The historic port city of Georgetown is located on the bay, and the bay generally serves as the terminating point for the Grand Strand.
The Chesapeake Bay National Estuarine Research Reserve is an estuary reserve in Maryland.

Great Bay is a tidal estuary located in Strafford and Rockingham counties in eastern New Hampshire, United States. The bay occupies over 6,000 acres (24 km2), not including its several tidal river tributaries. Its outlet is at Hilton Point in Dover, New Hampshire, where waters from the bay flow into the Piscataqua River, thence proceeding southeast to the Atlantic Ocean near Portsmouth. The northern end of the bay, near its outlet, is referred to as Little Bay.

The Jacques Cousteau National Estuarine Research Reserve, located in southeastern New Jersey, encompasses over 110,000 acres (450 km2) of terrestrial, wetland and aquatic habitats within the Mullica River-Great Bay Ecosystem.

Bird Island is approximately 1,300 acres (5.3 km2) adjacent to the town of Sunset Beach, North Carolina, US. Sunset Beach is on a barrier island and is the southernmost town in North Carolina. Bird Island can be reached by walking along the seashore toward the South Carolina border. Due to the contour of the Atlantic Coast at this point, the direction of travel to Bird Island is approximately West-Southwest. Previously, Bird Island was separated from Sunset Beach by a tidal creek that could be easily crossed only at low tide. Accretion of ocean sand has gradually filled in the tidal creek so that two separate islands became one.

Great Bay is located in southern New Jersey's Atlantic Coastal Plain in Ocean and Atlantic Counties, about ten miles (16 km) north of Atlantic City and is about 5.5 miles northwest of Brigantine, and 5.5 miles southwest of Beach Haven. The Mullica River flows into the bay, and together they form the Mullica River - Great Bay estuary habitat. The bay is connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Little Egg Inlet. Great Bay is considered one of the least-disturbed marine wetlands habitats in the northeastern United States.

Bahía de Jobos or Reserva Natural de Investigación Estuarina de Bahía de Jobos is a federally protected estuary in Aguirre, Salinas, Puerto Rico. The bay is an intertidal tropical ecosystem dominated by seagrass beds, coral reefs, and mangroves. In an area of 1,140 hectares, the reserve contains five distinct habitat types and provides sanctuary to several endangered species. Bahía de Jobos is one of 28 reserves that comprise the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) National Estuarine Research Reserve System. The reserve is operated in conjunction with the Puerto Rico Department of Natural and Environmental Resources (DRNA).

Elkhorn Slough is a 7-mile-long (11 km) tidal slough and estuary on Monterey Bay in Monterey County, California. It is California's second largest estuary and the United States' first estuarine sanctuary. The community of Moss Landing and the Moss Landing Power Plant are located at the mouth of the slough on the bay.

Currituck Banks North Carolina National Estuarine Research Reserve is a component site of the North Carolina National Estuarine Research Reserve on the Currituck Banks, north of Corolla, North Carolina. Currituck Banks is one of three original National Estuarine Research Reserve sites dedicated by NOAA in 1985. The reserve encompasses 965 acres of varied habitat and is bordered by the Currituck Sound. The Currituck banks are part of a 70-mile long barrier spit that extends from Virginia Beach to Oregon Inlet.

The Great Bay National Estuarine Research Reserve encompasses a diversity of land and water areas around Great Bay, an estuary in southeastern New Hampshire. Protected lands cover 10,235 acres (4,142 ha), including approximately 7,300 acres (3,000 ha) of open water and wetlands that include salt marshes, rocky shores, bluffs, woodlands, open fields, and riverine systems and tidal waters.

The Hudson River National Estuarine Research Reserve is a National Estuarine Research Reserve in the state of New York.

The Weeks Bay National Estuarine Research Reserve is a field laboratory and research facility along Weeks Bay estuary, about 6,000 acres (2,400 ha) in size. It receives freshwater from the Magnolia and Fish Rivers, and drains a 198 square miles (510 km2) watershed into the portion of Mobile Bay via a narrow opening. This sub-estuary of Mobile Bay averages just 4.8 ft deep and is fringed with marsh and swamp. The reserve lands also include upland and bottomland hardwood forests, freshwater marsh, submerged aquatic vegetation and unique bog habitats. Weeks Bay is a critical nursery for shrimp, bay anchovy, blue crab and multitudes of other fish, crustaceans and shellfish that support robust commercial fisheries providing $450 million/year for Alabama.
Designated in 1991, the Chesapeake Bay National Estuarine Research Reserve - Virginia (CBNERR-VA) is one of 29 protected areas that make up the National Estuarine Research Reserve System (NERRS). Established to promote informed management of the nation's estuaries and coastal habitats.
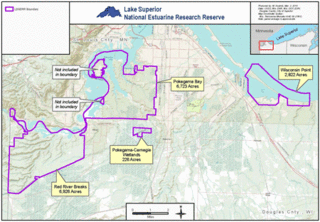
The Lake Superior National Estuarine Research Reserve includes land and water areas along the St. Louis River and Lake Superior in Douglas County, in the northwest corner of Wisconsin, United States. It is one of 29 National Estuarine Research Reserves. The Reserve is operated as a program of the Natural Resources Institute of the University of Wisconsin-Madison Division of Extension. It has an area of 16,697 acres (6,757 ha), and was designated in 2010.


















